
Michel Odent (born 1930) is a French obstetrician and childbirth specialist. [1]

Michel Odent (born 1930) is a French obstetrician and childbirth specialist. [1]
Born in a French village in 1930, Odent studied medicine in Paris and was educated as a surgeon in the 1950s. He has been presented in Lancet as “one of the last real general surgeons”. [2]
In charge of the surgical and maternity units of the Pithiviers hospital (France) from 1962 to 1985, Odent has developed a special interest in environmental factors influencing the birth process. [3] He introduced the concepts of birthing rooms, birthing pools, and singing sessions for pregnant women. After his hospital career he was involved in home birth, founded in London the Primal Health Research Centre, and designed a database (primalhealthhresearch.com) to compile epidemiological studies exploring correlations between conditions during the natal “primal period” and subsequent child and mother health. Odent is Visiting Professor at Odessa National Medical University and Doctor Honoris Causa of Brasilia University. [4]
Odent is the author of the first articles about the initiation of breastfeeding during the hour following birth, the first article about the use of birthing pools during labour, and the first article applying the Gate control theory of pain to obstetrics. [5] [6] [7] [8]
In a book published in 1986 (“Primal Health”) he provided evidence that homeostasis is established during the “primal period” (fetal life, birth and the months following birth): this is the phase of life when human basic adaptive systems are adjusting their “set point levels”. Odent is currently focusing on the possible evolution of Homo sapiens in relation to the modern ways to be born. [9] [10]
Odent is the author of 17 books published in 22 languages. In his books he is constantly referring to the concept of reduced neocortical activity as a key to rediscover the basic needs of labouring women and to make possible a real “fetus ejection reflex”. [11]
His books include:
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field.
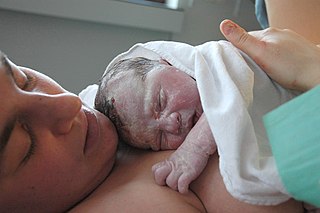
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million human births globally. In developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in developing countries most are home births.
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can often result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and sudden infant death syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive.
Natural childbirth is childbirth without routine medical interventions, particularly anesthesia. Natural childbirth arose in opposition to the techno-medical model of childbirth that has recently gained popularity in industrialized societies. Natural childbirth attempts to minimize medical intervention, particularly the use of anesthetic medications and surgical interventions such as episiotomies, forceps and ventouse deliveries and caesarean sections. Natural childbirth may occur during a physician or midwife attended hospital birth, a midwife attended homebirth, or an unassisted birth. The term "natural childbirth" was coined by obstetrician Grantly Dick-Read upon publication of his book Natural Childbirth in the 1930s, which was followed by the 1942 Childbirth Without Fear.

Water birth is childbirth that occurs in water, usually a birthing pool. It may include the use of water for relaxation and pain relief during the first stage of labour, birth into water in the second stage of labour, and the delivery of the placenta in the third stage of labour.
Tocolytics are medications used to suppress premature labor. Preterm birth accounts for 70% of neonatal deaths. Therefore, tocolytic therapy is provided when delivery would result in premature birth, postponing delivery long enough for the administration of glucocorticoids, which accelerate fetal lung maturity but may require one to two days to take effect.
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method, if available. Such methods include adding 14 days to a known duration since fertilization, or by obstetric ultrasonography. The popularity of using this measure of pregnancy is largely due to convenience: menstruation is usually noticed, while there is generally no convenient way to discern when fertilization or implantation occurred.

Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
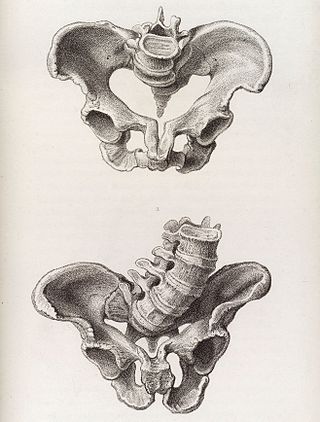
Obstructed labour, also known as labour dystocia, is the baby not exiting the pelvis because it is physically blocked during childbirth although the uterus contracts normally. Complications for the baby include not getting enough oxygen which may result in death. It increases the risk of the mother getting an infection, having uterine rupture, or having post-partum bleeding. Long-term complications for the mother include obstetrical fistula. Obstructed labour is said to result in prolonged labour, when the active phase of labour is longer than 12 hours.

