Intensive insulin therapy or flexible insulin therapy is a therapeutic regimen for diabetes mellitus treatment. This newer approach contrasts with conventional insulin therapy. Rather than minimize the number of insulin injections per day, the intensive approach favors flexible meal times with variable carbohydrate as well as flexible physical activities. The trade-off is the increase from 2 or 3 injections per day to 4 or more injections per day, which was considered "intensive" relative to the older approach. In North America in 2004, many endocrinologists prefer the term "flexible insulin therapy" (FIT) to "intensive therapy" and use it to refer to any method of replacing insulin that attempts to mimic the pattern of small continuous basal insulin secretion of a working pancreas combined with larger insulin secretions at mealtimes. The semantic distinction reflects changing treatment.

Blood glucose monitoring is the use of a glucose meter for testing the concentration of glucose in the blood (glycemia). Particularly important in diabetes management, a blood glucose test is typically performed by piercing the skin to draw blood, then applying the blood to a chemically active disposable 'test-strip'. The other main option is continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Different manufacturers use different technology, but most systems measure an electrical characteristic and use this to determine the glucose level in the blood. Skin-prick methods measure capillary blood glucose, whereas CGM correlates interstitial fluid glucose level to blood glucose level. Measurements may occur after fasting or at random nonfasting intervals, each of which informs diagnosis or monitoring in different ways.

The glucose tolerance test is a medical test in which glucose is given and blood samples taken afterward to determine how quickly it is cleared from the blood. The test is usually used to test for diabetes, insulin resistance, impaired beta cell function, and sometimes reactive hypoglycemia and acromegaly, or rarer disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. In the most commonly performed version of the test, an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), a standard dose of glucose is ingested by mouth and blood levels are checked two hours later. Many variations of the GTT have been devised over the years for various purposes, with different standard doses of glucose, different routes of administration, different intervals and durations of sampling, and various substances measured in addition to blood glucose.

Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Symptoms may also include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that do not heal. Often symptoms come on slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, strokes, diabetic retinopathy which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the limbs which may lead to amputations. The sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon.
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by decreasing glucose levels in the blood. With the exception of insulin, most GLP-1 receptor agonists, and pramlintide, all diabetes medications are administered orally and are thus called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of hypoglycemic drugs, and selection of the appropriate agent depends on the nature of diabetes, age, and situation of the person, as well as other patient factors.
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) refers to any of several hereditary forms of diabetes mellitus caused by mutations in an autosomal dominant gene disrupting insulin production. Along with neonatal diabetes, MODY is a form of the conditions known as monogenic diabetes. While the more common types of diabetes involve more complex combinations of causes involving multiple genes and environmental factors, each forms of MODY are caused by changes to a single gene (monogenic). GCK-MODY and HNF1A-MODY are the most common forms.
Glycated hemoglobin is a form of hemoglobin (Hb) that is chemically linked to a sugar. Most monosaccharides, including glucose, galactose and fructose, spontaneously bond with hemoglobin when present in the bloodstream. However, glucose is only 21% as likely to do so as galactose and 13% as likely to do so as fructose, which may explain why glucose is used as the primary metabolic fuel in humans.
Steroid diabetes or steroid-induced diabetes is characterized as an unusual rise in blood sugar that is linked to the use of glucocorticoids in a patient who may or may not have had diabetes mellitus in the past.
The term diabetes includes several different metabolic disorders that all, if left untreated, result in abnormally high concentrations of a sugar called glucose in the blood. Diabetes mellitus type 1 results when the pancreas no longer produces significant amounts of the hormone insulin, usually owing to the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Diabetes mellitus type 2, in contrast, is now thought to result from autoimmune attacks on the pancreas and/or insulin resistance. The pancreas of a person with type 2 diabetes may be producing normal or even abnormally large amounts of insulin. Other forms of diabetes mellitus, such as the various forms of maturity-onset diabetes of the young, may represent some combination of insufficient insulin production and insulin resistance. Some degree of insulin resistance may also be present in a person with type 1 diabetes.

Elliott Proctor Joslin was the first medical doctor in the United States to specialize in diabetes and was the founder of the present-day Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston, Massachusetts.
A diabetic diet is a diet that is used by people with diabetes mellitus or high blood sugar to minimize symptoms and dangerous complications of long-term elevations in blood sugar.

