
Michael Ellis DeBakey was an American general and cardiovascular surgeon, scientist and medical educator who became Chairman of the Department of Surgery, President, and Chancellor of Baylor College of Medicine at the Texas Medical Center in Houston, Texas. His career spanned nearly eight decades.
Lasker-DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award is one of four annual awards presented by the Lasker Foundation. The Lasker-DeBakey award is given to honor outstanding work for the understanding, diagnosis, prevention, treatment, and cure of disease. This award was renamed in 2008 in honor of Michael E. DeBakey. It was previously known as the Albert Lasker Award for Clinical Medical Research.

Harvey James Alter is an American medical researcher, virologist, physician and Nobel Prize laureate, who is best known for his work that led to the discovery of the hepatitis C virus. Alter is the former chief of the infectious disease section and the associate director for research of the Department of Transfusion Medicine at the Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in Bethesda, Maryland. In the mid-1970s, Alter and his research team demonstrated that most post-transfusion hepatitis cases were not due to hepatitis A or hepatitis B viruses. Working independently, Alter and Edward Tabor, a scientist at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, proved through transmission studies in chimpanzees that a new form of hepatitis, initially called "non-A, non-B hepatitis" caused the infections, and that the causative agent was probably a virus. This work eventually led to the discovery of the hepatitis C virus in 1988, for which he shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2020 along with Michael Houghton and Charles M. Rice.
Douglas D. Richman is an American infectious diseases physician and medical virologist. Richman's work has focused on the HIV/AIDS pandemic, since its appearance in the early 1980s. His major contributions have been in the areas of treatment, drug resistance, and pathogenicity.

Dennis Liotta is a chemistry professor at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. He is noted for his work on the development of antiviral drugs.

Nicholas B. Lydon FRS is a British scientist and entrepreneur. In 2009, he was awarded the Lasker Clinical Award and in 2012 the Japan Prize for the development of Gleevec, also known as Imatinib, a selective BCR-ABL inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML), which converted a fatal cancer into a manageable chronic condition.

Sofosbuvir, sold under the brand name Sovaldi among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is taken by mouth.

Daclatasvir, sold under the brand name Daklinza, is an antiviral medication used in combination with other medications to treat hepatitis C (HCV). The other medications used in combination include sofosbuvir, ribavirin, and interferon, vary depending on the virus type and whether the person has cirrhosis. It is taken by mouth.

John Charles Martin was an American billionaire businessman, and the former executive chairman (2016–2018) and CEO (1996–2016) of the American biotechnology company Gilead Sciences. He joined Gilead Sciences in 1990 as vice president for research and development. Gilead is known for developing drugs such as Atripla and commercializing Sovaldi (sofosbuvir) for the treatment of the liver virus hepatitis C. Martin is the recipient of a number of awards, including the Biotechnology Heritage Award (2017).

