A ballot is a device used to cast votes in an election and may be found as a piece of paper or a small ball used in voting. It was originally a small ball used to record decisions made by voters in Italy around the 16th century.
A voting machine is a machine used to record votes in an election without paper. The first voting machines were mechanical but it is increasingly more common to use electronic voting machines. Traditionally, a voting machine has been defined by its mechanism, and whether the system tallies votes at each voting location, or centrally. Voting machines should not be confused with tabulating machines, which count votes done by paper ballot.
Rebecca Mercuri is a computer scientist specializing in computer security and computer forensics. She is considered a leading expert on electronic voting systems.
Electronic voting is voting that uses electronic means to either aid or take care of casting and counting ballots.
Electoral fraud, sometimes referred to as election manipulation, voter fraud or vote rigging, involves illegal interference with the process of an election, either by increasing the vote share of a favored candidate, depressing the vote share of rival candidates, or both. It differs from but often goes hand-in-hand with voter suppression. What exactly constitutes electoral fraud varies from country to country.

Electronic voting is the standard means of conducting elections using Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) in India. The system was developed and tested by the state-owned Electronics Corporation of India and Bharat Electronics in the 1990s. They were introduced in Indian elections between 1998 and 2001, in a phased manner. Prior to the introduction of electronic voting, India used paper ballots and manual counting. The paper ballots method was widely criticised because of fraudulent voting and booth capturing, where party loyalists captured booths and stuffed them with pre-filled fake ballots. The printed paper ballots were also more expensive, requiring substantial post-voting resources to count hundreds of millions of individual ballots. Embedded EVM features such as "electronically limiting the rate of casting votes to five per minute", a security "lock-close" feature, an electronic database of "voting signatures and thumb impressions" to confirm the identity of the voter, conducting elections in phases over several weeks while deploying extensive security personnel at each booth have helped reduce electoral fraud and abuse, eliminate booth capturing and create more competitive and fairer elections. Indian EVMs are stand-alone machines built with Write once read many memory. The EVMs are produced with secure manufacturing practices, and by design, are self-contained, battery-powered and lack any networking capability. They do not have any wireless or wired internet components and interface. The M3 version of the EVMs includes the VVPAT system.
Black box voting signifies voting on voting machines which do not disclose how they operate such as with closed source or proprietary operations. If a voting machine does not provide a tangible record of individual votes cast then it can be described as black box voting.
An electronic voting machine is a voting machine based on electronics. Two main technologies exist: optical scanning and direct recording (DRE).
Vote counting is the process of counting votes in an election. It can be done manually or by machines. In the United States, the compilation of election returns and validation of the outcome that forms the basis of the official results is called canvassing.
Voter verifiable paper audit trail (VVPAT) or verified paper record (VPR) is a method of providing feedback to voters using a ballotless voting system. A VVPAT is intended as an independent verification system for voting machines designed to allow voters to verify that their vote was cast correctly, to detect possible election fraud or malfunction, and to provide a means to audit the stored electronic results. It contains the name of the candidate and symbol of the party/individual candidate. While it has gained in use in the United States compared with ballotless voting systems without it, it looks unlikely to overtake hand-marked ballots.
A DRE voting machine, or direct-recording electronic voting machine, records votes by means of a ballot display provided with mechanical or electro-optical components that can be activated by the voter. These are typically buttons or a touchscreen; and they process data using a computer program to record voting data and ballot images in memory components. After the election, it produces a tabulation of the voting data stored in a removable memory component and as printed copy. The system may also provide a means for transmitting individual ballots or vote totals to a central location for consolidating and reporting results from precincts at the central location. The device started to be massively used in 1996 in Brazil where 100% of the elections voting system is carried out using machines.
End-to-end auditable or end-to-end voter verifiable (E2E) systems are voting systems with stringent integrity properties and strong tamper resistance. E2E systems often employ cryptographic methods to craft receipts that allow voters to verify that their votes were counted as cast, without revealing which candidates were voted for. As such, these systems are sometimes referred to as receipt-based systems.
The term "software independence" (SI) was coined by Dr. Ron Rivest and NIST researcher John Wack. A software independent voting machine is one whose tabulation record does not rely solely on software. The goal of an SI system is to definitively determine whether all votes were recorded legitimately or in error.
Bingo voting is an electronic voting scheme for transparent, secure, end-to-end auditable elections. It was introduced in 2007 by Jens-Matthias Bohli, Jörn Müller-Quade, and Stefan Röhrich at the Institute of Cryptography and Security (IKS) of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT).
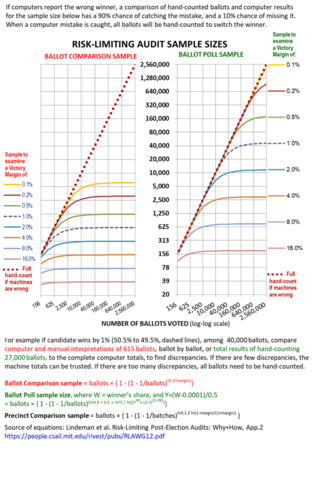
A risk-limiting audit (RLA) is a post-election tabulation auditing procedure which can limit the risk that the reported outcome in an election contest is incorrect. It generally involves (1) storing voter-verified paper ballots securely until they can be checked, and (2) manually examining a statistical sample of the paper ballots until enough evidence is gathered to meet the risk limit.

Electronic voting was first introduced to Brazil in 1996, with the first tests carried out in the state of Santa Catarina. The primary design goal of the voting machine is extreme simplicity, the model being a public phone booth. The voting machines perform three steps – voter identification, secure voting and tallying - in a single process, aiming to eliminate fraud based on forged or falsified public documents. Political parties have access to the voting machine's programs before the election for auditing.
A ballot marking device (BMD) or vote recorder is a type of voting machine used by voters to record votes on physical ballots. In general, ballot marking devices neither store nor tabulate ballots, but only allow the voter to record votes on ballots that are then stored and tabulated elsewhere.

An election audit is any review conducted after polls close for the purpose of determining whether the votes were counted accurately or whether proper procedures were followed, or both.
The Verified Voting Foundation is a non-governmental, nonpartisan organization founded in 2004 by David L. Dill, a computer scientist from Stanford University, focused on how technology impacts the administration of US elections. The organization’s mission is to “strengthen democracy for all voters by promoting the responsible use of technology in elections.” Verified Voting works with election officials, elected leaders, and other policymakers who are responsible for managing local and state election systems to mitigate the risks associated with novel voting technologies.

Electronic voting in the United States involves several types of machines: touchscreens for voters to mark choices, scanners to read paper ballots, scanners to verify signatures on envelopes of absentee ballots, and web servers to display tallies to the public. Aside from voting, there are also computer systems to maintain voter registrations and display these electoral rolls to polling place staff.




