
Mont Blanc is the highest mountain in the Alps and Western Europe, and the highest mountain in Europe outside the Caucasus mountains, rising 4,805.59 m (15,766 ft) above sea level, located on the French-Italian border. It is the second-most prominent mountain in Europe, after Mount Elbrus, and it is the eleventh most prominent mountain summit in the world.
A massif is simply a principal mountain mass, for example, a compact portion of a mountain range, containing one or more summits. In mountaineering literature, a massif is frequently used to denote the main mass of an individual mountain.

The Carnic Alps are a range of the Southern Limestone Alps in Austria and northeastern Italy. They are within Austrian East Tyrol and Carinthia, and Italian Friuli and marginally in Veneto.

Monte Rosa is a mountain massif in the eastern part of the Pennine Alps, on the border between Italy and Switzerland (Valais). The highest peak of the massif, amongst several peaks of over 4.000 m, is the Dufourspitze, the second highest mountain in the Alps and western Europe, after Mont Blanc. The east face of the Monte Rosa towards Italy has a height of about 2.400 meters and is the highest mountain wall of the Alps.

Monte Grappa is a mountain of the Venetian Prealps in Veneto, Italy. It lies between the Venetian plain to the south and the central alpine areas to the North. To the west, it is parted from the Asiago upland by the Brenta river, and to the east it is separated from the Cesen-Visentin massif by the Piave river. To the north lie Corlo lake and Feltre valley. In the past, the mountain was called Alpe Madre, and is currently divided among three provinces: Vicenza to the west, Treviso to the south and Belluno to the northeast. It is the highest peak of a small massif, which also includes many other peaks such as Col Moschin, Colle della Berretta, Monte Asolone, Monte Pertica, Prassolan, Monti Solaroli, Fontana Secca, Monte Peurna, Monte Santo, Monte Tomatico, Meatte, Monte Pallon, and Monte Tomba.

The Gorner Glacier is a valley glacier found on the west side of the Monte Rosa massif close to Zermatt in the canton of Valais, Switzerland. It is about 12.4 km (7.7 mi) long (2014) and 1 to 1.5 km wide. The entire glacial area of the glacier related to Gorner Glacier is 53 km2 (20 sq mi) (2007), which makes it the second largest glacial system in the Alps after the Aletsch Glacier system; however it ranks only third in length behind the Aletsch and Fiescher Glacier, respectively. Numerous smaller glaciers connect with the Gorner Glacier. Its (former) tributaries are : Gornergletscher, Monte Rosa Gletscher, Grenzgletscher, Zwillingsgletscher, Schwärzegletscher, Breithorngletscher, Triftjigletscher, and Unterer Theodulgletscher.

The Grenzgipfel is a peak of Monte Rosa Massif, located on the border between Italy and Switzerland.

The Pollino is a massif in the southern Apennines, on the border between Basilicata and Calabria, southern Italy. It became part of the Pollino National Park in 1992. The main peaks include Monte Pollino (2,248 m) and the massif's high point, Serra Dolcedorme (2,267 m), which overlooks the plain of Sibari.
The Caloris Montes are a range of mountains on Mercury. They are a system of linear hills and valleys that extend more than 1000 km to the northeast from the mountainous rim of Caloris Basin in the Shakespeare quadrangle (H-3). The range consists of numerous rectilinear massifs 1 to 3 km high and about 10 to 50 km long, mostly elongated radially from the center of the basin and separated by hackly-floored, radial troughs and gouge-like structures.

The Nereidum Montes is a mountain range on Mars. It stretches 1,143 km, northeast of Argyre Planitia. It is in the Argyre quadrangle. The mountains are named after a Classical albedo feature. Nereidum Montes has gullies in some areas.

Cristallo is a mountain massif in the Italian Dolomites, northeast of Cortina d'Ampezzo, in the province of Belluno, Veneto, northern Italy. It is a long, indented ridge with four summits higher than 3,000 metres. The mountain range is part of the Ampezzo Dolomites Natural Park.

The Monti della Meta are a massif of central Italy located around the junction point of the boundaries between the regions of Lazio, Abruzzo and Molise. The major of three massifs of the Parco Nazionale d'Abruzzo, Lazio e Molise, they take their name from one of the peaks, Monte Meta.

The Maiella (or Majella) is a massif in the Central Apennines, in Abruzzo, central Italy.
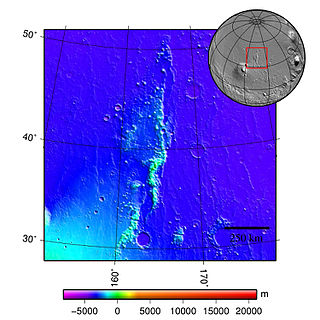
The Phlegra Montes are a system of eroded Hesperian–Noachian-aged massifs and knobby terrain in the mid-latitudes of the northern lowlands of Mars, extending northwards from the Elysium Rise towards Vastitas Borealis for nearly 1,400 km (870 mi). The mountain ranges separate the large plains provinces of Utopia Planitia (west) and Amazonis Planitia (east), and were named in the 1970s after a classical albedo feature. The massif terrains are flanked by numerous parallel wrinkle ridges known as the Phlegra Dorsa.

The Monte Arci is an isolated massif in the Uras plain in Campidano, south-western Sardinia, Italy. It is composed by three volcanic basalt towers, the highest one reaching an elevation of 812 m. The inner part of the massif is composed of trachyte.

The Monte Cinto massif is one of the main massifs in the island of Corsica, France, taking its name from the highest mountain in Corsica, Monte Cinto. It is the northernmost and highest of the four massifs that form the spine of the island. The massif is mostly in the Haute-Corse department, but the southwest of the massif is in the Corse-du-Sud department.

The Monte Astu massif is a chain of mountains in the northeast of the island of Corsica, France. It takes its name from Monte Astu, the highest peak.

The Monte Incudine massif is a chain of mountains in the south of the island of Corsica, France. It takes its name from Monte Incudine, the highest peak.

The Monte Renoso massif is a chain of mountains in the south of the island of Corsica, France. It takes its name from Monte Renoso, the highest peak.

The Monte Rotondo massif is a chain of mountains on the southern side of Corsica, France. It takes its name from Monte Rotondo, the highest peak.


