Complications of pregnancy are health problems that are related to, or arise during pregnancy. Complications that occur primarily during childbirth are termed obstetric labor complications, and problems that occur primarily after childbirth are termed puerperal disorders. While some complications improve or are fully resolved after pregnancy, some may lead to lasting effects, morbidity, or in the most severe cases, maternal or fetal mortality.
A contraction stress test (CST) is performed near the end of pregnancy to determine how well the fetus will cope with the contractions of childbirth. The aim is to induce contractions and monitor the fetus to check for heart rate abnormalities using a cardiotocograph. A CST is one type of antenatal fetal surveillance technique.
Tokophobia is a significant fear of childbirth. It is a common reason why some women request an elective cesarean section. Factors often include a fear of pain, death, unexpected problems, injury to the baby, sexual problems and a lack of self-belief of the capacity to birth a child. Treatment may occur via counselling.

The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) is a professional association based in London, United Kingdom. Its members, including people with and without medical degrees, work in the field of obstetrics and gynaecology, that is, pregnancy, childbirth, and female sexual and reproductive health. The college has over 16,000 members in over 100 countries with nearly 50% of those residing outside the British Isles. Catherine, Princess of Wales became the RCOG's patron in 2018.

Grantly Dick-Read was a British obstetrician and a leading advocate of natural childbirth.
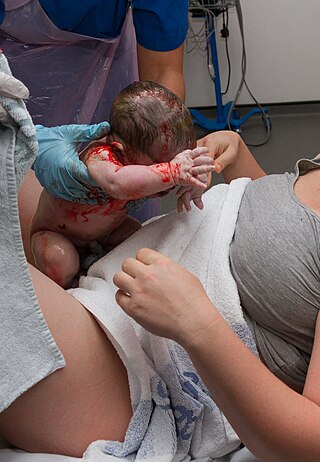
Maternal–fetal medicine (MFM), also known as perinatology, is a branch of medicine that focuses on managing health concerns of the mother and fetus prior to, during, and shortly after pregnancy.

Obstetrical forceps are a medical instrument used in childbirth. Their use can serve as an alternative to the ventouse method.
In obstetrics, asynclitic birth, or asynclitism, refers to the malposition of the fetal head in the uterus relative to the birth canal. Many babies enter the pelvis in an asynclitic presentation, but in most cases, it corrects itself spontaneously during labor. Asynclitic presentation is not to be confused with a shoulder presentation, where the shoulder leads first.
The Ferguson reflex is the neuroendocrine reflex comprising the self-sustaining cycle of uterine contractions initiated by pressure at the cervix, more precisely, the internal end of cervix, or vaginal walls. It is an example of positive feedback in biology. The Ferguson reflex occurs in mammals.

A perineal tear is a laceration of the skin and other soft tissue structures which, in women, separate the vagina from the anus. Perineal tears mainly occur in women as a result of vaginal childbirth, which strains the perineum. It is the most common form of obstetric injury. Tears vary widely in severity. The majority are superficial and may require no treatment, but severe tears can cause significant bleeding, long-term pain or dysfunction. A perineal tear is distinct from an episiotomy, in which the perineum is intentionally incised to facilitate delivery. Episiotomy, a very rapid birth, or large fetal size can lead to more severe tears which may require surgical intervention.
Norman Frederick Morris was a British pioneer of women's health. He was a professor of obstetrics and gynaecology at Charing Cross Hospital Medical School (1958–1985) and was also a university administrator. From 1971 to 1980, he was dean of medicine, and then deputy vice-chancellor at the University of London.