Related Research Articles
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membership group, reporting nearly 110,000 student and professional members as of 2022. Its headquarters are in New York City.
A memetic algorithm (MA) in computer science and operations research, is an extension of the traditional genetic algorithm (GA) or more general evolutionary algorithm (EA). It may provide a sufficiently good solution to an optimization problem. It uses a suitable heuristic or local search technique to improve the quality of solutions generated by the EA and to reduce the likelihood of premature convergence.
ACM SIGACT or SIGACT is the Association for Computing Machinery Special Interest Group on Algorithms and Computation Theory, whose purpose is support of research in theoretical computer science. It was founded in 1968 by Patrick C. Fischer.

Timothy Wilking Finin is the Willard and Lillian Hackerman Chair in Engineering and is a Professor of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC). His research has focused on the applications of artificial intelligence to problems in information systems and has included contributions to natural language processing, expert systems, the theory and applications of multiagent systems, the semantic web, and mobile computing.
Design, Automation & Test in Europe, or DATE is a yearly conference on the topic of electronic design automation. It is typically held in March or April of each year, alternating between France and Germany. It is sponsored by the SIGDA of the Association for Computing Machinery, the Electronic System Design Alliance, the European Design and Automation Association (EDAA), and the IEEE Council on Electronic Design Automation (CEDA). Technical co-sponsors include ACM SIGBED, the IEEE Solid-State Circuits Society (SSCS), IFIP, and the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET).
The IEEE Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS) is an academic conference in the field of theoretical computer science. FOCS is sponsored by the IEEE Computer Society.
SC, the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, is the annual conference established in 1988 by the Association for Computing Machinery and the IEEE Computer Society. In 2019, about 13,950 people participated overall; by 2022 attendance had rebounded to 11,830 both in-person and online. The not-for-profit conference is run by a committee of approximately 600 volunteers who spend roughly three years organizing each conference.
The Seymour Cray Computer Engineering Award, also known as the Seymour Cray Award, is an award given by the IEEE Computer Society, to recognize significant and innovative contributions in the field of high-performance computing. The award honors scientists who exhibit the creativity demonstrated by Seymour Cray, founder of Cray Research, Inc., and an early pioneer of supercomputing. Cray was an American electrical engineer and supercomputer architect who designed a series of computers that were the fastest in the world for decades, and founded Cray Research which built many of these machines. Called "the father of supercomputing," Cray has been credited with creating the supercomputer industry. He played a key role in the invention and design of the UNIVAC 1103, a landmark high-speed computer and the first computer available for commercial use.
Agent-oriented programming (AOP) is a programming paradigm where the construction of the software is centered on the concept of software agents. In contrast to object-oriented programming which has objects at its core, AOP has externally specified agents at its core. They can be thought of as abstractions of objects. Exchanged messages are interpreted by receiving "agents", in a way specific to its class of agents.

HRS Computing is an open-source scientific software which simulates the hyper Rayleigh scattering (HRS) in nonlinear optics. The software is designed for researchers, and it is used to verify the agreement between theoretical models and experimental data.

Victor Bahl is an American Technical Fellow and CTO of Azure for Operators at Microsoft. He started networking research at Microsoft. He is known for his research contributions to white space radio data networks, radio signal-strength based indoor positioning systems, multi-radio wireless systems, wireless network virtualization, edge computing, and for bringing wireless links into the datacenter. He is also known for his leadership of the mobile computing community as the co-founder of the ACM Special Interest Group on Mobility of Systems, Users, Data, and Computing (SIGMOBILE). He is the founder of international conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services Conference (MobiSys), and the founder of ACM Mobile Computing and Communications Review, a quarterly scientific journal that publishes peer-reviewed technical papers, opinion columns, and news stories related to wireless communications and mobility. Bahl has received important awards; delivered dozens of keynotes and plenary talks at conferences and workshops; delivered over six dozen distinguished seminars at universities; written over hundred papers with more than 65,000 citations and awarded over 100 US and international patents. He is a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery, IEEE, and American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Edward W. Knightly is an American professor and the department chair of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Rice University in Houston, Texas. He joined the Rice University faculty in 1996. He heads the Rice Networks Group.
The Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO) is the premier conference in the area of genetic and evolutionary computation. GECCO has been held every year since 1999, when it was first established as a recombination of the International Conference on Genetic Algorithms (ICGA) and the Annual Genetic Programming Conference (GP).

ACM SIGAI is the Association for Computing Machinery's Special Interest Group on Artificial Intelligence (AI), an interdisciplinary group of academic and industrial researchers, practitioners, software developers, end users, and students who work together to promote and support the growth and application of AI principles and techniques throughout computing. SIGAI is one of the oldest special interest groups in the ACM. SIGAI, previously called SIGART, started in 1966, publishing the SIGART Newsletter that later became the SIGART Bulletin and Intelligence Magazine.
The IEEE/WIC/ACM 'International Joint Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology' (WI-IAT) is a colocated conference focusing on Web intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology. The conference is a joint undertaking of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Computer Society Technical Committee on Intelligent Informatics (TCII), the Web Intelligence Consortium (WIC), SIGAI, and the Memetic Computing Society.
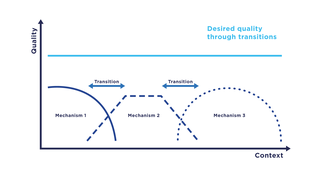
Transition refers to a computer science paradigm in the context of communication systems which describes the change of communication mechanisms, i.e., functions of a communication system, in particular, service and protocol components. In a transition, communication mechanisms within a system are replaced by functionally comparable mechanisms with the aim to ensure the highest possible quality, e.g., as captured by the quality of service.

ACM SIGARCH is the Association for Computing Machinery's Special Interest Group on computer architecture, a community of computer professionals and students from academia and industry involved in research and professional practice related to computer architecture and design. The organization sponsors many prestigious international conferences in this area, including the International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), recognized as the top conference in this area since 1975. Together with IEEE Computer Society's Technical Committee on Computer Architecture (TCCA), it is one of the two main professional organizations for people working in computer architecture.

Moustafa Youssef is an Egyptian computer scientist who was named Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2019 for contributions to wireless location tracking technologies and a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in 2019 for contributions to location tracking algorithms. He is the first and only ACM Fellow in the Middle East and Africa.
Yasamin Mostofi is an Iranian-American Scientist and a Professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of California Santa Barbara. Yasamin’s research is multi-disciplinary, expanding wireless communications, sensing, and control/robotics.