Related Research Articles

An axon, or nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons, such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three types – group A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. These groups include both sensory fibers and motor fibers. Another classification groups only the sensory fibers as Type I, Type II, Type III, and Type IV.

Myelin is a lipid-rich extramembranous structure found on the axons and dendrites of neuron in many bilaterian animals, mainly vertebrates, as well as some arthropods and annelids. A circumferential wrapping of myelin, known as a myelin sheath, increases the conduction speed of electrical impulses passing along the axon by generating saltatory conductions, which are much faster than conduction along an unmyelinated axon, and also reduce signal loss due to extrinsic disturbances.
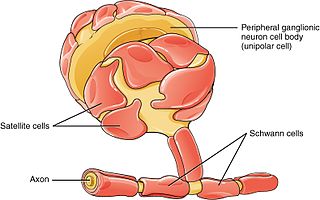
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells, olfactory ensheathing cells, enteric glia and glia that reside at sensory nerve endings, such as the Pacinian corpuscle. The two types of Schwann cells are myelinating and nonmyelinating. Myelinating Schwann cells wrap around axons of motor and sensory neurons to form the myelin sheath. The Schwann cell promoter is present in the downstream region of the human dystrophin gene that gives shortened transcript that are again synthesized in a tissue-specific manner.
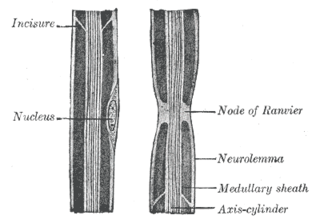
Neurilemma is the outermost nucleated cytoplasmic layer of Schwann cells that surrounds the axon of the neuron. It forms the outermost layer of the nerve fiber in the peripheral nervous system.

In neuroscience, saltatory conduction is the propagation of action potentials along myelinated axons from one node of Ranvier to the next node, increasing the conduction velocity of action potentials. The uninsulated nodes of Ranvier are the only places along the axon where ions are exchanged across the axon membrane, regenerating the action potential between regions of the axon that are insulated by myelin, unlike electrical conduction in a simple circuit.
Nervous tissue, also called neural tissue, is the main tissue component of the nervous system. The nervous system regulates and controls body functions and activity. It consists of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) comprising the branching peripheral nerves. It is composed of neurons, also known as nerve cells, which receive and transmit impulses, and neuroglia, also known as glial cells or glia, which assist the propagation of the nerve impulse as well as provide nutrients to the neurons.

Oligodendrocytes, also known as oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axons within the central nervous system (CNS) of jawed vertebrates. Their function is similar to that of Schwann cells, which perform the same task in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Oligodendrocytes accomplish this by forming the myelin sheath around axons. Unlike Schwann cells, a single oligodendrocyte can extend its processes to cover around 50 axons, with each axon being wrapped in approximately 1 μm of myelin sheath. Furthermore, an oligodendrocyte can provide myelin segments for multiple adjacent axons.

In neuroscience and anatomy, nodes of Ranvier, also known as myelin-sheath gaps, occur along a myelinated axon where the axolemma is exposed to the extracellular space. Nodes of Ranvier are uninsulated and highly enriched in ion channels, allowing them to participate in the exchange of ions required to regenerate the action potential. Nerve conduction in myelinated axons is referred to as saltatory conduction due to the manner in which the action potential seems to "jump" from one node to the next along the axon. This results in faster conduction of the action potential.

In neuroscience, the axolemma is the cell membrane of an axon, the branch of a neuron through which signals are transmitted. The axolemma is a three-layered, bilipid membrane. Under standard electron microscope preparations, the structure is approximately 8 nanometers thick.
Sulfatide, also known as 3-O-sulfogalactosylceramide, SM4, or sulfated galactocerebroside, is a class of sulfolipids, specifically a class of sulfoglycolipids, which are glycolipids that contain a sulfate group. Sulfatide is synthesized primarily starting in the endoplasmic reticulum and ending in the Golgi apparatus where ceramide is converted to galactocerebroside and later sulfated to make sulfatide. Of all of the galactolipids that are found in the myelin sheath, one fifth of them are sulfatide. Sulfatide is primarily found on the extracellular leaflet of the myelin plasma membrane produced by the oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and in the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. However, sulfatide is also present on the extracellular leaflet of the plasma membrane of many cells in eukaryotic organisms.

