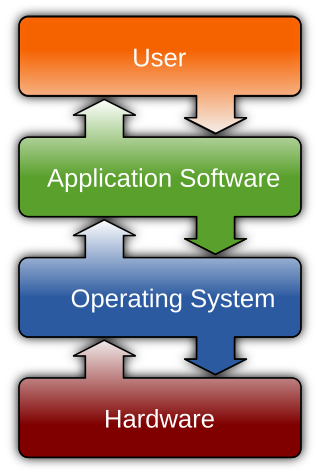
Software is a collection of programs and data that tell a computer how to perform specific tasks. Software often includes associated software documentation. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.

Free software, libre software, or libreware is computer software distributed under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, and distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program. Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices.
Freeware is software, most often proprietary, that is distributed at no monetary cost to the end user. There is no agreed-upon set of rights, license, or EULA that defines freeware unambiguously; every publisher defines its own rules for the freeware it offers. For instance, modification, redistribution by third parties, and reverse engineering are permitted by some publishers but prohibited by others. Unlike with free and open-source software, which are also often distributed free of charge, the source code for freeware is typically not made available. Freeware may be intended to benefit its producer by, for example, encouraging sales of a more capable version, as in the freemium and shareware business models.
Shareware is a type of proprietary software that is initially shared by the owner for trial use at little or no cost. Often the software has limited functionality or incomplete documentation until the user sends payment to the software developer. Shareware is often offered as a download from a website. Shareware differs from freeware, which is fully-featured software distributed at no cost to the user but without source code being made available; and free and open-source software, in which the source code is freely available for anyone to inspect and alter.

The Windows API, informally WinAPI, is the foundational application programming interface (API) that allows a computer program to access the features of the Microsoft Windows operating system in which the program is running.
The Open Sound System (OSS) is an interface for making and capturing sound in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is based on standard Unix devices system calls. The term also sometimes refers to the software in a Unix kernel that provides the OSS interface; it can be thought of as a device driver for sound controller hardware. The goal of OSS is to allow the writing of sound-based applications that are agnostic of the underlying sound hardware.
Software development is the process used to create software. Programming and maintaining the source code is the central step of this process, but it also includes conceiving the project, evaluating its feasibility, analyzing the business requirements, software design, testing, to release. Software engineering, in addition to development, also includes project management, employee management, and other overhead functions. Software development may be sequential, in which each step is complete before the next begins, but iterative development methods where multiple steps can be executed at once and earlier steps can be revisited have also been devised to improve flexibility, efficiency, and scheduling.

Open-source software (OSS) is computer software that is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative, public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration, meaning any capable user is able to participate online in development, making the number of possible contributors indefinite. The ability to examine the code facilitates public trust in the software.

Kodi is a free and open-source media player and technology convergence software application developed by the Kodi Foundation, a non-profit technology consortium. Kodi is available for multiple operating systems and hardware platforms, with a software 10-foot user interface for use with televisions and remote controls. It allows users to play and view most streaming media, such as videos, music, podcasts, and videos from the Internet, as well as all common digital media files from local and network storage media, or TV gateway viewer.

Delicious Library is a digital asset management app for Mac OS X, developed by Delicious Monster to allow the user to keep track and manage their physical collections of books, movies, CDs, and video games.
FAAC is a software project which includes the AAC encoder FAAC and decoder FAAD2. It supports MPEG-2 AAC as well as MPEG-4 AAC. It supports several MPEG-4 Audio object types, file formats, multichannel and gapless encoding/decoding and MP4 metadata tags. The encoder and decoder is compatible with standard-compliant audio applications using one or more of these object types and facilities. It also supports Digital Radio Mondiale.

FreeRTOS is a real-time operating system kernel for embedded devices that has been ported to 35 microcontroller platforms. It is distributed under the MIT License.
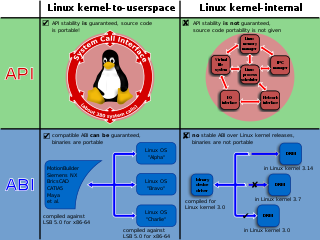
The Linux kernel provides multiple interfaces to user-space and kernel-mode code that are used for varying purposes and that have varying properties by design. There are two types of application programming interface (API) in the Linux kernel:
- the "kernel–user space" API; and
- the "kernel internal" API.

GeoGebra is an interactive geometry, algebra, statistics and calculus application, intended for learning and teaching mathematics and science from primary school to university level. GeoGebra is available on multiple platforms, with apps for desktops, tablets and web. It is presently owned by Indian edutech firm Byju's.

Network Security Services (NSS) is a collection of cryptographic computer libraries designed to support cross-platform development of security-enabled client and server applications with optional support for hardware TLS/SSL acceleration on the server side and hardware smart cards on the client side. NSS provides a complete open-source implementation of cryptographic libraries supporting Transport Layer Security (TLS) / Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and S/MIME. NSS releases prior to version 3.14 are tri-licensed under the Mozilla Public License 1.1, the GNU General Public License, and the GNU Lesser General Public License. Since release 3.14, NSS releases are licensed under GPL-compatible Mozilla Public License 2.0.

Aptana, Inc. is a company that makes web application development tools for use with a variety of programming languages. Aptana's main products include Aptana Studio, Aptana Cloud and Aptana Jaxer.

CNR, or One-Click & Run, was a free one-click software delivery service that was created to make finding and installing Linux software easier. It assisted the user in finding and installing software on their computer, and sat dormant in the system tray when not in use.

Abandonware is a product, typically software, ignored by its owner and manufacturer, which can no longer be found for sale, and for which no official support is available.
Proprietary software is software that grants its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner a legal monopoly by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing the software or modifying it, and—in some cases, as is the case with some patent-encumbered and EULA-bound software—from making use of the software on their own, thereby restricting their freedoms.

Software categories are groups of software. They allow software to be understood in terms of those categories, instead of the particularities of each package. Different classification schemes consider different aspects of software.













