Meristem is a type of tissue found in plants.
Meristem may also refer to:
- Meristem (school), a California school for autistic young adults.
- Meristem Securities, a Nigerian Capital Market.
Meristem is a type of tissue found in plants.
Meristem may also refer to:

A cotyledon is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant, and is defined as "the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or more of which are the first to appear from a germinating seed." The number of cotyledons present is one characteristic used by botanists to classify the flowering plants (angiosperms). Species with one cotyledon are called monocotyledonous ("monocots"). Plants with two embryonic leaves are termed dicotyledonous ("dicots").

An inflorescence, in a flowering plant, is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a system of branches. An inflorescence is categorized on the basis of the arrangement of flowers on a main axis (peduncle) and by the timing of its flowering.
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:

In biology, tissue is a historically derived biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is therefore often thought of as an assembly of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same embryonic origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.

The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular plants. It produces secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary phloem outwards, towards the bark.

Cork cambium is a tissue found in many vascular plants as a part of the epidermis. It is one of the many layers of bark, between the cork and primary phloem. The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for secondary growth that replaces the epidermis in roots and stems. It is found in woody and many herbaceous dicots, gymnosperms and some monocots. It is one of the plant's meristems – the series of tissues consisting of embryonic disk cells from which the plant grows. The function of cork cambium is to produce the cork, a tough protective material.
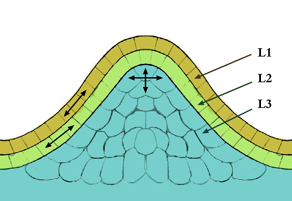
The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until a time when they get differentiated and then lose the ability to divide.
Apical means "pertaining to an apex". It may refer to:

Sympodial growth is a bifurcating branching pattern where one branch develops more strongly than the other, resulting in the stronger branches forming the primary shoot and the weaker branches appearing laterally. A sympodium, also referred to as a sympode or pseudaxis, is the primary shoot, comprising the stronger branches, formed during sympodial growth. The pattern is similar to dichotomous branching; it is characterized by branching along stems or hyphae.
Sam, SAM or variants may refer to:

Micropropagation or tissue culture is the practice of rapidly multiplying plant stock material to produce many progeny plants, using modern plant tissue culture methods.

The axillary bud is an embryonic or organogenic shoot located in the axil of a leaf. Each bud has the potential to form shoots, and may be specialized in producing either vegetative shoots or reproductive shoots (flowers). Once formed, a bud may remain dormant for some time, or it may form a shoot immediately.

Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. There are also two meristems associated with vascular tissue: the vascular cambium and the cork cambium. All the vascular tissues within a particular plant together constitute the vascular tissue system of that plant.
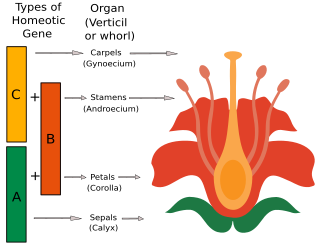
The ABC model of flower development is a scientific model of the process by which flowering plants produce a pattern of gene expression in meristems that leads to the appearance of an organ oriented towards sexual reproduction, a flower. There are three physiological developments that must occur in order for this to take place: firstly, the plant must pass from sexual immaturity into a sexually mature state ; secondly, the transformation of the apical meristem's function from a vegetative meristem into a floral meristem or inflorescence; and finally the growth of the flower's individual organs. The latter phase has been modelled using the ABC model, which aims to describe the biological basis of the process from the perspective of molecular and developmental genetics.

In botany, secondary growth is the growth that results from cell division in the cambia or lateral meristems and that causes the stems and roots to thicken, while primary growth is growth that occurs as a result of cell division at the tips of stems and roots, causing them to elongate, and gives rise to primary tissue. Secondary growth occurs in most seed plants, but monocots usually lack secondary growth. If they do have secondary growth, it differs from the typical pattern of other seed plants.
Important structures in plant development are buds, shoots, roots, leaves, and flowers; plants produce these tissues and structures throughout their life from meristems located at the tips of organs, or between mature tissues. Thus, a living plant always has embryonic tissues. By contrast, an animal embryo will very early produce all of the body parts that it will ever have in its life. When the animal is born, it has all its body parts and from that point will only grow larger and more mature. However, both plants and animals pass through a phylotypic stage that evolved independently and that causes a developmental constraint limiting morphological diversification.

A cambium, in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues.
The quiescent centre is a group of cells, up to 1,000 in number, in the form of a hemisphere, with the flat face toward the root tip of vascular plants. It is a region in the apical meristem of a root where cell division proceeds very slowly or not at all, but the cells are capable of resuming meristematic activity when the tissue surrounding them is damaged. Cells of root apical meristems do not all divide at the same rate. Determinations of relative rates of DNA synthesis show that primary roots of Zea, Vicia and Allium have quiescent centres to the meristems, in which the cells divide rarely or never in the course of normal root growth. Such a quiescent centre includes the cells at the apices of the histogens of both stele and cortex. Its presence can be deduced from the anatomy of the apex in Zea, but not in the other species which lack discrete histogens.
Meristem Securities Limited is a Nigerian Capital Market Conglomerate regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), based in Lagos State, Nigeria. Formerly known as Great Africa Securities Limited and founded in 2003, the company had a change of name to Meristem in 2005. The company consists of six subsidiaries: Meristem Stockbrokers, Meristem Wealth, Meristem Registrars and Probate Services, Meristem Capital, Meristem Trustees, and Meristem Finance.