Myelin incisures are small pockets of cytoplasm left behind during the Schwann cell myelination process.
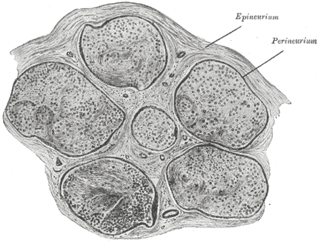
The perineurium is a protective sheath that surrounds a nerve fascicle. This bundles together axons targeting the same anatomical location. The perineurium is composed from fibroblasts.

The endoneurium is a layer of delicate connective tissue around the myelin sheath of each myelinated nerve fiber in the peripheral nervous system. Its component cells are called endoneurial cells. The endoneuria with their enclosed nerve fibers are bundled into groups called nerve fascicles, each fascicle within its own protective sheath called a perineurium. In sufficiently large nerves multiple fascicles, each with its blood supply and fatty tissue, may be bundled within yet another sheath, the epineurium.

Nerve injury is an injury to nervous tissue. There is no single classification system that can describe all the many variations of nerve injuries. In 1941, Seddon introduced a classification of nerve injuries based on three main types of nerve fiber injury and whether there is continuity of the nerve. Usually, however, peripheral nerve injuries are classified in five stages, based on the extent of damage to both the nerve and the surrounding connective tissue, since supporting glial cells may be involved.

Myelin protein zero is a single membrane glycoprotein which in humans is encoded by the MPZ gene. P0 is a major structural component of the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Myelin protein zero is expressed by Schwann cells and accounts for over 50% of all proteins in the peripheral nervous system, making it the most common protein expressed in the PNS. Mutations in myelin protein zero can cause myelin deficiency and are associated with neuropathies like Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease and Dejerine–Sottas disease.
A nerve sheath tumor is a type of tumor of the nervous system which is made up primarily of the myelin surrounding nerves. From benign tumors like schwannoma to high grade malignant neoplasms known as malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors, peripheral nerve sheath tumors include a range of clearly characterized clinicopathologic entities. A peripheral nerve sheath tumor (PNST) is a nerve sheath tumor in the peripheral nervous system. Benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors include schwannomas and neurofibromas.
Myelinogenesis is the formation and development of myelin sheaths in the nervous system, typically initiated in late prenatal neurodevelopment and continuing throughout postnatal development. Myelinogenesis continues throughout the lifespan to support learning and memory via neural circuit plasticity as well as remyelination following injury. Successful myelination of axons increases action potential speed by enabling saltatory conduction, which is essential for timely signal conduction between spatially separate brain regions, as well as provides metabolic support to neurons.

Gap junction beta-1 protein (GJB1), also known as connexin 32 (Cx32), is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the GJB1 gene. Gap junction beta-1 protein is a member of the gap junction connexin family of proteins that regulates and controls the transfer of communication signals across cell membranes, primarily in the liver and peripheral nervous system. However, the protein is expressed in multiple organs, including in oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system.

Growth arrest-specific protein 3 (GAS-3), also called peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PMP22 gene.
Anti-MAG peripheral neuropathy is a specific type of peripheral neuropathy in which the person's own immune system attacks cells that are specific in maintaining a healthy nervous system. As these cells are destroyed by antibodies, the nerve cells in the surrounding region begin to lose function and create many problems in both sensory and motor function. Specifically, antibodies against myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) damage Schwann cells. While the disorder occurs in only 10% of those afflicted with peripheral neuropathy, people afflicted have symptoms such as muscle weakness, sensory problems, and other motor deficits usually starting in the form of a tremor of the hands or trouble walking. There are, however, multiple treatments that range from simple exercises in order to build strength to targeted drug treatments that have been shown to improve function in people with this type of peripheral neuropathy.
References
- ↑ Webster, HENRY DEF. (2005-01-01), Dyck, Peter J.; Thomas, P. K. (eds.), "Chapter 1 - Introduction", Peripheral Neuropathy (Fourth Edition), Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 3–8, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7216-9491-7.50004-1, ISBN 978-0-7216-9491-7
- 1 2 Morell, Pierre; Quarles, Richard H. (1999). "The Myelin Sheath". Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular and Medical Aspects. 6th edition.