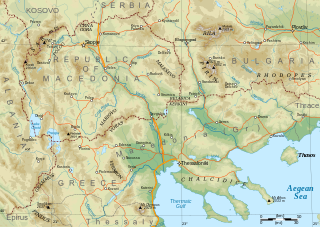
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid-19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: all of North Macedonia, large parts of Greece and Bulgaria, and smaller parts of Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately 67,000 square kilometres (25,869 sq mi) and has a population of around five million. Greek Macedonia comprises about half of Macedonia's area and population.

The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid Sultanate. However, a sequence of economic and political events culminated in the Crusader army's 1202 siege of Zara and the 1204 sack of Constantinople, rather than the conquest of Egypt as originally planned. This led to the Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae or the partition of the Byzantine Empire by the Crusaders and their Venetian allies leading to a period known as Frankokratia, or "Rule of the Franks" in Greek.
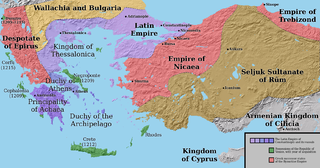
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantine Empire as the Western-recognized Roman Empire in the east, with a Catholic emperor enthroned in place of the Eastern Orthodox Roman emperors. The main objective to form a Latin Empire was planned over the course of the Fourth Crusade, promoted by crusade leaders such as Boniface of Montferrat, as well as the Republic of Venice.
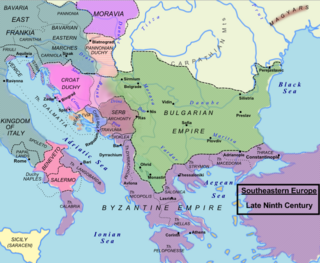
The Principality of Serbia was one of the early medieval states of the Serbs, located in the western regions of Southeastern Europe. It existed from the 8th century up to c. 969–971 and was ruled by the Vlastimirović dynasty. Its first ruler known by name was Višeslav who started ruling around 780. While by that time, starting from the year 680–681, the Bulgarian state had taken the lands to the east. Vlastimir resisted and defeated the Bulgarian army in a three-year-war (839–842), and the two powers lived in peace for some decades. Vlastimir's three sons succeeded in ruling Serbia together, although not for long; Serbia became a key part in the power struggle between the Byzantines and Bulgarians, predominantly allied with the Byzantines, which also resulted in major dynastic wars for a period of three decades. The principality was annexed in 924 by Simeon I and subjected to Bulgarian rule until 933 when Serbian prince Časlav was established as ruler of the Serbian land, becoming the most powerful ruler of the Vlastimirović dynasty.

When the Roman Empire divided into east and west in 395, the territories of modern Albania became a part of the Byzantine Empire. At the end of the 12th century, the Principality of Arbanon was formed which lasted until mid 13th century, after its dissolution it was followed with the creation of the Albanian Kingdom after an alliance between the Albanian noblemen and Angevin dynasty. After a war against the Byzantine empire led the kingdom occasionally decrease in size until the Angevins eventually lost their rule in Albania and led the territory ruled by several different Albanian chieftains until the mid 14th century which for a short period of time were conquered by the short-lived empire of Serbia. After its fall in 1355 several chieftains regained their rule and significantly expanded until the arrival of the Ottomans after the Battle of Savra.
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 1500.

Byzantine Greece has a history that mainly coincides with that of the Byzantine Empire itself.
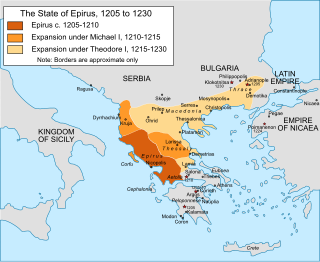
The Despotate of Epirus was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claimed to be the legitimate successor of the Byzantine Empire during the subsequent struggle for Constantinople, along with the Empire of Nicaea and the Empire of Trebizond; its rulers briefly proclaiming themselves as Emperors in 1227–1242. The term "Despotate of Epirus" is, like "Byzantine Empire" itself, a modern historiographic convention and not a name in use at the time.

The Serbian Despotate was a medieval Serbian state in the first half of the 15th century. Although the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 is mistakenly considered the end of medieval Serbia, the Despotate, a successor of the Serbian Empire and Moravian Serbia, lasted for another sixty years, experiencing a cultural, economic, and political renaissance, especially during the reign of Despot Stefan Lazarević. After the death of Despot Đurađ Branković in 1456, the Despotate continued to exist for another three years before it finally fell under Ottoman rule in 1459.
The Second Bulgarian Empire was a medieval Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1396. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II before gradually being conquered by the Ottomans in the early 15th century.

Despot or despotes was a senior Byzantine court title that was bestowed on the sons or sons-in-law of reigning emperors, and initially denoted the heir-apparent of the Byzantine emperor.

