Methylpentane may refer to:
You could also have been looking for:
Methylpentane may refer to:
You could also have been looking for:

Fluorocarbons, sometimes referred to as perfluorocarbons or PFCs, are organofluorine compounds with the formula CxFy, i.e., they contain only carbon and fluorine. The terminology is not strictly followed and many fluorine-containing organic compounds are called fluorocarbons. Compounds with the prefix perfluoro- are hydrocarbons, including those with heteroatoms, wherein all C-H bonds have been replaced by C-F bonds. Fluorocarbons includes perfluoroalkanes, fluoroalkenes, fluoroalkynes, and perfluoroaromatic compounds. Fluorocarbons and their derivatives are used as fluoropolymers, refrigerants, solvents, and anesthetics.
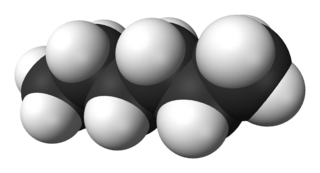
Hexane is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane with six carbon atoms and has the molecular formula C6H14.
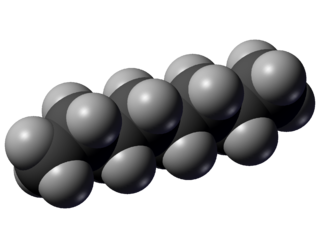
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18, and the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)6CH3. Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the amount and location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (commonly called iso-octane) is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.
Isomerases are a general class of enzymes that convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:

Corn oil is oil extracted from the germ of corn (maize). Its main use is in cooking, where its high smoke point makes refined corn oil a valuable frying oil. It is also a key ingredient in some margarines. Corn oil is generally less expensive than most other types of vegetable oils.
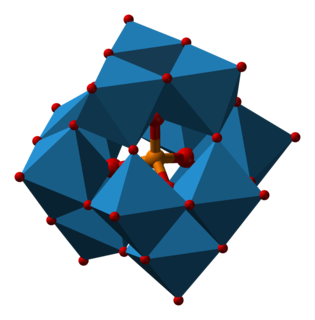
A heteropoly acid is a class of acid made up of a combination of hydrogen and oxygen with particular metals and non-metals.
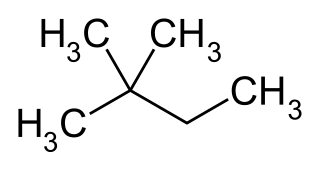
2,2-Dimethylbutane, trivially known as neohexane, is an organic compound with formula C6H14 or (H3C-)3-C-CH2-CH3. It is therefore an alkane, indeed the most compact and branched of the hexane isomers — the only one with a quaternary carbon and a butane (C4) backbone. It can be synthesised by the hydroisomerisation of 2,3-dimethylbutane using an acid catalyst.
Be bold may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H14 may refer to:
Neutral point of view may refer to:
3-Methylpentane is a branched-chain alkane with the molecular formula C6H14. It is a structural isomer of hexane composed of a methyl group bonded to the third carbon atom in a pentane chain. It is of similar structure to the isomeric 2-methylpentane, which has the methyl group located on the second carbon of the pentane chain.
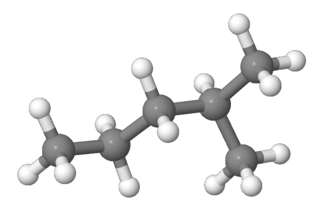
2-Methylpentane, trivially known as isohexane, is a branched-chain alkane with the molecular formula C6H14. It is a structural isomer of hexane composed of a methyl group bonded to the second carbon atom in a pentane chain.
The molecular formula C8H18 may refer to:

2-Methyl-2-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It can be added to a gas chromatograph to help distinguish between branched compounds, especially alcohols. Its presence in urine can be used to test for exposure to 2-methylpentane. As with many other short-chain alcohols, 2-methyl-2-pentanol can produce intoxication and sedative effects similar to those of ethanol, though it is more irritating to mucous membranes and generally more toxic to the body.
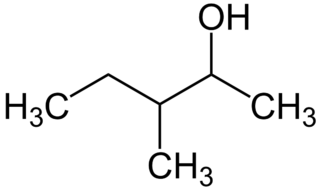
3-Methyl-2-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It has been identified as a component of hops. Its presence in urine can be used to test for exposure to 3-methylpentane.
Red link may refer to:

1,3-Dimethylbutylamine, is a stimulant drug structurally related to methylhexanamine where a butyl group replaces the pentyl group. The compound is an aliphatic amine.

2-Methylglutaronitrile (α-methyl-valerodinitrile) is a nitrile with an attached methyl group which is obtained in the large-scale synthesis of adiponitrile. It is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor.
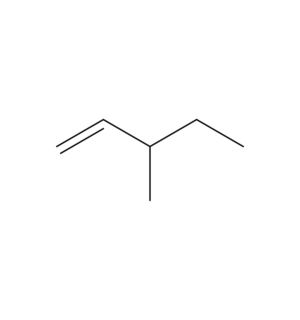
Methylpentene is an alkene with a molecular formula C6H12. The prefix "methyl-" is derived from the fact that there is a methyl(CH3) branch, the word root "-pent-" is derived from the fact that there are 5 carbon atoms in the parent chain, while the "-ene" suffix denotes that there is a double bond present, as per IUPAC nomenclature. Following are the possible structural isomers of methylpentane: