The maxilla in vertebrates is the upper fixed bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible, which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw.

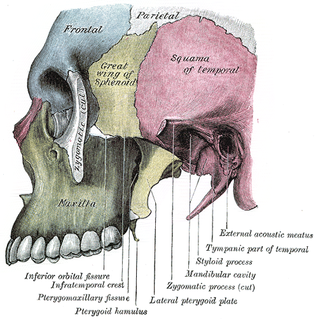
In the human skull, the zygomatic bone is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. It is situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek, part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit, and parts of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal fossa. It presents a malar and a temporal surface; four processes, and four borders.
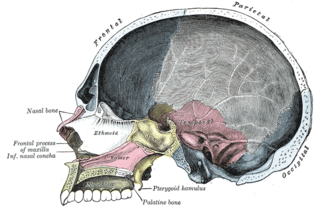
In anatomy, the palatine bones are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxillae, they comprise the hard palate.

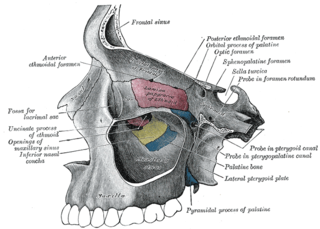
The lacrimal bone is a small and fragile bone of the facial skeleton; it is roughly the size of the little fingernail. It is situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. It has two surfaces and four borders. Several bony landmarks of the lacrimal bone function in the process of lacrimation or crying. Specifically, the lacrimal bone helps form the nasolacrimal canal necessary for tear translocation. A depression on the anterior inferior portion of the bone, the lacrimal fossa, houses the membranous lacrimal sac. Tears or lacrimal fluid, from the lacrimal glands, collect in this sac during excessive lacrimation. The fluid then flows through the nasolacrimal duct and into the nasopharynx. This drainage results in what is commonly referred to a runny nose during excessive crying or tear production. Injury or fracture of the lacrimal bone can result in posttraumatic obstruction of the lacrimal pathways.
The inferior nasal concha is one of the three paired nasal conchae in the nose. It extends horizontally along the lateral wall of the nasal cavity and consists of a lamina of spongy bone, curled upon itself like a scroll,. The inferior nasal conchae are considered a pair of facial bones. As the air passes through the turbinates, the air is churned against these mucosa-lined bones in order to receive warmth, moisture and cleansing. Superior to inferior nasal concha are the middle nasal concha and superior nasal concha which arise from the cranial portion of the skull. Hence, these two are considered as a part of the cranial bones.

The vomer is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms the inferior part of the nasal septum, with the superior part formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The name is derived from the Latin word for a ploughshare and the shape of the bone.

The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the osteomeatal complex.

In the ethmoid bone, a sickle shaped projection, the uncinate process, projects posteroinferiorly from the ethmoid labyrinth. Between the posterior edge of this process and the anterior surface of the ethmoid bulla, there is a two-dimensional space, resembling a crescent shape. This space continues laterally as a three-dimensional slit-like space - the ethmoidal infundibulum. This is bounded by the uncinate process, medially, the orbital lamina of ethmoid bone, laterally, and the ethmoidal bulla, posterosuperiorly. This concept is easier to understand if one imagine the infundibulum as a prism so that its medial face is the hiatus semilunaris. The "lateral face" of this infundibulum contains the ostium of the maxillary sinus, which, therefore, opens into the infundibulum.
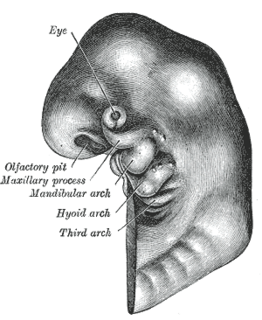
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches, are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches.

In human anatomy, the pterygopalatine fossa is a fossa in the skull. A human skull contains two pterygopalatine fossae—one on the left side, and another on the right side. Each fossa is a cone-shaped paired depression deep to the infratemporal fossa and posterior to the maxilla on each side of the skull, located between the pterygoid process and the maxillary tuberosity close to the apex of the orbit. It is the indented area medial to the pterygomaxillary fissure leading into the sphenopalatine foramen. It communicates with the nasal and oral cavities, infratemporal fossa, orbit, pharynx, and middle cranial fossa through eight foramina.

The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid, one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone; there is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.

The tympanic part of the temporal bone is a curved plate of bone lying below the squamous part of the temporal bone, in front of the mastoid process, and surrounding the external part of the ear canal.
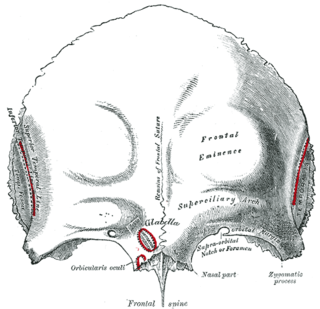
There are two surfaces of the squamous part of the frontal bone: the external surface, and the internal surface.

The stomodeum, also called stomatodeum or stomatodaeum, is a depression between the brain and the pericardium in an embryo, and is the precursor of the mouth and the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.

The perpendicular plate of palatine bone is the vertical part of the palatine bone, and is thin, of an oblong form, and presents two surfaces and four borders.

The frontonasal process, or frontonasal prominence is one of the five swellings that develop to form the face. The frontonasal process is unpaired, and the others are the paired maxillary prominences, and the paired mandibular prominences. During the fourth week of embryonic development, an area of thickened ectoderm develops, on each side of the frontonasal process called the nasal placodes or olfactory placodes, and appear immediately under the forebrain.

The intermaxillary segment in an embryo is a mass of tissue formed by the merging of tissues in the vicinity of the nose. It is essential for human survival. It is primordial, since in the further development of the embryo this particular mass no longer appears, but parts of it remain in "the intermaxillary portion of the upper jaw, the portion of the upper lip, and the primary palate".

The human nose is the most protruding part of the face. It bears the nostrils and is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two. On average the nose of a male is larger than that of a female.
The face and neck development of the human embryo refers to the development of the structures from the third to eighth week that give rise to the future head and neck. They consist of three layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, which form the mesenchyme, neural crest and neural placodes. The paraxial mesoderm forms structures named somites and somitomeres that contribute to the development of the floor of the brain and voluntary muscles of the craniofacial region. The lateral plate mesoderm consists of the laryngeal cartilages. The three tissue layers give rise to the pharyngeal apparatus, formed by six pairs of pharyngeal arches, a set of pharyngeal pouches and pharyngeal grooves, which are the most typical feature in development of the head and neck. The formation of each region of the face and neck is due to the migration of the neural crest cells which come from the ectoderm. These cells determine the future structure to develop in each pharyngeal arch. Eventually, they also form the neurectoderm, which forms the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain, cartilage, bone, dentin, tendon, dermis, pia mater and arachnoid mater, sensory neurons, and glandular stroma.