Related Research Articles

The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that carries sensory fibers that create a pathway that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract.
Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a medical condition wherein a person's blood pressure drops when they are standing up (orthostasis) or sitting down. Primary orthostatic hypotension is also often referred to as neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. The drop in blood pressure may be sudden, within 3 minutes or gradual. It is defined as a fall in systolic blood pressure of at least 20 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure of at least 10 mmHg after 3 minutes of standing. It occurs predominantly by delayed constriction of the lower body blood vessels, which is normally required to maintain adequate blood pressure when changing the position to standing. As a result, blood pools in the blood vessels of the legs for a longer period, and less is returned to the heart, thereby leading to a reduced cardiac output and inadequate blood flow to the brain.

Urination is the release of urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Urine is released through the urethra and exits the penis or vulva through the urinary meatus in placental mammals, but is released through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, uresis, or, rarely, emiction, and known colloquially by various names including peeing, weeing, pissing, and euphemistically number one. The process of urination is under voluntary control in healthy humans and other animals, but may occur as a reflex in infants, some elderly individuals, and those with neurological injury. It is normal for adult humans to urinate up to seven times during the day.

The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
Baroreceptors are stretch receptors that sense blood pressure. Thus, increases in the pressure of blood vessel triggers increased action potential generation rates and provides information to the central nervous system. This sensory information is used primarily in autonomic reflexes that in turn influence the heart cardiac output and vascular smooth muscle to influence vascular resistance. Baroreceptors act immediately as part of a negative feedback system called the baroreflex, as soon as there is a change from the usual mean arterial blood pressure, returning the pressure toward a normal level. These reflexes help regulate short-term blood pressure. The solitary nucleus in the medulla oblongata of the brain recognizes changes in the firing rate of action potentials from the baroreceptors, and influences cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance.

Flushing is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished from blushing, since blushing is psychosomatic, milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or ears, and generally assumed to reflect emotional stress, such as embarrassment, anger, or romantic stimulation. Flushing is also a cardinal symptom of carcinoid syndrome—the syndrome that results from hormones being secreted into systemic circulation.

Palpitations are perceived abnormalities of the heartbeat characterized by awareness of cardiac muscle contractions in the chest, which is further characterized by the hard, fast and/or irregular beatings of the heart.
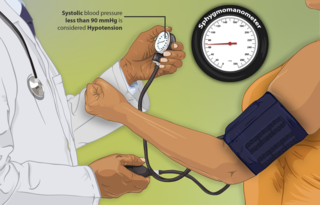
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure and the diastolic blood pressure, which are the maximum and minimum blood pressures within the cardiac cycle, respectively. A systolic blood pressure of less than 90 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or diastolic of less than 60 mmHg is generally considered to be hypotension. Different numbers apply to children. However, in practice, blood pressure is considered too low only if noticeable symptoms are present.

Reflex syncope is a brief loss of consciousness due to a neurologically induced drop in blood pressure and/or a decrease in heart rate. Before an affected person passes out, there may be sweating, a decreased ability to see, or ringing in the ears. Occasionally, the person may twitch while unconscious. Complications of reflex syncope include injury due to a fall.

Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, mild lower abdominal pain, and a weak urine stream. Those with long-term problems are at risk of urinary tract infections.

In human anatomy, the carotid sinus is a dilated area at the base of the internal carotid artery just superior to the bifurcation of the internal carotid and external carotid at the level of the superior border of thyroid cartilage. The carotid sinus extends from the bifurcation to the "true" internal carotid artery. The carotid sinus is sensitive to pressure changes in the arterial blood at this level. It is the major baroreception site in humans and most mammals.

A paraganglioma is a rare neuroendocrine neoplasm that may develop at various body sites. When the same type of tumor is found in the adrenal gland, they are referred to as a pheochromocytoma. They are rare tumors, with an overall estimated incidence of 1 in 300,000. There is no test that determines benign from malignant tumors; long-term follow-up is therefore recommended for all individuals with paraganglioma.

A tilt table test (TTT), occasionally called upright tilt testing (UTT), is a medical procedure often used to diagnose dysautonomia or syncope. Patients with symptoms of dizziness or lightheadedness, with or without a loss of consciousness (fainting), suspected to be associated with a drop in blood pressure or positional tachycardia are good candidates for this test.
Blood phobia is an extreme irrational fear of blood, a type of specific phobia. Severe cases of this fear can cause physical reactions that are uncommon in most other fears, specifically vasovagal syncope (fainting). Similar reactions can also occur with trypanophobia and traumatophobia. For this reason, these phobias are categorized as blood-injection-injury phobia by the DSM-IV. Some early texts refer to this category as "blood-injury-illness phobia."
The Bezold–Jarisch reflex involves a variety of cardiovascular and neurological processes which cause hypopnea, hypotension and bradycardia in response to noxious stimuli detected in the cardiac ventricles. The reflex is named after Albert von Bezold and Adolf Jarisch Junior. The significance of the discovery is that it was the first recognition of a chemical (non-mechanical) reflex.

Syncope, commonly known as fainting or passing out, is a loss of consciousness and muscle strength characterized by a fast onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain, typically from low blood pressure. There are sometimes symptoms before the loss of consciousness such as lightheadedness, sweating, pale skin, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, or feeling warm. Syncope may also be associated with a short episode of muscle twitching. Psychiatric causes can also be determined when a patient experiences fear, anxiety, or panic; particularly before a stressful event, usually medical in nature. When consciousness and muscle strength are not completely lost, it is called presyncope. It is recommended that presyncope be treated the same as syncope.
Blood-injection-injury (BII) type phobia is a type of specific phobia characterized by the display of excessive, irrational fear in response to the sight of blood, injury, or injection, or in anticipation of an injection, injury, or exposure to blood. Blood-like stimuli may also cause a reaction. This is a common phobia with an estimated 3-4% prevalence in the general population, though it has been found to occur more often in younger and less educated groups. Prevalence of fear of needles which does not meet the BII phobia criteria is higher. A proper name for BII has yet to be created.
A choke-out is a hand-to-hand combat tactic involving the use of a chokehold to cause syncope, or temporary loss of consciousness, at which point the choke is released. Common chokeholds in grappling used to accomplish a choke-out include the rear naked choke, arm triangle, triangle choke, and the guillotine.
Hair-grooming syncope is a form of syncope associated with combing and brushing one's hair. It is most typically seen in children aged five to sixteen.
In neurourology, post-micturition convulsion syndrome (PMCS), also known informally as pee shivers or piss shivers, is the experience of shivering during or after urination. The syndrome seems to be experienced equally by men and women.
References
- ↑ Padevit C.; John H.; Gunz A.; Wiesli P.; Hauri D.; Schmid C. (2005). "Micturition Syncope due to Paraprostatic Pheochromocytoma". Urol Int. 74 (3): 276–277. doi:10.1159/000083563. PMID 15812218.
- ↑ "Fainting during urination (micturition syncope): What causes it? - Mayo Clinic".