The University of Auckland is a public research university based in Auckland, New Zealand. The institution was established in 1883 as a constituent college of the University of New Zealand. Originally it was housed in a disused courthouse. Today, the University of Auckland is New Zealand's largest university by enrollment, hosting about 40,000 students on five Auckland campuses. The City Campus, in the Auckland central business district, has the bulk of the students and faculties. There are eight faculties, including a law school, as well as three associated research institutes.
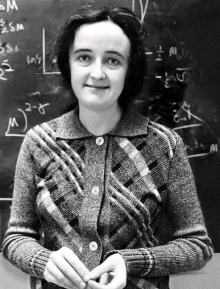
Beatrice Muriel Hill Tinsley was a British-born New Zealand astronomer and cosmologist, and the first female professor of astronomy at Yale University, whose research made fundamental contributions to the astronomical understanding of how galaxies evolve, grow and die.

Sexuality in older age concerns the sexual drive, sexual activity, interests, orientation, intimacy, self-esteem, behaviors, and overall sexuality of people in middle age and old age, and the social perceptions concerning sexuality in older age. Older people engage in a variety of sexual acts from time to time for a variety of reasons. Desire for intimacy does not disappear with age, yet there are many restrictions placed on the elderly preventing sexual expressions and discouraging the fulfillment of sexual needs. Sexuality in older age is often considered a taboo, yet it is considered to be quite a healthy practice; however, this stigma can affect how older individuals experience their sexuality. While the human body has some limits on the maximum age for reproduction, sexual activity can be performed or experienced well into the later years of life.

The Rutherford Medal is the most prestigious award offered by the Royal Society of New Zealand, consisting of a medal and prize of $100,000. It is awarded at the request of the New Zealand Government to recognize exceptional contributions to the advancement and promotion of public awareness, knowledge and understanding in addition to eminent research or technological practice by a person or group in any field of science, mathematics, social science, or technology. It is funded by the New Zealand government and awarded annually.
Sir Albert William Liley was a New Zealand medical practitioner, renowned for developing techniques to improve the health of foetuses in utero.

Auckland City Hospital is a public hospital located in Grafton, Auckland, New Zealand. It is the largest hospital in New Zealand, as well as one of the oldest medical facilities in the country. It provides a total of 1,165 beds. It was established in 2003 as an amalgam of Auckland Hospital, Starship Hospital, Green Lane Hospital and National Women's Hospital. Public hospitals in Auckland have been run by Te Whatu Ora – Health New Zealand since 2022.

Waikato Hospital is a major regional hospital in Hamilton, New Zealand. It provides specialised and emergency healthcare for the Midlands and Waikato area with patients referred there from feeder hospitals like Whakatāne, Lakes area, Tauranga, Thames, Tokoroa and Rotorua.

Sir Peter David Gluckman is a New Zealand scientist. Originally trained as a paediatrician, he served as the inaugural Chief Science Advisor to the New Zealand Prime Minister from 2009 to 2018. He is a founding member and was inaugural chair of the International Network for Government Science Advice, and is president of the International Science Council.

Sir Mason Harold Durie is a New Zealand professor of Māori Studies and research academic at Massey University. He is known for his contributions to Māori health. In 2020, he was appointed to the Order of New Zealand, the highest honour in New Zealand's royal honours system.
The Marsden Medal is a yearly award given by the New Zealand Association of Scientists. It is named after Sir Ernest Marsden and honours "a lifetime of outstanding service to the cause or profession of science, in recognition of service rendered to the cause or profession of science in the widest connotation of the phrase." It rivals the Rutherford Medal from the Royal Society of New Zealand.

M. R. Rajagopal is an Indian palliative care physician (anesthesiologist) and professor referred to as the 'father of palliative care in India' in honour of his significant contribution to the palliative care scene in India.

Michael George Baker is an epidemiologist with the University of Otago. Baker is a member of the New Zealand Food Safety Authority's Academy and of the New Zealand Ministry of Health's Pandemic Influenza Technical Advisory Group (PITAG).

Felicity Anne Goodyear-Smith is a medical doctor, academic, and public health advocate from New Zealand. She is Academic Head of Department & Goodfellow Postgraduate Chair of General Practice & Primary Health Care in the Faculty of Medical and Health Science at the University of Auckland, New Zealand.
The 2015 Queen's Birthday Honours in New Zealand, celebrating the official birthday of Queen Elizabeth II, were appointments made by the Queen in her right as Queen of New Zealand, on the advice of the New Zealand government, to various orders and honours to reward and highlight good works by New Zealanders. They were announced on 1 June 2015.

Merryn Tawhai is a New Zealand engineering scientist. She is a professor at the University of Auckland, director of the Auckland Bioengineering Institute, where she was a fellow from 2002, and a former director of MedTech CoRE. She is known for the development of mathematical models of the lungs that will help scientists understand differences between physiologically normal lungs and the pathological changes that might occur in a disease. She was inducted into the International Academy of Medical and Biological Engineering in June 2018. In November 2018, Tawhai was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of New Zealand.
Matire Louise Ngarongoa Harwood is a New Zealand clinical researcher and trainee general practitioner. She is an associate professor at the University of Auckland. Harwood was the 2017 New Zealand L'Oréal UNESCO For Women in Science Fellow. Her expertise is in Māori health, focussed on reducing health inequity by improving indigenous health and well-being.
Cristin Gregor (Cris) Print is a New Zealand academic using genomics and bioinfomatics to research cancer. He is currently a Professor of Molecular Medicine and Pathology at the University of Auckland.

Karen Jean Hoare is a New Zealand professor at Massey University, and is New Zealand's first active nurse practitioner to also be a professor. Her research focuses on models for care for children and young people.

Ageing Well is one of New Zealand's eleven collaborative research programmes known as National Science Challenges. Running from 2015 to 2024, the focus of Ageing Well National Science Challenge (AWNSC) research is sustaining health and wellbeing towards the end of life, particularly in Māori and Pacific populations in New Zealand.

Ofanaite Ana Dewes is a New Zealand academic, and an Associate Investigator at the Maurice Wilkins Centre and a Research Fellow at the University of Auckland, New Zealand.