
Fujian is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou, while its largest city by population is Quanzhou, both located near the coast of the Taiwan Strait in the east of the province.

Min is a broad group of Sinitic languages spoken by about 30 million people in Fujian province as well as by the descendants of Min speaking colonists on Leizhou peninsula and Hainan, or assimilated natives of Chaoshan, parts of Zhongshan, three counties in southern Wenzhou, Zhoushan archipelago, and Taiwan. The name is derived from the Min River in Fujian, which is also the abbreviated name of Fujian Province. Min varieties are not mutually intelligible with one another nor with any other variety of Chinese.
Hokkien is a dialect of Southern Min Chinese spoken in Southern Fujian, Taiwan, Southeast Asia, and elsewhere.

Southern Min, Minnan or Banlam, is a group of linguistically similar and historically related Sinitic languages that form a branch of Min Chinese spoken in Fujian, most of Taiwan, Eastern Guangdong, Hainan, and Southern Zhejiang. The Minnan dialects are also spoken by descendants of emigrants from these areas in diaspora, most notably the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, San Francisco, Los Angeles and New York City. It is the most populous branch of Min Chinese, spoken by an estimated 48 million people in ca. 2017–2018.
Minnan or Banlam may refer to:

Fuzhou, alternately romanized as Foochow, is the capital and one of the largest cities in Fujian province, China. Along with the many counties of Ningde, those of Fuzhou are considered to constitute the Mindong linguistic and cultural area.

The Min River is a 577 kilometres (359 mi)-long river in Fujian province, People's Republic of China. It is the largest river in Fujian, and an important water transport channel. Most of northern and central Fujian is within its drainage area.

Fujian Province ; also romanized as Fuchien and rendered as Fukien is a nominal province of the Republic of China without formal administrative function. It includes three small archipelagos off the coast of the Fujian Province of the People's Republic of China, namely the Matsu Islands, which make up Lienchiang County, and the Wuqiu Islands and Kinmen Islands, which make up Kinmen County. De jure, Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, and Guangdong to the south. Its claimed capital is Fuzhou, while its claimed largest city by population is Quanzhou, both located near the coast of the Taiwan Strait in the east of the province. The seat of the provincial government is Jincheng Township of Kinmen County serves as its de facto capital.
The subgroups of the Han Chinese people, Chinese dialect groups or just dialect groups, are defined based on linguistic, cultural, ethnic, genetic and regional features. The terminology used in Mandarin to describe the groups is: "minxi", used in Mainland China or "zuqun", used in Taiwan. No Han subgroup is recognized as one of People's Republic of China's 56 official minority ethnic groups. Scholars like James W. Hayes have described the Han Chinese subgroups as "ethnic group" outright, at least in the context of Hong Kong society.

Min was one of the Ten Kingdoms which was in existence between the years of 909 and 945. It existed in a mountainous region of modern-day Fujian province of China and had a history of quasi-independent rule. Its capital was Fuzhou. It was founded by Wang Shenzhi.

Fujian cuisine or Fujianese cuisine, also known as Min cuisine or Hokkien cuisine, is one of the native Chinese cuisines derived from the native cooking style of China's Fujian Province, most notably from the provincial capital, Fuzhou. Fujian cuisine is known to be light but flavourful, soft, and tender, with particular emphasis on umami taste, known in Chinese cooking as xianwei, as well as retaining the original flavour of the main ingredients instead of masking them.

Nanping is a third-tier prefecture-level city in northwestern Fujian Province, People's Republic of China. It borders Ningde to the east, Sanming to the south, and the provinces of Zhejiang and Jiangxi to the north and west respectively. Part of the famous Wuyi Mountains range is located in this prefecture. Its population was 2,680,645 as of the 2020 census whom 795,448 lived in the built-up area made up of Yanping and Jianyang urban districts.

Eastern Min or Min Dong, is a branch of the Min group of Sinitic languages of China. The prestige form and most-cited representative form is the Fuzhou dialect, the speech of the capital of Fujian.

Puxian, also known as Pu-Xian Chinese, Puxian Min, Xinghua, Henghwa or Hinghwa, is a Sinitic language that forms a branch of Min Chinese. Puxian is a transitional variety of Coastal Min which shares characteristics with both Eastern Min and Southern Min, although it is closer to the latter.
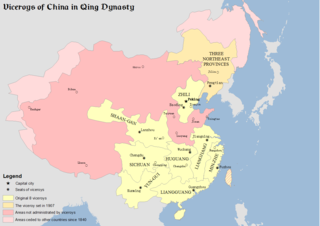
The Viceroy of Min-Zhe, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Taiwan, Fujian and Zhejiang Provinces and Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs and Food Production, Manager of Waterways, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight Viceroys in China proper during the Qing dynasty. The "Zhe" refers to Zhejiang Province while "Min" is the abbreviation of Fujian Province. Taiwan was also under the Viceroy's control until after the 1895 Treaty of Shimonoseki.
The Putian people, are Han Chinese people from Putian, part of Fujian Province, China. They are also known as the Henghua, Henghwa, Hinghwa or Xinghua people after the historical name of the area. They speak Puxian Min, a Min language. Min is one of the Sinitic languages.

Zhenan Min, is a Min Nan Chinese language spoken in the vicinity of Wenzhou, in the southeast of Zhejiang province.
Shehua is an unclassified Sinitic language spoken by the She people of Southeastern China. It is also called Shanha, San-hak (山哈) or Shanhahua (山哈话). Shehua speakers are located mainly in Fujian and Zhejiang provinces of Southeastern China, with smaller numbers of speakers in a few locations of Jiangxi, Guangdong and Anhui provinces.










