
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of most vertebrates that manipulates food for mastication and is used in the act of swallowing. It has importance in the digestive system and is the primary organ of taste in the gustatory system. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and vocalization in other animals.
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing is an important part of eating and drinking. If the process fails and the material goes through the trachea, then choking or pulmonary aspiration can occur. In the human body the automatic temporary closing of the epiglottis is controlled by the swallowing reflex.

The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve, or simply CN VII. It emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerves typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.

The glossopharyngeal nerve, known as the ninth cranial nerve, is a mixed nerve that carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. It exits the brainstem out from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, while the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies at the level of the base of the mandible in the front and the third cervical vertebra (C3) behind.

Pharyngeal slits are filter-feeding organs found among deuterostomes. Pharyngeal slits are repeated openings that appear along the pharynx caudal to the mouth. With this position, they allow for the movement of water in the mouth and out the pharyngeal slits. It is postulated that this is how pharyngeal slits first assisted in filter-feeding, and later with the addition of gills along their walls, aided in respiration of aquatic chordates. These repeated segments are controlled by similar developmental mechanisms. Some hemichordate species can have as many as 200 gill slits. Pharyngeal clefts resembling gill slits are transiently present during the embryonic stages of tetrapod development. The presence of pharyngeal arches and clefts in the neck of the developing human embryo famously led Ernst Haeckel to postulate that "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny"; this hypothesis, while false, contains elements of truth, as explored by Stephen Jay Gould in Ontogeny and Phylogeny. However, it is now accepted that it is the vertebrate pharyngeal pouches and not the neck slits that are homologous to the pharyngeal slits of invertebrate chordates. Pharyngeal arches, pouches, and clefts are, at some stage of life, found in all chordates. One theory of their origin is the fusion of nephridia which opened both on the outside and the gut, creating openings between the gut and the environment.

The palatoglossus, glossopalatinus, or palatoglossal muscle is a small fleshy fasciculus, narrower in the middle than at either end, forming, with the mucous membrane covering its surface, the glossopalatine arch.

The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a muscle in the pharynx. It is the highest located muscle of the three pharyngeal constrictors. The muscle is a quadrilateral muscle, thinner and paler than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle.

The stylopharyngeus is a muscle in the head that stretches between the temporal styloid process and the pharynx.
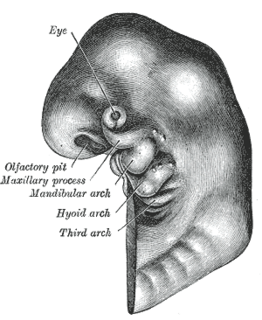
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches, are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches.

In the embryonic development of vertebrates, pharyngeal pouches form on the endodermal side between the pharyngeal arches. The pharyngeal grooves form the lateral ectodermal surface of the neck region to separate the arches.

The aortic arches or pharyngeal arch arteries are a series of six paired embryological vascular structures which give rise to the great arteries of the neck and head. They are ventral to the dorsal aorta and arise from the aortic sac.

The copula linguae or copula, is a swelling that forms from the second pharyngeal arch, late in the fourth week of embryogenesis. During the fifth and sixth weeks the copula becomes overgrown and covered by the hypopharyngeal eminence which forms mostly from the third pharyngeal arch and in part from the fourth pharyngeal arch.

The median tongue bud marks the beginning of the development of the tongue. It appears as a midline swelling from the first pharyngeal arch late in the fourth week of embryogenesis. In the fifth week, a pair of lateral lingual swellings develop above and in line with the median tongue bud. These swellings grow downwards towards each other, quickly overgrowing the median tongue bud. The line of the fusion of the distal tongue buds is marked by the median sulcus.

The lung bud sometimes referred to as the respiratory bud forms from the respiratory diverticulum, an embryological endodermal structure that develops into the respiratory tract organs such as the larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. It arises from part of the laryngotracheal tube.

Branchial arches, or gill arches, are a series of bony "loops" present in fish, which support the gills. As gills are the primitive condition of vertebrates, all vertebrate embryos develop pharyngeal arches, though the eventual fate of these arches varies between taxa. In jawed fish, the first arch develops into the jaws, the second into the hyomandibular complex, with the posterior arches supporting gills. In amphibians and reptiles, many elements are lost including the gill arches, resulting in only the oral jaws and a hyoid apparatus remaining. In mammals and birds, the hyoid is still more simplified.

The pharynx is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and larynx – the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species.
Neural crest cells are multipotent cells required for the development of cells, tissues and organ systems. A subpopulation of neural crest cells are the cardiac neural crest complex. This complex refers to the cells found amongst the midotic placode and somite 3 destined to undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transformation and migration to the heart via pharyngeal arches 3, 4 and 6.
The face and neck development of the human embryo refers to the development of the structures from the third to eighth week that give rise to the future head and neck. They consist of three layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, which form the mesenchyme, neural crest and neural placodes. The paraxial mesoderm forms structures named somites and somitomeres that contribute to the development of the floor of the brain and voluntary muscles of the craniofacial region. The lateral plate mesoderm consists of the laryngeal cartilages. The three tissue layers give rise to the pharyngeal apparatus, formed by six pairs of pharyngeal arches, a set of pharyngeal pouches and pharyngeal grooves, which are the most typical feature in development of the head and neck. The formation of each region of the face and neck is due to the migration of the neural crest cells which come from the ectoderm. These cells determine the future structure to develop in each pharyngeal arch. Eventually, they also form the neurectoderm, which forms the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain, cartilage, bone, dentin, tendon, dermis, pia mater and arachnoid mater, sensory neurons, and glandular stroma.
Hyoid suspension also known as hyoid myotomy and suspension or hyoid advancement, is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the hyoid bone and its muscle attachments to the tongue and airway are pulled forward with the aim of increasing airway size and improving airway stability in the retrolingual and hypopharyngeal airway. The horseshoe shaped hyoid bone sits directly below the base of tongue with the arms of the bone flanking the airway. Hyoid suspension is typically performed as a treatment for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This procedure is frequently performed with a uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) which targets sites of obstruction higher in the airway. Typically, a hyoid suspension is considered successful when the patient’s apnea-hypopnea index is significantly reduced after surgery.















