| C77 | |
|---|---|
| ILO Convention | |
| Date of adoption | October 9, 1946 |
| Date in force | December 29, 1950 |
| Classification | Medical Examination |
| Subject | Elimination of Child Labour and Protection of Children and Young Persons |
| Previous | Wages, Hours of Work and Manning (Sea) Convention, 1946 |
| Next | Medical Examination of Young Persons (Non-Industrial Occupations) Convention, 1946 |
Medical Examination of Young Persons (Industry) Convention, 1946 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
It was established in 1946 with the preamble stating:
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to medical examination for fitness for employment in industry of children and young persons,...
As of 2013, the convention has been ratified by 43 states.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The Convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.
The International Opium Convention, signed at The Hague on January 23, 1912 during the First International Opium Conference, was the first international drug control treaty. The United States was unsuccessful in its attempts to have cannabis included in the 1912 Convention. It was registered in League of Nations Treaty Series on January 23, 1922. The United States convened a 13-nation conference of the International Opium Commission in 1909 in Shanghai, China, in response to increasing criticism of the opium trade. The treaty was signed by Germany, the United States, China, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Persia, Portugal, Russia, and Siam. The Convention provided, "The contracting Powers shall use their best endeavours to control, or to cause to be controlled, all persons manufacturing, importing, selling, distributing, and exporting morphine, cocaine, and their respective salts, as well as the buildings in which these persons carry such an industry or trade."

The Protocol Amending the Agreements, Conventions and Protocols on Narcotic Drugs concluded at The Hague on 23 January 1912, at Geneva on 11 February 1925 and 19 February 1925, and 13 July 1931, at Bangkok on 27 November 1931 and at Geneva on 26 June 1936 was a treaty, signed on 11 December 1946 at Lake Success, that shifted the drug control functions previously assigned to the League of Nations to the United Nations. As the Protocol's official title says, it modifies the provisions of the:
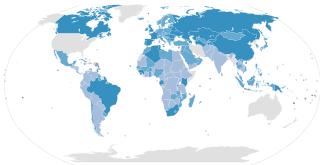
The ILO Convention concerning Minimum Age for Admission to Employment C138, is a convention adopted in 1973 by the International Labour Organization. It requires ratifying states to pursue a national policy designed to ensure the effective abolition of child labour and to raise progressively the minimum age for admission to employment or work. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions. Convention C138 replaces several similar ILO conventions in specific fields of labour.
Medical Examination of Young Persons (Sea) Convention, 1921 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Medical Examination (Seafarers) Convention, 1946 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Medical Examination of Young Persons Convention, 1946 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Medical Examination (Fishermen) Convention, 1959 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Radiation Protection Convention, 1960 is an International Labour Organization Convention to restrict workers from exposure of ionising radiation and to prohibit persons under 16 engaging in work that causes such exposure.
Medical Examination of Young Persons Convention, 1965 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Prevention of Accidents (Seafarers) Convention, 1970 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Safety and Health in Mines Convention, 1995 is an International Labour Organization Convention. It was adopted at the 82nd International Labour Conference (ILC) of the International Labour Organization (ILO). The ILO is an agency under the United Nations that deals with international labor issues while promoting workers rights and opportunities. One of ILO's goals is to hold annual labor conventions to create legally binding contracts for participating nations to ratify. During the Safety and Health in Mines Convention (C176), it was recognized that there are inherent hazards in the mining workplace, and a need for a convention was mandatory.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the United Nations:
Work in Fishing Convention (2007) C 188, was adopted at the 96th International Labour Conference (ILC) of the International Labour Organization ILO in 2007. The objectives of the Convention is to ensure that fishers have decent conditions of work on board fishing vessels with regard to minimum requirements for work on board; conditions of service; accommodation and food; occupational safety and health protection; medical care and social security. It applies to all fishers and fishing vessels engaged in commercial fishing operations. It supersedes the old Conventions relating to fishermen.

The timeline of young peoples' rights in the United States, including children and youth rights, includes a variety of events ranging from youth activism to mass demonstrations. There is no "golden age" in the American children's rights movement.
C77 may refer to :

The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) is an International Labour Organization convention, number 186, established in 2006 as the fourth pillar of international maritime law and embodies "all up-to-date standards of existing international maritime labour Conventions and Recommendations, as well as the fundamental principles to be found in other international labour Conventions". The other "pillars are the SOLAS, STCW and MARPOL. The treaties applies to all ships entering the harbours of parties to the treaty, as well as to all ships flying the flag of state party.
The Conventions concerning Employment of Women during the Night are conventions drafted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) which prohibit women from performing industrial work during the night. The first convention was adopted in 1919 and revised versions were adopted in 1934 and 1948. A protocol to the convention was adopted in 1990 allowing for easing of the restriction under conditions. As of April 2011 the conventions had 27, 15, 46 (undenounced) ratifications respectively. The protocol was ratified 5 and denounced by 2.
Child labour laws are statutes placing restrictions and regulations on the work of minors.

Azerbaijan ranks fairly poorly in terms of its commitment to the protection of animal welfare and freedom from suffering. It is ranked 36th out of 50 countries on the Voiceless Animal Cruelty Index. According to the Animal Protection Index, it has not pledged support for the Universal Declaration on Animal Welfare, there is no policy or legislation in the country preventing animal suffering by deliberate acts or negligence, and there are no animal protection laws in reference to animals used in farming. The country does have legislation on the conservation of wild animals, which also apply to animals kept in confinement. It implies a duty of care, in limited situations, but its effectiveness is hard to assess.