AIDA is a freeware computer program that permits the interactive simulation of plasma insulin and blood glucose profiles for demonstration, teaching, self-learning, and research purposes. Originally developed in 1991, it has been updated and enhanced since, and made available without charge from 1996 on the World Wide Web. The program, which is still being updated, has gone through a number of revisions and developments in the 16+ years since its original internet launch. During this time over 2.5 million visits have been logged at the AIDA Websites and more than 400,000 copies of the program have been downloaded. Further copies of the simulator have been made available, in the past, on diskette by the system developers and from the British Diabetic Association (BDA) — now called 'Diabetes UK' — London, England, following the BDA's own independent evaluation of the software. More than 1,075,000 diabetes simulations have been run via a web-based version of the AIDA diabetes simulator.
Diabulimia, also known as ED-DMT1 in the US or T1ED in the UK, is an eating disorder in which people with type 1 diabetes deliberately give themselves less insulin than they need or stop taking it altogether for the purpose of weight loss. Diabulimia is not recognized as a formal psychiatric diagnosis in the DSM-5. Because of this, some in the medical or psychiatric communities use the phrases "disturbed eating behavior" or "disordered eating behavior" and disordered eating (DE) are quite common in medical and psychiatric literature addressing patients who have type 1 diabetes and manipulate insulin doses to control weight along with exhibiting bulimic behavior.
Prediabetes is a component of metabolic syndrome and is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that fall below the threshold to diagnose diabetes mellitus. It usually does not cause symptoms but people with prediabetes often have obesity, dyslipidemia with high triglycerides and/or low HDL cholesterol, and hypertension. It is also associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Prediabetes is more accurately considered an early stage of diabetes as health complications associated with type 2 diabetes often occur before the diagnosis of diabetes.
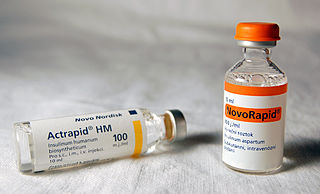
As a medication, insulin is any pharmaceutical preparation of the protein hormone insulin that is used to treat high blood glucose. Such conditions include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. Insulin is also used along with glucose to treat hyperkalemia. Typically it is given by injection under the skin, but some forms may also be used by injection into a vein or muscle. There are various types of insulin, suitable for various time spans. The types are often all called insulin in the broad sense, although in a more precise sense, insulin is identical to the naturally occurring molecule whereas insulin analogues have slightly different molecules that allow for modified time of action. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2021, it was the 179th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.

MiniMed Paradigm is a series of insulin pumps manufactured by Medtronic for patients with diabetes mellitus. The pump operates with a single AAA battery and uses a piston-plunger pump to infuse a programmed amount of insulin into the patient through a length of tubing. The Paradigm uses a one-way wireless radio frequency link to receive blood sugar measurements from select glucose meters. The Paradigm RT series adds the ability to receive data from a mated continuous blood-glucose monitor. Although the pump can use these measurements to assist in calculating a dose of insulin, no actual change in insulin delivery occurs without manual user-intervention.
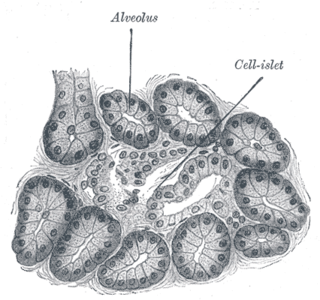
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which the beta cells of the endocrine pancreas either stop producing insulin or can no longer produce it in enough quantity for the body's needs. The disease can affect humans as well as animals such as dogs.

Insulin degludec (INN/USAN) is an ultralong-acting basal insulin analogue that was developed by Novo Nordisk under the brand name Tresiba. It is administered via subcutaneous injection to help control the blood sugar level of those with diabetes. It has a duration of action that lasts up to 42 hours, making it a once-daily basal insulin, that is one that provides a base insulin level, as opposed to the fast- and short-acting bolus insulins.

Diabetes mellitus, often known simply as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to the hormone's effects. Classic symptoms include thirst, polyuria, weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Untreated or poorly treated diabetes accounts for approximately 1.5 million deaths every year.
Lorena Alarcon-Casas Wright is a physician (endocrinologist) and an Associate Professor at the University of Washington School of Medicine who serves as the Clinical Director of the LatinX Diabetes Clinic at UW Medicine's Diabetes Institute. Wright specializes in Metabolism, Endocrinology, and Nutrition at the UW Medical Center, Harborview Medical Center, and the UW Diabetes Institute Clinic.









