
A roof is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of temperature, and wind. A roof is part of the building envelope.

A staple gun or powered stapler is a hand-held machine used to drive heavy metal staples into wood, plastic, or masonry. Staple guns are used for many different applications and to affix a variety of materials, including insulation, house wrap, roofing, wiring, carpeting, upholstery, and hobby and craft materials. These devices are also known as trigger tackers.
Terne plate is a form of tinplate: a thin steel sheet coated with an alloy of lead and tin. The terne alloy was in the ratio of 10-20% tin and the remainder lead. The low tin content made it cheaper than other tinplates.

Corrugated galvanised iron or steel, colloquially corrugated iron, wriggly tin, pailing, corrugated sheet metal, zinc or custom orb / corro sheet (Australia) and occasionally abbreviated CGI is a building material composed of sheets of hot-dip galvanised mild steel, cold-rolled to produce a linear ridged pattern in them. Although it is still popularly called "iron" in the UK, the material used is actually steel, and only the surviving vintage sheets may actually be made up of 100% iron. The corrugations increase the bending strength of the sheet in the direction perpendicular to the corrugations, but not parallel to them, because the steel must be stretched to bend perpendicular to the corrugations. Normally each sheet is manufactured longer in its strong direction.

A flat roof is a roof which is almost level in contrast to the many types of sloped roofs. The slope of a roof is properly known as its pitch and flat roofs have up to approximately 10°. Flat roofs are an ancient form mostly used in arid climates and allow the roof space to be used as a living space or a living roof. Flat roofs, or "low-slope" roofs, are also commonly found on commercial buildings throughout the world. The U.S.-based National Roofing Contractors Association defines a low-slope roof as having a slope of 3 in 12 (1:4) or less.

Roof shingles are a roof covering consisting of individual overlapping elements. These elements are typically flat, rectangular shapes laid in courses from the bottom edge of the roof up, with each successive course overlapping the joints below. Shingles are held by the roof rafters and are made of various materials such as wood, slate, flagstone, metal, plastic, and composite materials such as fibre cement and asphalt shingles. Ceramic roof tiles, which still dominate in Europe and some parts of Asia, are still usually called tiles. Roof shingles may deteriorate faster and need to repel more water than wall shingles. They are a very common roofing material in the United States.

A batten is most commonly a strip of solid material, historically wood but can also be of plastic, metal, or fiberglass. Battens are variously used in construction, sailing, and other fields.

Flashing refers to thin pieces of impervious material installed to prevent the passage of water into a structure from a joint or as part of a weather resistant barrier system. In modern buildings, flashing is intended to decrease water penetration at objects such as chimneys, vent pipes, walls, windows and door openings to make buildings more durable and to reduce indoor mold problems. Metal flashing materials include lead, aluminium, copper, stainless steel, zinc alloy, and other materials.

A metal roof is a roofing system featuring metal pieces or tiles exhibiting corrosion resistance, impermeability to water, and long life. It is a component of the building envelope. The metal pieces may be a covering on a structural, non-waterproof roof, or they could be self-supporting sheets.
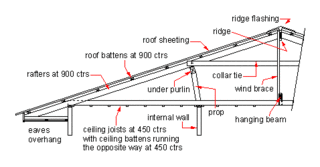
Domestic roof construction is the framing and roof covering which is found on most detached houses in cold and temperate climates. Such roofs are built with mostly timber, take a number of different shapes, and are covered with a variety of materials.

A roofer, roof mechanic, or roofing contractor is a tradesperson who specializes in roof construction. Roofers replace, repair, and install the roofs of buildings, using a variety of materials, including shingles, bitumen, and metal. Roofing work includes the hoisting, storage, application, and removal of roofing materials and equipment, including related insulation, sheet metal, vapor barrier work, and green technologies rooftop jobs such as vegetative roofs, rainwater harvesting systems, and photovoltaic products, such as solar shingles and solar tiles.

The Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning Contractors' National Association is an international trade association with more than 4,500 contributing contractor members in 103 chapters throughout the United States, Canada, Australia and Brazil. Its headquarters is in Chantilly, Virginia.

Metals used for architectural purposes include lead, for water pipes, roofing, and windows; tin, formed into tinplate; zinc, copper and aluminium, in a range of applications including roofing and decoration; and iron, which has structural and other uses in the form of cast iron or wrought iron, or made into steel. Metal alloys used in building include bronze ; brass ; monel metal and nickel silver, mainly consisting of nickel and copper; and stainless steel, with important components of nickel and chromium.
The Metal Building Manufacturers Association (MBMA) was founded in 1956 and promotes the design and construction of metal building systems in the low-rise, nonresidential building marketplace. A nonprofit trade organization, MBMA's headquarters is in Cleveland, Ohio. The organization consists of Building Systems members that are certified according to standards that have been set by the International Accreditation Service, and Associate members that work in the metal building industry. MBMA has a general manager, and it has a chairman and Board of Directors who are elected by members on an annual basis.
RoofTG is a manufacturer of stone chip coated metal roof tiles based in Auckland, New Zealand and with plants in New Zealand, United States (California), Hungary and Malaysia. The company sells under both the Gerard and Decra brand names.
A stone coated metal roof is a roof made from steel or some other metal; the metal is then coated with stone chips and attached to the steel with an acrylic film. The goal is a more durable roof that still retains the aesthetic advantages of a more traditional roofing material

Copper has earned a respected place in the related fields of architecture, building construction, and interior design. From cathedrals to castles and from homes to offices, copper is used for a variety of architectural elements, including roofs, flashings, gutters, downspouts, domes, spires, vaults, wall cladding, and building expansion joints.

An ice dam is an ice build-up on the eaves of sloped roofs of heated buildings that results from melting snow under a snow pack reaching the eave and freezing there. Freezing at the eave impedes the drainage of meltwater, which adds to the ice dam and causes backup of the meltwater, which may cause water leakage into the roof and consequent damage to the building and its contents if the water leaks through the roof.
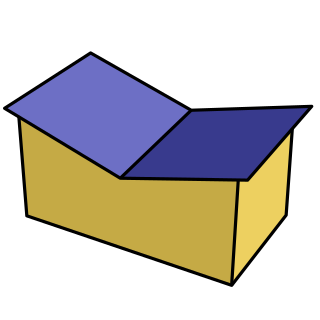
A butterfly roof is a form of roof characterised by an inversion of a standard roof form, with two roof surfaces sloping down from opposing edges to a valley near the middle of the roof. It is so called because its shape resembles a butterfly's wings.














