
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude.

A micrometer, sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device incorporating a calibrated screw widely used for accurate measurement of components in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier, and digital calipers. Micrometers are usually, but not always, in the form of calipers. The spindle is a very accurately machined screw and the object to be measured is placed between the spindle and the anvil. The spindle is moved by turning the ratchet knob or thimble until the object to be measured is lightly touched by both the spindle and the anvil.

A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat.
In mechanical engineering and control engineering, a servomechanism is a control system for the position and its time derivatives of a mechanical system using closed-loop control to reduce steady-state error and improved dynamic response. In closed-loop control, error-sensing negative feedback is used to correct the action of the mechanism. In displacement-controlled applications, it usually includes a built-in encoder or other position feedback mechanism to ensure the output is achieving the desired effect. Following a specified motion trajectory is called servoing, where "servo" is used as a verb. The servo prefix originates from the Latin word servus meaning slave.

A spirit level, bubble level, or simply a level, is an instrument designed to indicate whether a surface is horizontal (level) or vertical (plumb). Two basic designs exist: tubular and bull's eye . Different types of spirit levels may be used by carpenters, stonemasons, bricklayers, other building trades workers, surveyors, millwrights and other metalworkers, and in some photographic or videographic work.

A speedometer or speed meter is a gauge that measures and displays the instantaneous speed of a vehicle. Now universally fitted to motor vehicles, they started to be available as options in the early 20th century, and as standard equipment from about 1910 onwards. Other vehicles may use devices analogous to the speedometer with different means of sensing speed, eg. boats use a pit log, while aircraft use an airspeed indicator.

A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is an automated transmission that can change through a continuous range of gear ratios. This contrasts with other transmissions that provide a limited number of gear ratios in fixed steps. The flexibility of a CVT with suitable control may allow the engine to operate at a constant angular velocity while the vehicle moves at varying speeds.

An inverted microscope is a microscope with its light source and condenser on the top, above the stage pointing down, while the objectives and turret are below the stage pointing up. It was invented in 1850 by J. Lawrence Smith, a faculty member of Tulane University.
A reamer is a type of rotary cutting tool used in metalworking. Precision reamers are designed to enlarge the size of a previously formed hole by a small amount but with a high degree of accuracy to leave smooth sides. There are also non-precision reamers which are used for more basic enlargement of holes or for removing burrs. The process of enlarging the hole is called reaming. There are many different types of reamer and they may be designed for use as a hand tool or in a machine tool, such as a milling machine or drill press.

A chart recorder is an electromechanical device that records an electrical or mechanical input trend onto a piece of paper. Chart recorders may record several inputs using different color pens and may record onto strip charts or circular charts. Chart recorders may be entirely mechanical with clockwork mechanisms, electro-mechanical with an electrical clockwork mechanism for driving the chart, or entirely electronic with no mechanical components at all.

In various contexts of science, technology, and manufacturing, an indicator is any of various instruments used to accurately measure small distances and angles, and amplify them to make them more obvious. The name comes from the concept of indicating to the user that which their naked eye cannot discern; such as the presence, or exact quantity, of some small distance.

Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, describes a helix toolpath by moving more or less linearly while the workpiece rotates.

An articulated robot is a robot with rotary joints. Articulated robots can range from simple two-jointed structures to systems with 10 or more interacting joints and materials. They are powered by a variety of means, including electric motors.

In machining, boring is the process of enlarging a hole that has already been drilled by means of a single-point cutting tool, such as in boring a gun barrel or an engine cylinder. Boring is used to achieve greater accuracy of the diameter of a hole, and can be used to cut a tapered hole. Boring can be viewed as the internal-diameter counterpart to turning, which cuts external diameters.

Intelligent lighting refers to lighting that has automated or mechanical abilities beyond those of traditional, stationary illumination. Although the most advanced intelligent lights can produce extraordinarily complex effects, the intelligence lies with the human lighting designer, control system programmer(For example, Chamsys and Avolites), or the lighting operator, rather than the fixture itself. For this reason, intelligent lighting (ILS) is also known as automated lighting, moving lights, moving heads, or simply movers.
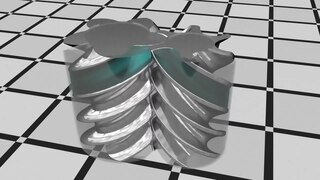
A rotary-screw compressor is a type of gas compressor, such as an air compressor, that uses a rotary-type positive-displacement mechanism. These compressors are common in industrial applications and replace more traditional piston compressors where larger volumes of compressed gas are needed, e.g. for large refrigeration cycles such as chillers, or for compressed air systems to operate air-driven tools such as jackhammers and impact wrenches. For smaller rotor sizes the inherent leakage in the rotors becomes much more significant, leading to this type of mechanism being less suitable for smaller compressors than piston compressors.

A parallel manipulator is a mechanical system that uses several computer-controlled serial chains to support a single platform, or end-effector. Perhaps, the best known parallel manipulator is formed from six linear actuators that support a movable base for devices such as flight simulators. This device is called a Stewart platform or the Gough-Stewart platform in recognition of the engineers who first designed and used them.

A digital microscope is a variation of a traditional optical microscope that uses optics and a digital camera to output an image to a monitor, sometimes by means of software running on a computer. A digital microscope often has its own in-built LED light source, and differs from an optical microscope in that there is no provision to observe the sample directly through an eyepiece. Since the image is focused on the digital circuit, the entire system is designed for the monitor image. The optics for the human eye are omitted.

The stereo, stereoscopic or dissecting microscope is an optical microscope variant designed for low magnification observation of a sample, typically using light reflected from the surface of an object rather than transmitted through it. The instrument uses two separate optical paths with two objectives and eyepieces to provide slightly different viewing angles to the left and right eyes. This arrangement produces a three-dimensional visualization of the sample being examined. Stereomicroscopy overlaps macrophotography for recording and examining solid samples with complex surface topography, where a three-dimensional view is needed for analyzing the detail.

Vertico spatially modulated illumination (Vertico-SMI) is the fastest light microscope for the 3D analysis of complete cells in the nanometer range. It is based on two technologies developed in 1996, SMI and SPDM. The effective optical resolution of this optical nanoscope has reached the vicinity of 5 nm in 2D and 40 nm in 3D, greatly surpassing the λ/2 resolution limit applying to standard microscopy using transmission or reflection of natural light according to the Abbe resolution limit That limit had been determined by Ernst Abbe in 1873 and governs the achievable resolution limit of microscopes using conventional techniques.




















