Related Research Articles

A citation is a reference to a source. More precisely, a citation is an abbreviated alphanumeric expression embedded in the body of an intellectual work that denotes an entry in the bibliographic references section of the work for the purpose of acknowledging the relevance of the works of others to the topic of discussion at the spot where the citation appears.
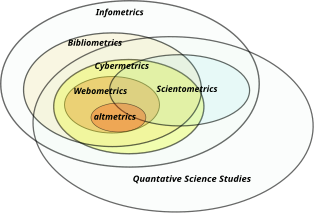
Information science is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of information. Practitioners within and outside the field study the application and the usage of knowledge in organizations in addition to the interaction between people, organizations, and any existing information systems with the aim of creating, replacing, improving, or understanding the information systems.

Bibliography, as a discipline, is traditionally the academic study of books as physical, cultural objects; in this sense, it is also known as bibliology. English author and bibliographer John Carter describes bibliography as a word having two senses: one, a list of books for further study or of works consulted by an author ; the other one, applicable for collectors, is "the study of books as physical objects" and "the systematic description of books as objects".

This page is a glossary of library and information science.
Document classification or document categorization is a problem in library science, information science and computer science. The task is to assign a document to one or more classes or categories. This may be done "manually" or algorithmically. The intellectual classification of documents has mostly been the province of library science, while the algorithmic classification of documents is mainly in information science and computer science. The problems are overlapping, however, and there is therefore interdisciplinary research on document classification.
Source criticism is the process of evaluating an information source, i.e.: a document, a person, a speech, a fingerprint, a photo, an observation, or anything used in order to obtain knowledge. In relation to a given purpose, a given information source may be more or less valid, reliable or relevant. Broadly, "source criticism" is the interdisciplinary study of how information sources are evaluated for given tasks.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to library and information science:

Grey literature is material and research produced by organizations outside of the traditional commercial or academic publishing and distribution channels. Common grey literature publication types include reports, working papers, government documents, white papers and evaluations. Organizations that produce grey literature include government departments and agencies, civil society or non-governmental organizations, academic centres and departments, and private companies and consultants.
Cambridge Scientific Abstracts was a division of Cambridge Information Group and provider of online databases, based in Bethesda, Maryland, before merging with ProQuest of Ann Arbor, Michigan, in 2007. CSA hosted databases of abstracts and developed taxonomic indexing of scholarly articles. These databases were hosted on the CSA Illumina platform and were available alongside add-on products like CSA Illustrata. The company produced numerous bibliographic databases in different fields of the arts and humanities, natural and social sciences, and technology. Thus, coverage included materials science, environmental sciences and pollution management, biological sciences, aquatic sciences and fisheries, biotechnology, engineering, computer science, sociology, linguistics, and other areas.
Inspec is a major indexing database of scientific and technical literature, published by the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET), and formerly by the Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE), one of the IET's forerunners.
The GeoRef database is a bibliographic database that indexes scientific literature in the geosciences, including geology. Coverage ranges from 1666 to the present for North American literature, and 1933 to the present for the rest of the world. It currently contains more than 4.3 million references. It is widely considered one of the preeminent literature databases for those studying the earth sciences.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to knowledge:
ProQuest Dissertations and Theses (PQDT) is an online database that indexes, abstracts, and provides full-text access to dissertations and theses. The database includes over 2.4 million records and covers 1637 to the present. It is produced by ProQuest and was formerly known as ProQuest Digital Dissertations. The bibliographic database is known as Dissertation Abstracts or Dissertation Abstracts International.
A bibliographic index is a bibliography intended to help find a publication. Citations are usually listed by author and subject in separate sections, or in a single alphabetical sequence under a system of authorized headings collectively known as controlled vocabulary, developed over time by the indexing service. Indexes of this kind are issued in print periodical form, online, or both. Since the 1970s, they are typically generated as output from bibliographic databases.
The Energy Science and Technology Database (EDB) is a multidisciplinary file containing worldwide references to basic and applied scientific and technical research literature. The information is collected for use by government managers, researchers at the national laboratories, and other research efforts sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy, and the results of this research are transferred to the public. Abstracts are included for records from 1976 to the present day.
CAB Direct is a source of references for the applied life sciences It incorporates two bibliographic databases: CAB Abstracts and Global Health. CAB Direct is an access point for multiple bibliographic databases produced by CABI. This database contains over 11 million bibliographic records, which includes 746,000 full text articles. It also includes noteworthy literature reviews. News articles and reports are also part of this combined database. CAB Direct has now migrated to CABI's new platform CABI Digital Library - the new home of CABI's research content.
A pathfinder is a bibliography created to help begin research in a particular topic or subject area. Pathfinders are also called subject guides, topic guides, research guides, libguides, information portals, resource lists or study guides. Pathfinders produced by the Library of Congress are known as "tracer bullets". What is special about a pathfinder is that it only refers to the information in a specific location, i.e. the shelves of a local library.
A Guide to information sources is a kind of metabibliography. Ideally it is not just a listing of bibliographies, reference works and other source texts, but more like a textbook introducing users to the information sources in a given field.
FLUIDEX is an online bibliographic database that covers fluids behavior, applications, and engineering in civil engineering and process engineering. It is published by Elsevier.
References
- ↑ Patrick Wilson, Two kinds of Power: an essay on bibliographical control. Berkeley, Calif.: University of California Press, 1968, p. 148