A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.

In geometry, a hexagon is a six-sided polygon or 6-gon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
In computing, a symbolic link is a term for any file that contains a reference to another file or directory in the form of an absolute or relative path and that affects pathname resolution.

The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system is a system of geographic grid references used in Great Britain, distinct from latitude and longitude. It is often called British National Grid (BNG).
A GIS file format is a standard of encoding geographical information into a computer file. They are created mainly by government mapping agencies or by GIS software developers.
A geocode is a code that represents a geographic entity. It is a unique identifier of the entity, to distinguish it from others in a finite set of geographic entities. In general the geocode is a human-readable and short identifier.
The Natural Area Code is a proprietary geocode system for identifying an area anywhere on the Earth, or a volume of space anywhere around the Earth. The use of thirty alphanumeric characters instead of only ten digits makes a NAC shorter than its numerical latitude/longitude equivalent.

A geodetic datum or geodetic system is a coordinate system, and a set of reference points, used to locate places on the Earth. An approximate definition of sea level is the datum WGS 84, an ellipsoid, whereas a more accurate definition is Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008), using at least 2,159 spherical harmonics. Other datums are defined for other areas or at other times; ED50 was defined in 1950 over Europe and differs from WGS 84 by a few hundred meters depending on where in Europe you look. Mars has no oceans and so no sea level, but at least two martian datums have been used to locate places there.
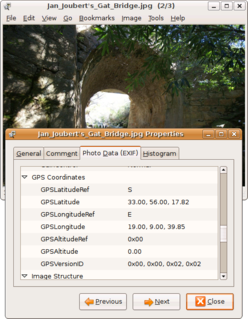
Geotagging, or GeoTagging, is the process of adding geographical identification metadata to various media such as a geotagged photograph or video, websites, SMS messages, QR Codes or RSS feeds and is a form of geospatial metadata. This data usually consists of latitude and longitude coordinates, though they can also include altitude, bearing, distance, accuracy data, and place names, and perhaps a time stamp.
In the Domain Name System, a LOC record is a means for expressing geographic location information for a domain name.

The shapefile format is a geospatial vector data format for geographic information system (GIS) software. It is developed and regulated by Esri as a mostly open specification for data interoperability among Esri and other GIS software products. The shapefile format can spatially describe vector features: points, lines, and polygons, representing, for example, water wells, rivers, and lakes. Each item usually has attributes that describe it, such as name or temperature.
VMDS abbreviates the relational database technology called Version Managed Data Store provided by GE Energy as part of its Smallworld technology platform and was designed from the outset to store and analyse the highly complex spatial and topological networks typically used by enterprise utilities such as power distribution and telecommunications.
Georeferencing means that the internal coordinate system of a map or aerial photo image can be related to a ground system of geographic coordinates. The relevant coordinate transforms are typically stored within the image file, though there are many possible mechanisms for implementing georeferencing. The most visible effect of georeferencing is that display software can show ground coordinates and also measure ground distances and areas. In other words, Georeferencing means to associate something with locations in physical space. The term is commonly used in the geographic information systems field to describe the process of associating a physical map or raster image of a map with spatial locations. Georeferencing may be applied to any kind of object or structure that can be related to a geographical location, such as points of interest, roads, places, bridges, or buildings.

In geometry, a polygonal chain is a connected series of line segments. More formally, a polygonal chain P is a curve specified by a sequence of points called its vertices. The curve itself consists of the line segments connecting the consecutive vertices.
In the Unicode standard, a plane is a continuous group of 65,536 (216) code points. There are 17 planes, identified by the numbers 0 to 16, which corresponds with the possible values 00–1016 of the first two positions in six position hexadecimal format (U+hhhhhh). Plane 0 is the Basic Multilingual Plane (BMP), which contains most commonly-used characters. The higher planes 1 through 16 are called "supplementary planes". The very last code point in Unicode is the last code point in plane 16, U+10FFFF. As of Unicode version 12.1, six of the planes have assigned code points (characters), and four are named.
In mathematics, the Fréchet distance is a measure of similarity between curves that takes into account the location and ordering of the points along the curves. It is named after Maurice Fréchet.

WinFIG is a proprietary shareware vector graphics editor application. The file format and rendering are as close to Xfig as possible, but the program takes advantage of Windows features like clipboard, printer preview, multiple documents etc.

The geo URI scheme is a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) scheme defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force's RFC 5870 as:
a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) for geographic locations using the 'geo' scheme name. A 'geo' URI identifies a physical location in a two- or three-dimensional coordinate reference system in a compact, simple, human-readable, and protocol-independent way.
The Mobile Location Protocol (MLP) is an application-level protocol for receiving the position of Mobile Stations independent of underlying network technology.