
The Adler Planetarium is a public museum in Chicago, Illinois, dedicated to astronomy and astrophysics. It was founded in 1930 by local businessman Max Adler. Located on the northeastern tip of Northerly Island on Lake Michigan, the Adler Planetarium was the first planetarium in the United States. It is part of Chicago's Museum Campus, which includes the John G. Shedd Aquarium and The Field Museum. The Planetarium's mission is to inspire exploration and understanding of the universe.
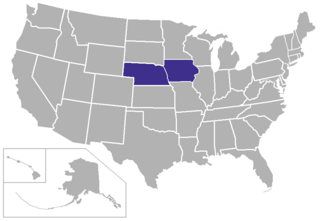
The American Rivers Conference (A-R-C) is an intercollegiate athletic conference that competes in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division III. From 1927 until August 9, 2018, it was known officially as the Iowa Intercollegiate Athletic Conference (IIAC) and commonly as the Iowa Conference.

Winer Observatory is an astronomical observatory near Sonoita, Arizona in the United States. It is a private, non-profit observatory, operated by Mark and Pat Trueblood since 1983. It has been the site of a number of significant small telescopes and famous robotic telescopes, including the Iowa Robotic Observatory, Michael Schwartz's supernova survey telescope, and the Kilodegree Extremely Little Telescope that discovered over 30 exoplanets. It now houses the Iowa telescope, a telescope owned by a university in Poland, and the Sutter Survey telescope owned by asteroid mining company TransAstra.
The Fick Observatory was an astronomical observatory owned and operated by Iowa State University. Located southwest of Boone, Iowa, it was named after Davenport, Iowa, amateur astronomer Erwin W. Fick. The observatory closed in 2015.

Dinsmore Alter was an American astronomer, meteorologist, and United States Army officer. He is known for his work with the Griffith Observatory and his creation of a lunar atlas.

Ambrose Swasey was an American mechanical engineer, inventor, entrepreneur, manager, astronomer, and philanthropist. With Worcester R. Warner he co-founded the Warner & Swasey Company.

885 Ulrike is an elongated Themistian asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 23 September 1917, by Soviet astronomer Sergey Belyavsky at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The presumed C-type asteroid has a short rotation period of 4.9 hours and measures approximately 33 kilometers in diameter. It was likely named after Ulrike von Levetzow, last love of Goethe.
931 Whittemora is a metallic background asteroid, approximately 46 kilometers in diameter, located in the outer region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered by French astronomer François Gonnessiat at the Algiers Observatory in North Africa on 19 March 1920. The M-type asteroid has a rotation period of 19.2 hours. It was named after American archaeologist Thomas Whittemore (1871–1950).

The Warner and Swasey Observatory is the astronomical observatory of Case Western Reserve University. Named after Worcester R. Warner and Ambrose Swasey, who built it at the beginning of the 20th century, it was initially located on Taylor Road in East Cleveland, Ohio, USA. The observatory, which at that time housed a 9.5-inch (24 cm) refractor, was donated in 1919 to the Case School of Applied Science. The newer 24-inch (61 cm) Burrell Schmidt telescope was built in 1939.

The Warner & Swasey Company was an American manufacturer of machine tools, instruments, and special machinery. It operated as an independent business firm, based in Cleveland, from its founding in 1880 until its acquisition in 1980. It was founded as a partnership in 1880 by Worcester Reed Warner (1846–1929) and Ambrose Swasey (1846–1937). The company was best known for two general types of products: astronomical telescopes and turret lathes. It also did a large amount of instrument work, such as equipment for astronomical observatories and military instruments The themes that united these various lines of business were the crafts of toolmaking and instrument-making, which have often overlapped technologically. In the decades after World War II, it also entered the heavy equipment industry with its acquisition of the Gradall brand.

1999 Hirayama is a dark background asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 34 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 27 February 1973, by Czech astronomer Luboš Kohoutek at the Hamburger Bergedorf Observatory in Germany, and later named after Japanese astronomer Kiyotsugu Hirayama.

Observatory is a suburb in Cape Town, South Africa, colloquially known as Obs. Bordered by Mowbray to the south and Salt River to the northwest, the area is best known as a student neighbourhood associated with the nearby University of Cape Town and Groote Schuur Hospital. It takes its name from the South African Astronomical Observatory headquarters, built in 1829 by the Royal Observatory.

1116 Catriona is a carbonaceous asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 39 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 5 April 1929, by South African astronomer Cyril Jackson at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg. The asteroid was probably named after the 1893-novel Catriona by Robert Louis Stevenson.

St. Ambrose University (SAU) is a private Catholic university in Davenport, Iowa. It was founded as a school of commerce for young men in 1882.
Sebastian G. Menke was an American Catholic priest and academic administrator, who served as the tenth president of St. Ambrose College in Davenport, Iowa from 1964 to 1973.

2094 Magnitka (prov. designation: 1971 TC2) is a Flora asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 12 kilometers (7.5 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 12 October 1971, at and by the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnyj, on the Crimean peninsula. The discovery has not been attributed to an observing astronomer. It was later named for the city of Magnitogorsk.
1185 Nikko, provisional designation 1927 WC, is a stony asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 10 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 17 November 1927 by Okuro Oikawa at the Tokyo Astronomical Observatory, Japan. The asteroid was named after the Japanese city of Nikkō.
The Ohio Sky Survey was an astronomical survey of extragalactic radio sources. Data were taken between 1965 and 1971 using the Big Ear radio telescope at the Ohio State University Radio Observatory (OSURO), also known as the "Big Ear Radio Observatory (BERO)".
Marvin Alfred Mottet was a 20th and 21st century Roman Catholic priest in the Diocese of Davenport in the US state of Iowa. He was a noted advocate of social justice causes.
James Dixon was an orchestra conductor and music educator in the United States. During his career he was principally associated with the University of Iowa and the Quad City Symphony Orchestra.













