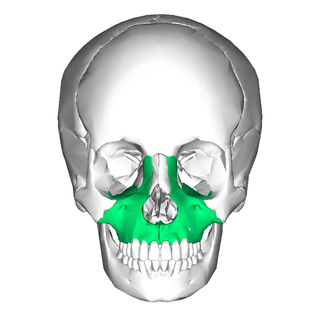
In vertebrates, the maxilla is the upper fixed bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible, which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw.

The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm and endoderm. It emerges and originates from the outer layer of germ cells. The word ectoderm comes from the Greek ektos meaning "outside", and derma meaning "skin".

The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract.

The olfactory epithelium is a specialized epithelial tissue inside the nasal cavity that is involved in smell. In humans, it measures 5 cm2 (0.78 sq in) and lies on the roof of the nasal cavity about 7 cm (2.8 in) above and behind the nostrils. The olfactory epithelium is the part of the olfactory system directly responsible for detecting odors.

The philtrum or medial cleft is a vertical indentation in the middle area of the upper lip, common to therian mammals, extending in humans from the nasal septum to the tubercle of the upper lip. Together with a glandular rhinarium and slit-like nostrils, it is believed to constitute the primitive condition for at least therian mammals. Monotremes lack a philtrum, though this could be due to the specialised, beak-like jaws in living species.
In embryology, a neurogenic placode is an area of thickening of the epithelium in the embryonic head ectoderm layer that gives rise to neurons and other structures of the sensory nervous system.

The rhinarium is the furless skin surface surrounding the external openings of the nostrils in many mammals. Commonly it is referred to as the tip of the snout, and breeders of cats and dogs sometimes use the term nose leather. Informally, it may be called a "truffle", "wet snout," or "wet nose” because its surface is moist in some species: for example, healthy dogs and cats.
In embryology, Carnegie stages are a standardized system of 23 stages used to provide a unified developmental chronology of the vertebrate embryo.

Continuous with the dorsal end of the first pharyngeal arch, and growing forward from its cephalic border, is a triangular process, the maxillary prominence, the ventral extremity of which is separated from the mandibular arch by a ">"-shaped notch.
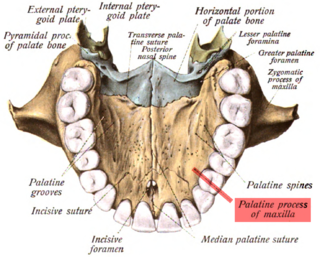
In human anatomy of the mouth, the palatine process of maxilla, is a thick, horizontal process of the maxilla. It forms the anterior three quarters of the hard palate, the horizontal plate of the palatine bone making up the rest. It is the most important bone in the midface. It provides structural support for the viscerocranium.

The development of the secondary palate commences in the sixth week of human embryonic development. It is characterised by the formation of two palatal shelves on the maxillary prominences, the elevation of these shelves to a horizontal position, and then a process of palatal fusion between the horizontal shelves. The shelves will also fuse anteriorly upon the primary palate, with the incisive foramen being the landmark between the primary palate and secondary palate. This forms what is known as the roof of the mouth, or the hard palate.

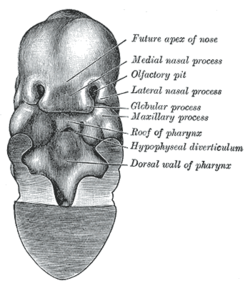
The frontonasal process or frontonasal prominence is one of the five swellings that develop to form the face. The frontonasal process is unpaired, and the others are the paired maxillary prominences, and the paired mandibular prominences. During the fourth week of embryonic development, an area of thickened ectoderm develops, on each side of the frontonasal process called the nasal placodes or olfactory placodes, and appear immediately under the forebrain.

The intermaxillary segment in an embryo is a mass of tissue formed by the merging of tissues in the vicinity of the nose. It is essential for human survival. It is primordial, since in the further development of the embryo this particular mass no longer appears, but parts of it remain in "the intermaxillary portion of the upper jaw, the portion of the upper lip, and the primary palate".

The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum, which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two.

A nose is a sensory organ and respiratory structure in vertebrates. It consists of a nasal cavity inside the head, and an external nose on the face. The external nose houses the nostrils, or nares, a pair of tubes providing airflow through the nose for respiration. Where the nostrils pass through the nasal cavity they widen, are known as nasal fossae, and contain turbinates and olfactory mucosa. The nasal cavity also connects to the paranasal sinuses. From the nasal cavity, the nostrils continue into the pharynx, a switch track valve connecting the respiratory and digestive systems.

Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Human embryonic development covers the first eight weeks of development, which have 23 stages, called Carnegie stages. At the beginning of the ninth week, the embryo is termed a fetus. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features and a more complete set of developing organs.

The premaxilla is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammals has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or os premaxillare, intermaxillary bone or os intermaxillare, and Goethe's bone.

The pharynx is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx.

In human anatomy, the mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and produces saliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth.
The face and neck development of the human embryo refers to the development of the structures from the third to eighth week that give rise to the future head and neck. They consist of three layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, which form the mesenchyme, neural crest and neural placodes. The paraxial mesoderm forms structures named somites and somitomeres that contribute to the development of the floor of the brain and voluntary muscles of the craniofacial region. The lateral plate mesoderm consists of the laryngeal cartilages. The three tissue layers give rise to the pharyngeal apparatus, formed by six pairs of pharyngeal arches, a set of pharyngeal pouches and pharyngeal grooves, which are the most typical feature in development of the head and neck. The formation of each region of the face and neck is due to the migration of the neural crest cells which come from the ectoderm. These cells determine the future structure to develop in each pharyngeal arch. Eventually, they also form the neurectoderm, which forms the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain, cartilage, bone, dentin, tendon, dermis, pia mater and arachnoid mater, sensory neurons, and glandular stroma.