The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of most vertebrates that manipulates food for mastication, and is used in the act of swallowing. It is of importance in the digestive system and is the primary organ of taste in the gustatory system. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and vocalization in other animals.

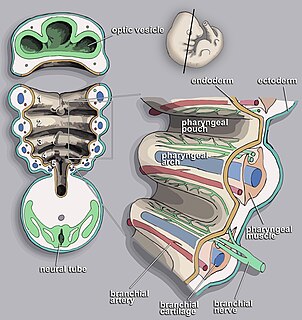
Pharyngeal slits are filter-feeding organs found in vertebrate chordates. Pharyngeal slits are repeated openings that appear along the pharynx caudal to the mouth. With this position, they allow for the movement of water in the mouth and out the pharyngeal slits. It is postulated that this is how pharyngeal slits first assisted in filter-feeding, and later with the addition of gills along their walls, aided in respiration of aquatic chordates. These repeated segments are controlled by similar developmental mechanisms. Some hemichordate species can have as many as 200 gill slits. Pharyngeal slits resembling gill slits are transiently present during the embryonic stages of tetrapod development. The presence of gill-like slits in the neck of the developing human embryo famously led Ernst Haeckel to postulate that "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny"; this hypothesis, while false, contains elements of truth, as explored by Stephen Jay Gould in Ontogeny and Phylogeny. However, it is now accepted that it is the vertebrate pharyngeal pouches and not the neck slits that are homologous to the pharyngeal slits of invertebrate chordates. Gill slits are, at some stage of life, found in all chordates. One theory of their origin is the fusion of nephridia which opened both on the outside and the gut, creating openings between the gut and the environment.

The mylohyoid muscle is a paired muscle running from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the mouth. It is named after its two attachments near the molar teeth. These muscles are mesodermal in embryologic origin. The mylohyoid muscle is derived from the first pharyngeal arch.

The palatoglossus, glossopalatinus, or palatoglossal muscle is a small fleshy fasciculus, narrower in the middle than at either end, forming, with the mucous membrane covering its surface, the glossopalatine arch.

The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a muscle in the pharynx. It is the highest located muscle of the three pharyngeal constrictors. The muscle is a quadrilateral muscle, thinner and paler than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle.

In the embryonic development of vertebrates, pharyngeal pouches form on the endodermal side between the pharyngeal arches. The pharyngeal grooves form the lateral ectodermal surface of the neck region to separate the arches.

The aortic arches or pharyngeal arch arteries are a series of six paired embryological vascular structures which give rise to the great arteries of the neck and head. They are ventral to the dorsal aorta and arise from the aortic sac.
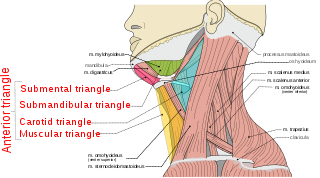
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck.

Continuous with the dorsal end of the first pharyngeal arch, and growing forward from its cephalic border, is a triangular process, the maxillary prominence, the ventral extremity of which is separated from the mandibular arch by a ">"-shaped notch.

The median tongue bud marks the beginning of the development of the tongue. It appears as a midline swelling from the first pharyngeal arch late in the fourth week of embryogenesis. In the fifth week, a pair of lateral lingual swellings develop above and in line with the median tongue bud. These swellings grow downwards towards each other, quickly overgrowing the median tongue bud. The line of the fusion of the distal tongue buds is marked by the median sulcus.
Special visceral efferent fibers (SVE) are the efferent nerve fibers that provide motor innervation to the muscles of the pharyngeal arches in humans, and the branchial arches in fish.

During Human embryogenesis the mandibular arch and hyoid arch grow more rapidly than those behind them, with the result that the latter become, to a certain extent, telescoped within the former, and a deep depression, the cervical sinus, is formed on either side of the neck.
The pharyngeal branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve are three or four filaments which unite, opposite the Constrictor pharyngis medius, with the pharyngeal branches of the vagus and sympathetic, to form the pharyngeal plexus.

The lung bud sometimes referred to as the respiratory bud forms from the respiratory diverticulum, an embryological endodermal structure that develops into the respiratory tract organs such as the larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. It arises from part of the laryngotracheal tube.

The two lateral lingual swellings or distal tongue buds form from the first pharyngeal arch, in the fifth week of embryogenesis following the development of the median tongue bud in the fourth week. These swellings grow downwards and towards each other covering the median tongue bud. Their line of fusion is marked by the median sulcus of the tongue. They will form the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and their boundary with the hypopharyngeal eminence (which will form the posterior one-third of the tongue is marked by the terminal sulcus.

Human embryonic development, or human embryogenesis, refers to the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Embryonic development in the human, covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.

The pharynx is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity and above the esophagus and larynx, or the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species.
The face and neck development of the human embryo refers to the development of the structures from the third to eighth week that give rise to the future head and neck. They consist of three layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, which form the mesenchyme, neural crest and neural placodes. The paraxial mesoderm forms structures named somites and somitomeres that contribute to the development of the floor of the brain and voluntary muscles of the craniofacial region. The lateral plate mesoderm consists of the laryngeal cartilages. The three tissue layers give rise to the pharyngeal apparatus, formed by six pairs of pharyngeal arches, a set of pharyngeal pouches and pharyngeal grooves, which are the most typical feature in development of the head and neck. The formation of each region of the face and neck is due to the migration of the neural crest cells which come from the ectoderm. These cells determine the future structure to develop in each pharyngeal arch. Eventually, they also form the neurectoderm, which forms the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain, cartilage, bone, dentin, tendon, dermis, pia mater and arachnoid mater, sensory neurons, and glandular stroma.