Related Research Articles
The Book of Exodus is the second book of the Bible. It is a narrative of the Exodus, the origin myth of the Israelites leaving slavery in Biblical Egypt through the strength of their deity named Yahweh, who according to the story chose them as his people. The Israelites then journey with the legendary prophet Moses to Mount Sinai, where Yahweh gives the 10 commandments and they enter into a covenant with Yahweh, who promises to make them a "holy nation, and a kingdom of priests" on condition of their faithfulness. He gives them their laws and instructions to build the Tabernacle, the means by which he will come from heaven and dwell with them and lead them in a holy war to conquer Canaan, which has earlier, according to the myth of Genesis, been promised to the "seed" of Abraham, the legendary patriarch of the Israelites.

Midrash is expansive Jewish Biblical exegesis using a rabbinic mode of interpretation prominent in the Talmud. The word itself means "textual interpretation", "study", or "exegesis", derived from the root verb darash (דָּרַשׁ), which means "resort to, seek, seek with care, enquire, require".

Sabine Baring-Gould of Lew Trenchard in Devon, England, was an Anglican priest, hagiographer, antiquarian, novelist, folk song collector and eclectic scholar. His bibliography consists of more than 1,240 publications, though this list continues to grow.

Thomas Wright was an English antiquarian and writer. He is chiefly remembered as an editor of medieval texts.
The Old English Bible translations are the partial translations of the Bible prepared in medieval England into the Old English language. The translations are from Latin texts, not the original languages.

The Junius manuscript is one of the four major codices of Old English literature. Written in the 10th century, it contains poetry dealing with Biblical subjects in Old English, the vernacular language of Anglo-Saxon England. Modern editors have determined that the manuscript is made of four poems, to which they have given the titles Genesis, Exodus, Daniel, and Christ and Satan. The identity of their author is unknown. For a long time, scholars believed them to be the work of Cædmon, accordingly calling the book the Cædmon manuscript. This theory has been discarded due to the significant differences between the poems.

In heraldry, an escutcheon is a shield that forms the main or focal element in an achievement of arms. The word can be used in two related senses. In the first sense, an escutcheon is the shield upon which a coat of arms is displayed. In the second sense, an escutcheon can itself be a charge within a coat of arms.

The Jahwist, or Yahwist, often abbreviated J, is one of the most widely recognized sources of the Pentateuch (Torah), together with the Deuteronomist, the Priestly source and the Elohist. The existence of the Jahwist text is somewhat controversial, with a number of scholars, especially in Europe, denying that it ever existed as a coherent independent document. Nevertheless, many scholars do assume its existence. The Jahwist is so named because of its characteristic use of the term Yahweh for God.
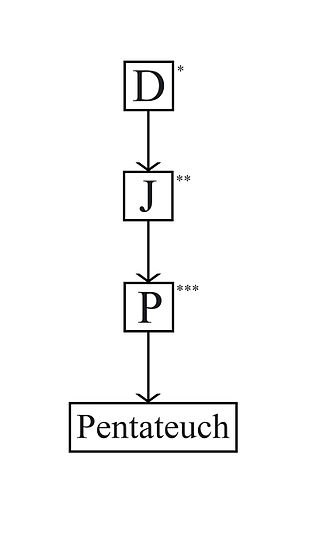
The Priestly source is perhaps the most widely recognized of the sources underlying the Torah, both stylistically and theologically distinct from other material in it. It is considered by most scholars as the latest of all sources, and “meant to be a kind of redactional layer to hold the entirety of the Pentateuch together,” It includes a set of claims that are contradicted by non-Priestly passages and therefore uniquely characteristic: no sacrifice before the institution is ordained by Yahweh (God) at Sinai, the exalted status of Aaron and the priesthood, and the use of the divine title El Shaddai before God reveals his name to Moses, to name a few.

The Tz'enah Ur'enah, also spelt Tsene-rene and Tseno Ureno, sometimes called the Women's Bible, is a Yiddish-language prose work whose structure parallels the weekly Torah portions and Haftarahs used in Jewish prayer services. The book was written by Jacob ben Isaac Ashkenazi (1550–1625) of Janów Lubelski, and mixes Biblical passages with teachings from Judaism's Oral Torah such as the Talmud's Aggadah and Midrash, which are sometimes called "parables, allegories, short stories, anecdotes, legends, and admonitions" by secular writers.

James De Mille was a professor at Dalhousie University, Nova Scotia, and an early Canadian novelist who published numerous works of popular fiction from the late 1860s through the 1870s.

The Early English Text Society (EETS) is a text publication society founded in 1864 which is dedicated to the editing and publication of early English texts, especially those only available in manuscript. Most of its volumes contain editions of Middle English or Old English texts. It is known for being the first to print many important English manuscripts, including Cotton Nero A.x, which contains Pearl, Sir Gawain and the Green Knight, and other poems.

Jehovah is a Latinization of the Hebrew יְהֹוָהYəhōwā, one vocalization of the Tetragrammaton יהוה (YHWH), the proper name of the God of Israel in the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament. The Tetragrammaton יהוה is considered one of the seven names of God in Judaism and a form of God's name in Christianity.

The Book of the Thousand Nights and a Night (1888), subtitled A Plain and Literal Translation of the Arabian Nights Entertainments, is the only complete English language translation of One Thousand and One Nights to date – a collection of Middle Eastern and South Asian stories and folk tales compiled in Arabic during the Islamic Golden Age – by the British explorer and Arabist Richard Francis Burton (1821–1890). It stands as the only complete translation of the Macnaghten or Calcutta II edition of the "Arabian Nights".

Genesis A is an Old English poetic adaptation of about the first half of the biblical book of Genesis. The poem is fused with a passage known today as Genesis B, translated and interpolated from the Old Saxon Genesis.
The Story of the Glittering Plain is an 1891 fantasy novel by William Morris, perhaps the first modern fantasy writer to unite an imaginary world with the element of the supernatural, and thus the precursor of much of present-day fantasy literature. It is also important for its exploration of the socialist themes that interested Morris.

The Old English Hexateuch, or Aelfric Paraphrase, is the collaborative project of the late Anglo-Saxon period that translated the six books of the Hexateuch into Old English, presumably under the editorship of Abbot Ælfric of Eynsham. It is the first English vernacular translation of the first six books of the Old Testament, i.e. the five books of the Torah and Joshua. It was probably made for use by lay people.
The Durham Proverbs is a collection of 46 mediaeval proverbs from various sources. They were written down as a collection, in the eleventh century, on some pages of a manuscript that were originally left blank. The manuscript is currently in the collection of Durham Cathedral, to which it was donated in the eighteenth century. The Proverbs form the first part of the manuscript. The second part, to which it is bound, is a copy of Ælfric's Grammar. Each proverb is written in both Latin and Old English, with the former preceding the latter. Olof Arngart's opinion is that the Proverbs were originally in Old English and translated to Latin, but this has since been disputed in a conference paper by T. A. Shippey.
Biblical translations into the indigenous languages of North and South America have been produced since the 16th century.
References
- ↑ Birch 2009.
- 1 2 3 Morris 1865.
- ↑ Arngart 1968.