See also
- Cresol (methylphenol, hydroxytoluene)
- Trihydroxytoluene
Methylbenzenediol, also known as dihydroxytoluene, may refer to:

In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical or unsymmetrical.
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified.
In organic chemistry, dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three structural isomers: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.

The Controlled Drugs and Substances Act is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeals the Narcotic Control Act and Parts III and IV of the Food and Drugs Act, and establishes eight Schedules of controlled substances and two Classes of precursors. It provides that "The Governor in Council may, by order, amend any of Schedules I to VIII by adding to them or deleting from them any item or portion of an item, where the Governor in Council deems the amendment to be necessary in the public interest."
The molecular formula C4H8O2 may refer to:

Ethane-1,2-dithiol, also known as EDT, is a colorless liquid with the formula C2H4(SH)2. It has a very characteristic odor which is compared by many people to rotten cabbage. It is a common building block in organic synthesis and an excellent ligand for metal ions.
Propanediol may refer to any of four isomeric organic chemical compounds:
Butanediol, also called butylene glycol, may refer to any one of four stable structural isomers:
The molecular formula C3H6O2 may refer to:
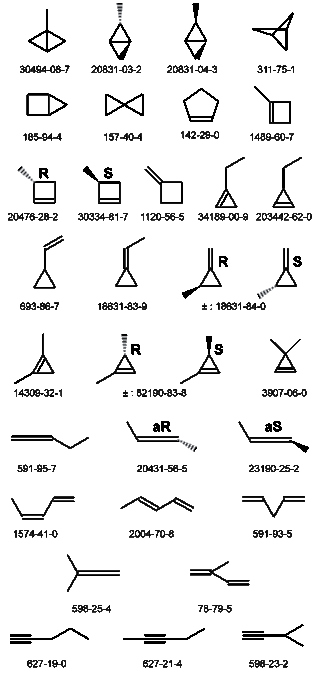
The molecular formula C5H8 may refer to any of the following hydrocarbons:
The molecular formula C6H6O2 (molar mass: 110.1 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C3H8O2 may refer to:
In enzymology, a cis-1,2-dihydroxy-4-methylcyclohexa-3,5-diene-1-carboxylate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.1.67) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lignin peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

3-MCPD (3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol or 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol) is an organic chemical compound with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CH2Cl. It is a colorless liquid. It is a versatile multifunctional building block. The compound has attracted attention as the most common member of chemical food contaminants known as chloropropanols. It is suspected to be carcinogenic in humans.

In organic chemistry, a dithiol is a type of organosulfur compound with two thiol functional groups. Their properties are generally similar to those of monothiols in terms of solubility, odor, and volatility. They can be classified according to the relative location of the two thiol groups on the organic backbone.

4-Methylcatechol is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(OH)2 A white solid, it is one of the isomers of methylbenzenediol.
Chloropropanols are chlorohydrins related to propanols containing chloride functional group. Eight isomers are possible. Two of these derivatives, 1,3-dichloropropanol (1,3-DCP) and 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol (3-MCPD), are carcinogenic contaminants in processed foods. Several isomers are encountered in industrial chemistry.

The C3-benzenes are a class of organic aromatic compounds which contain a benzene ring and three other carbon atoms. For the hydrocarbons with no further unsaturation, there are four isomers. The chemical formula for all the saturated isomers is C9H12.
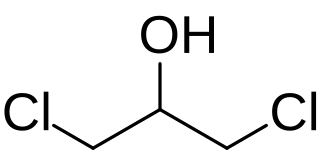
1,3-Dichloropropan-2-ol (1,3-DCP) is an organic compound with the formula HOCH2CHClCH2Cl. It is a colorless liquid. It is an intermediate in the production of epichlorohydrin.