Arbutus Biopharma Corporation is a publicly traded Canadian biopharmaceutical company with an expertise in liposomal drug delivery and RNA interference, and is developing drugs for hepatitis B infection.
TKM-Ebola was an experimental antiviral drug for Ebola disease that was developed by Arbutus Biopharma in Vancouver, Canada. The drug candidate was formerly known as Ebola-SNALP.
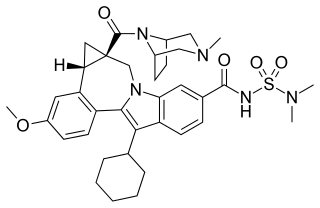
Beclabuvir is an antiviral drug for the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection that has been studied in clinical trials. In February 2017, Bristol-Myers Squibb began sponsoring a post-marketing trial of beclabuvir, in combination with asunaprevir and daclatasvir, to study the combination's safety profile with regard to liver function. From February 2014 to November 2016, a phase II clinical trial was conducted on the combination of asunaprevir/daclatasvir/beclabuvir on patients infected with both HIV and HCV. Furthermore, a recent meta-analysis of six published six clinical trials showed high response rates in HCV genotype 1-infected patients treated with daclatasvir, asunaprevir, and beclabuvir irrespective of ribavirin use, prior interferon-based therapy, or restriction on noncirrhotic patients, IL28B genotype, or baseline resistance-associated variants
Thomas Charles Merigan was born January 18, 1934 in San Francisco. He is an American virologist and the George E. and Lucy Becker Professor of Medicine, Emeritus at the Stanford University School of Medicine. Merigan's research first focused on human viral pathogenesis, basic and clinical studies of interferon, and then developing the first systemically active antiviral drugs including those effectively treatIng HIV/AIDS, several herpesviruses and hepatitis B. He is also credited with helping to develop the use of interferons as antiviral, immunomodulating and antitumor therapies. Merigan joined the Stanford faculty in 1963 and assumed full emeritus status in 2007. In 2004 he was also identified as one of the 250 most cited investigators in clinical medicine over the last 20 years by the Institute for Scientific Information. Merigan also was ranked 23rd among the 1000 top US microbiologists by Research.com in 2022. His papers have been cited over 45,000 times. He had over 95 postdoctoral fellows, students and visiting scientists with whom he published 577 papers, 24 books monographs and published symposia, and held 11 US patents. Two of his books went into multiple editions- one into a 4th edition and the other into a 3rd. His students have become leaders in the fields of infectious diseases and microbiology both in the US and the world. Seven of his students subsequently joined the Stanford medical faculty. He was a board member of 28 journals and a member of 23 learned societies. He told his life story in a book entitled Pioneering Viral Therapy,a Life in Academic Medicine, published by Amazon/Kindle/CreateSpace in 2017.

Nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) inhibitors are direct acting antiviral agents (DAAs) that target viral proteins, and their development was a culmination of increased understanding of the viral life cycle combined with advances in drug discovery technology. However, their mechanism of action is complex and not fully understood. NS5A inhibitors were the focus of much attention when they emerged as a part of the first curative treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections in 2014. Favorable characteristics have been introduced through varied structural changes, and structural similarities between NS5A inhibitors that are clinically approved are readily apparent. Despite the recent introduction of numerous new antiviral drugs, resistance is still a concern and these inhibitors are therefore always used in combination with other drugs.

Charles Moen Rice is an American virologist and Nobel Prize laureate whose main area of research is the hepatitis C virus. He is a professor of virology at the Rockefeller University in New York City and an adjunct professor at Cornell University and Washington University School of Medicine. At the time of the award he was a faculty at Rockefeller.
Ralf F. W. Bartenschlager is a German virologist who has been researching hepatitis C since 1989. He is a professor in the Department of Infectious Diseases at the Heidelberg University.
Raymond F. Schinazi is an American organic medicinal chemist at Emory University with expertise in antiviral agents, pharmacology, and biotechnology. His research focuses on developing treatments for infections caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B (HBV), hepatitis C (HCV), herpes, dengue fever, zika, chikungunya, and other emerging viruses. These treatment options include antiviral agents as well as synthetic, biochemical, pharmacological and molecular genetic approaches, including molecular modeling and gene therapy.
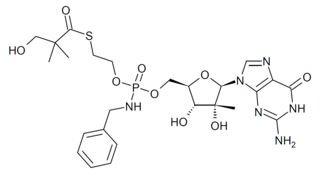
IDX-184 is an antiviral drug which was developed as a treatment for hepatitis C, acting as a NS5B RNA polymerase inhibitor. While it showed reasonable effectiveness in early clinical trials it did not progress past Phase IIb. However research using this drug has continued as it shows potentially useful activity against other emerging viral diseases such as Zika virus, and coronaviruses including MERS, and SARS-CoV-2.
The International Society for Antiviral Research (ISAR) is a scientific society that focuses on the discovery and clinical application of antiviral agents. It was founded in 1987 to encourage the exchange of information and collaborative research on the development of antiviral, biological and chemical agents.
The 2020 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to the American virologists Harvey J. Alter, Michael Houghton and Charles M. Rice "for the discovery of Hepatitis C virus." During the award ceremony on December 10, 2020, Prof. Gunilla Karlsson-Hedestam said:
"The discovery of the Hepatitis C virus by this year’s Laureates laid the foundation for our current understanding about how the virus survives in its niche during the long chronic phase of the infection, and how liver disease develops. And importantly, it led to the development of highly effective anti-viral medicines that now cure the infection in almost all treated persons."











