
Obstetrics and Gynaecology is the medical specialty that encompasses the two subspecialties of obstetrics and gynecology.

An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of patients who present without prior appointment; either by their own means or by that of an ambulance. The emergency department is usually found in a hospital or other primary care center.

The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 21, 1996. It modernized the flow of healthcare information, stipulates how personally identifiable information maintained by the healthcare and healthcare insurance industries should be protected from fraud and theft, and addressed some limitations on healthcare insurance coverage. It generally prohibits healthcare providers and healthcare businesses, called covered entities, from disclosing protected information to anyone other than a patient and the patient's authorized representatives without their consent. With limited exceptions, it does not restrict patients from receiving information about themselves. It does not prohibit patients from voluntarily sharing their health information however they choose, nor does it require confidentiality where a patient discloses medical information to family members, friends, or other individuals not a part of a covered entity.
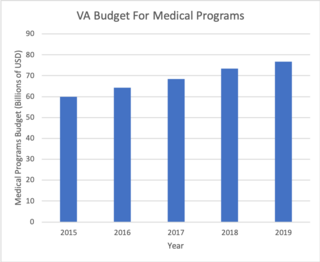
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the component of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) led by the Under Secretary of Veterans Affairs for Health that implements the healthcare program of the VA through a nationalized healthcare service in the United States, providing healthcare and healthcare-adjacent services to Veterans through the administration and operation of 146 VA Medical Centers (VAMC) with integrated outpatient clinics, 772 Community Based Outpatient Clinics (CBOC), and 134 VA Community Living Centers Programs. It is the largest division in the Department, and second largest in the entire federal government, employing over 350,000 employees. All VA hospitals, clinics and medical centers are owned by and operated by the Department of Veterans Affairs as opposed to private companies, and all of the staff employed in VA hospitals are government employees. Because of this, Veterans that qualify for VHA healthcare do not pay premiums or deductibles for their healthcare but may have to make copayments depending on what procedure they are having. VHA is distinct from the U.S. Department of Defense Military Health System of which it is not a part.
Community health refers to simple health services that are delivered by laymen outside hospitals and clinics. Community health is also the subset of public health that is taught to and practiced by clinicians. Community health volunteers and community health workers work with Primary Care Providers to facilitate entry into, exit from and utilization of the formal health system by community members.
Clinical audit is a process that has been defined as a quality improvement process that seeks to improve patient care and outcomes through systematic review of care against explicit criteria and the implementation of change
Health information exchange (HIE) is the mobilization of health care information electronically across organizations within a region, community or hospital system. Participants in data exchange are called in the aggregate Health Information Networks (HIN). In practice, the term HIE may also refer to the health information organization (HIO) that facilitates the exchange.
Utilization management (UM) or utilization review is the use of managed care techniques such as prior authorization that allow payers, particularly health insurance companies, to manage the cost of health care benefits by assessing its appropriateness before it is provided using evidence-based criteria or guidelines.
Case management is a managed care technique within the health care coverage system of the United States. It involves an integrated system that manages the delivery of comprehensive healthcare services for enrolled patients. Case managers are employed in almost every aspect of health care and these employ different approaches in the control of clinical actions.
The medical home, also known as the patient-centered medical home (PCMH), is a team-based health care delivery model led by a health care provider to provide comprehensive and continuous medical care to patients with a goal to obtain maximal health outcomes. It is described in the "Joint Principles" as "an approach to providing comprehensive primary care for children, youth and adults."
Health administration, healthcare administration, healthcare management or hospital management is the field relating to leadership, management, and administration of public health systems, health care systems, hospitals, and hospital networks in all the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors.
A clinical pathway, also known as care pathway, integrated care pathway, critical pathway, or care map, is one of the main tools used to manage the quality in healthcare concerning the standardisation of care processes. It has been shown that their implementation reduces the variability in clinical practice and improves outcomes. Clinical pathways aim to promote organised and efficient patient care based on evidence-based medicine, and aim to optimise outcomes in settings such as acute care and home care. A single clinical pathway may refer to multiple clinical guidelines on several topics in a well specified context.
Ambulatory care nursing is the nursing care of patients who receive treatment on an outpatient basis, ie they do not require admission to a hospital for an overnight stay. Ambulatory care includes those clinical, organizational and professional activities engaged in by registered nurses with and for individuals, groups, and populations who seek assistance with improving health and/or seek care for health-related problems. The American Academy of Ambulatory Care Nursing (AAACN) describes ambulatory care nursing as a comprehensive practice which is built on a broad knowledge base of nursing and health sciences, and applies clinical expertise rooted in the nursing process.
Case management is the coordination of community-based services by a professional or team to provide quality mental health care customized accordingly to individual patients' setbacks or persistent challenges and aid them to their recovery. Case management seeks to reduce hospitalizations and support individuals' recovery through an approach that considers each person's overall biopsychosocial needs without making disadvantageous economic costs. As a result, care coordination includes traditional mental health services but may also encompass primary healthcare, housing, transportation, employment, social relationships, and community participation. It is the link between the client and care delivery system.
Case management is the coordination of services on behalf of an individual person who may be considered a case in different settings such as health care, nursing, rehabilitation, social work, disability insurance, employment, and law. Case management may refer to:
An accountable care organization (ACO) is a healthcare organization that ties provider reimbursements to quality metrics and reductions in the cost of care. ACOs in the United States are formed from a group of coordinated health-care practitioners. They use alternative payment models, normally, capitation. The organization is accountable to patients and third-party payers for the quality, appropriateness and efficiency of the health care provided. According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, an ACO is "an organization of health care practitioners that agrees to be accountable for the quality, cost, and overall care of Medicare beneficiaries who are enrolled in the traditional fee-for-service program who are assigned to it".
An ambulatist is a licensed health care provider who specializes in the prevention, management, and care coordination of ambulatory patients with chronic diseases by using lifestyle medicine and drug therapy.
Occupational health nursing is a specialty nursing practice that provides for and delivers health and safety programs and services to workers, worker populations, and community groups. The practice focuses on promotion, maintenance and restoration of health, prevention of illness and injury, and protection from work‐related and environmental hazards. Occupational health nurses (OHNs) aim to combine knowledge of health and business to balance safe and healthful work environments and a "healthy" bottom line.
The Donabedian model is a conceptual model that provides a framework for examining health services and evaluating quality of health care. According to the model, information about quality of care can be drawn from three categories: “structure,” “process,” and “outcomes." Structure describes the context in which care is delivered, including hospital buildings, staff, financing, and equipment. Process denotes the transactions between patients and providers throughout the delivery of healthcare. Finally, outcomes refer to the effects of healthcare on the health status of patients and populations. Avedis Donabedian, a physician and health services researcher at the University of Michigan, developed the original model in 1966. While there are other quality of care frameworks, including the World Health Organization (WHO)-Recommended Quality of Care Framework and the Bamako Initiative, the Donabedian Model continues to be the dominant paradigm for assessing the quality of health care.
Health policy and management is the field relating to leadership, management, and administration of public health systems, health care systems, hospitals, and hospital networks. Health care administrators are considered health care professionals.




