
Brittany is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an independent kingdom and then a duchy before being united with the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province governed as a separate nation under the crown. Brittany is the traditional homeland of the Breton people and is one of the six Celtic nations, retaining a distinct cultural identity that reflects its history.

The Duchy of Brittany was a medieval feudal state that existed between approximately 939 and 1547. Its territory covered the northwestern peninsula of Europe, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the English Channel to the north. It was also less definitively bordered by the river Loire to the south, and Normandy, and other French provinces, to the east. The Duchy was established after the expulsion of Viking armies from the region around 939. The Duchy, in the 10th and 11th centuries, was politically unstable, with the dukes holding only limited power outside their own personal lands. The Duchy had mixed relationships with the neighbouring Duchy of Normandy, sometimes allying itself with Normandy, and at other times, such as the Breton–Norman War, entering into open conflict.

Odo of Rennes, Count of Penthièvre, was the youngest of the three sons of Duke Geoffrey I of Brittany and Hawise of Normandy, daughter of Richard I of Normandy. Eudon married Agnes of Cornouaille, the daughter of Alan Canhiart, Count of Cornouaille and sister of Hoel II, Duke of Brittany who was married in 1066 to Eudon's niece Hawise, Duchess of Brittany.

Joan of Penthièvre reigned as Duchess of Brittany together with her husband, Charles of Blois, between 1341 and 1364. Her ducal claims were contested by the House of Montfort, which prevailed only after an extensive civil war, the War of the Breton Succession. After the war, Joan remained titular Duchess of Brittany to her death. She was Countess of Penthièvre in her own right throughout her life.

The War of the Breton Succession was a conflict between the Counts of Blois and the Montforts of Brittany for control of the Sovereign Duchy of Brittany, then a fief of the Kingdom of France. It was fought between 1341 and 12 April 1365. It is also known as the War of the Two Jeannes due to the involvement of two rival duchesses of that name.

John of Montfort, sometimes known as John IV of Brittany, and 6th Earl of Richmond from 1341 to his death. He was the son of Arthur II, Duke of Brittany and his second wife, Yolande de Dreux. He contested the inheritance of the Duchy of Brittany by his niece, Joan of Penthièvre, which led to the War of the Breton Succession, which in turn evolved into being part of the Hundred Years' War between England and France. John's patron in his quest was King Edward III of England. He died in 1345, 19 years before the end of the war, and the victory of his son John IV over Joan of Penthièvre and her husband, Charles of Blois.

Charles of Blois-Châtillon, nicknamed "the Saint", was the legalist Duke of Brittany from 1341 until his death, via his marriage to Joan, Duchess of Brittany and Countess of Penthièvre, holding the title against the claims of John of Montfort. The cause of his possible canonization was the subject of a good deal of political maneuvering on the part of his cousin, Charles V of France, who endorsed it, and his rival, Montfort, who opposed it. The cause fell dormant after Pope Gregory XI left Avignon in 1376, but was revived in 1894. Charles of Blois was beatified in 1904.
John V, sometimes numbered as VI, bynamed John the Wise, was Duke of Brittany and Count of Montfort from 1399 to his death. His rule coincided with the height of the Hundred Years' War between England and France. John's reversals in that conflict, as well as in other internal struggles in France, served to strengthen his duchy and to maintain its independence.

The history of Brittany may refer to the entire history of the Armorican peninsula or only to the creation and development of a specifically Brythonic culture and state in the Early Middle Ages and the subsequent history of that state.

The House of Rohan is a Breton family of viscounts, later dukes and princes in the French nobility, coming from the locality of Rohan in Brittany. Their line descends from the viscounts of Porhoët and is said to trace back to the legendary Conan Meriadoc. Through the Porhoët family, the Rohans are related to the Dukes of Brittany, with whom the family intermingled again after its inception. During the Middle Ages, it was one of the most powerful families in the Duchy of Brittany. The Rohans developed ties with the French and English royal houses as well, and they played an important role in French and European history.
Breton nationalism is the nationalism of the historical province of Brittany, France. Brittany is considered to be one of the six Celtic nations.
Stephen of Penthièvre, Count of Tréguier, 3rd Lord of Richmond was a Breton noble and a younger son of Odo, Count of Penthièvre and Agnes of Cornouaille, sister of Hoël II, Duke of Brittany. In 1093, he succeeded to the title of Count of Tréguier; in 1098, he succeeded his brother Alain as Lord of Richmond in Yorkshire, England.

Arthur Le Moyne de La Borderie, was a Breton historian, regarded as a father of Brittany's historiography.
Lady Joan Holland was Duchess of Brittany as the second wife of John IV, Duke of Brittany. She was the daughter of Joan of Kent and Thomas Holland, 1st Earl of Kent. Her mother's second husband was Edward the Black Prince, and the child of that marriage was King Richard II of England.

Henri Bourde de La Rogerie was a French archivist and historian of Brittany.

Jeanne de Clisson (1300–1359), also known as Jeanne de Belleville and the Lioness of Brittany, was a French/Breton noblewoman who became a privateer to avenge her husband after he was executed for treason by King Philip VI of France. She crossed the English Channel targeting French ships and often slaughtering their crew. It was her practice to leave at least one sailor alive to carry her message of vengeance.
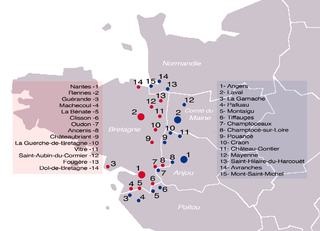
The French–Breton War lasted from 1487 to 1491. The cause of this war was the approaching death of the Breton Duke Francis II of Brittany, who had no clear successor. If not resolved, this meant a resumption of issues from a previous War of the Breton Succession (1341–1364), which had rival claimants allying with England or France, resulting in an ambiguous peace treaty that failed to prevent future succession disputes.
François Prelati was an Italian cleric and alchemist who took part in the murders committed by Gilles de Rais in the 15th century. He claimed he could summon demons and involved Gilles in this practice.

Herve VII of Léon was a Breton lord, son of Herve VI, Lord of Léon and his wife Joanna of Montmorency. Also known as Herve. He succeeded his father as Lord of Léon in 1337. He was also Lord of Noyon-sur-Andelle. The Lords of Léon were a junior branch of the Viscounts of Léon which was founded by Harvey I, second son of Guihomar IV, Viscount of Léon. Herve VII won fame during the War of the Breton Succession.
Olivier was Count of Penthièvre and Lord of Avesnes from 1404 until his death.