The Frankokratia, also known as Latinokratia and, for the Venetian domains, Venetokratia or Enetokratia, was the period in Greek history after the Fourth Crusade (1204), when a number of primarily French and Italian states were established by the Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae on the territory of the dismantled Byzantine Empire.
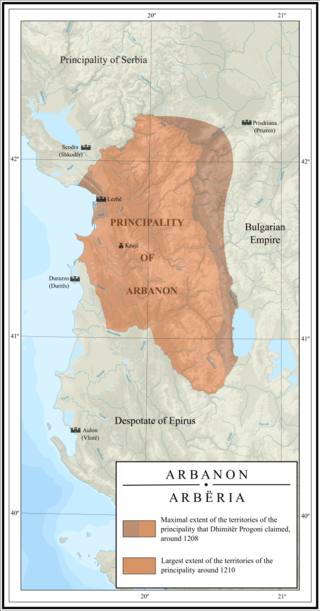
Arbanon was a medieval principality in present-day Albania, ruled by the native Progoni family, and the first Albanian state to emerge in recorded history. The principality was established in 1190 by the Albanian archon Progon in the region surrounding Kruja, to the east and northeast of Venetian territories. Progon was succeeded by his sons Gjin and then Demetrius (Dhimitër), who managed to retain a considerable degree of autonomy from the Byzantine Empire. In 1204, Arbanon attained full, though temporary, political independence, taking advantage of the weakening of Constantinople following its pillage during the Fourth Crusade. However, Arbanon lost its large autonomy ca. 1216, when the ruler of Epirus, Michael I Komnenos Doukas, started an invasion northward into Albania and Macedonia, taking Kruja and ending the independence of the principality. From this year, after the death of Demetrius, the last ruler of the Progoni family, Arbanon was successively controlled by the Despotate of Epirus, then by the Bulgarian Empire and, from 1235, by the Empire of Nicaea.
After the weakening of the Byzantine Empire and the Bulgarian Empire in the middle and late 13th century, the northern territory of modern-day Albania became part of Serbia. Firstly, as part of Serbian Grand Principality and later as part of Serbian Empire. Serb control in southern Albania is unclear. Some suggest they acquired towns, but others believe they only obtained submission, possibly nominal, from Albanian tribes. Central and southern Albanian towns were not conquered until 1343–45. Between 1272 and 1368, some areas of the modern-day state were also ruled by the Angevins as the Kingdom of Albania. In the late 14th century, Albanian Principalities were created throughout Albania.
Vagenetia or Vagenitia was a medieval region on the coast of Epirus, roughly corresponding to modern Thesprotia. The region likely derived its name from the Slavic tribe of the Baiounitai. It is first attested as a sclavinia under some sort of Byzantine control in the 8th/9th centuries. It passed under Bulgarian rule in the late 9th century, and returned to Byzantine rule in the 11th. It passed to the Despotate of Epirus after 1204, where it formed a separate province. Vagenetia came under Albanian rule in the 1360s, until conquered by the Ottoman Empire in 1430.

The Kingdom of Serbia, or the Serbian Kingdom, was a medieval Serbian kingdom in Southern Europe comprising most of what is today Serbia, Kosovo, and Montenegro, as well as southeastern Bosnia and Herzegovina, parts of coastal Croatia south of the Neretva river, Albania north of the Drin River, North Macedonia, and a small part of western Bulgaria. The medieval Kingdom of Serbia existed from 1217 to 1346 and was ruled by the Nemanjić dynasty. The Grand Principality of Serbia was elevated with the regal coronation of Stefan Nemanjić as king, after the reunification of Serbian lands. In 1219, Serbian Orthodox Church was reorganized as an autocephalous archbishopric, headed by Saint Sava. The kingdom was proclaimed an empire in 1346, but kingship was not abolished as an institution, since the title of a king was used as an official designation for a co-ruler of the emperor.
Kran is a town in central Bulgaria. It is located just south of the Balkan Mountains and is administratively part of Kazanlak Municipality, Stara Zagora Province. Kran was an important castle of the Second Bulgarian Empire in the 13th–14th century. Among the local sights are a conserved ancient Thracian tomb, a much older Thracian sanctuary and the ruins of the medieval fortress.
Dryinopolis or Dryinoupolis is a historical region in southwestern Albania and northwestern Greece in Epirus. The heartland of this region is the valley of the Drino river and Dropull/Dropolis. A Greek-Orthodox bishopric under this name was established at 449 AD as well as a theme (district) of the Byzantine Empire and the Despotate of Epirus. Today the name of Dryinopolis is preserved in the local metropolitan bishopric of the Church of Greece for the Greek part of the region, while the Albanian part is under the religious jurisdiction of the metropolis of Gjirokaster of the Autocephalous Orthodox Church of Albania.

Kolonjë is a municipality in Korçë County, southeastern Albania. It was created in 2015 by the merger of the former municipalities Barmash, Çlirim, Ersekë, Leskovik, Mollas, Novoselë, Qendër Ersekë and Qendër Leskovik. The seat of the municipality is the town Ersekë. The total population is 11,070, in a total area of 865 km2 (334 sq mi). It is an ethnographic region.













