
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice through setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and oldest specialised agency of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.
Labour laws are those that mediate the relationship between workers, employing entities, trade unions and the government. Collective labour law relates to the tripartite relationship between employee, employer and union. Individual labour law concerns employees' rights at work also through the contract for work. Employment standards are social norms for the minimum socially acceptable conditions under which employees or contractors are allowed to work. Government agencies enforce labour law.

Child labor laws in the United States address issues related to the employment and welfare of working children in the United States. The most sweeping federal law that restricts the employment and abuse of child workers is the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 (FLSA). Child labor provisions under FLSA are designed to protect the educational opportunities of youth and prohibit their employment in jobs that are detrimental to their health and safety. FLSA restricts the hours that youth under 16 years of age can work and lists hazardous occupations too dangerous for young workers to perform.
Labor rights or workers' rights are both legal rights and human rights relating to labor relations between workers and employers. These rights are codified in national and international labor and employment law. In general, these rights influence working conditions in relations of employment. One of the most prominent is the right to freedom of association, otherwise known as the right to organize. Workers organized in trade unions exercise the right to collective bargaining to improve working conditions.
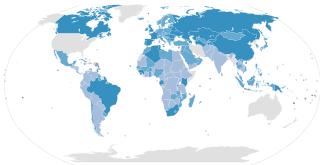
The ILO Convention concerning Minimum Age for Admission to Employment C138, is a convention adopted in 1973 by the International Labour Organization. It requires ratifying states to pursue a national policy designed to ensure the effective abolition of child labour and to raise progressively the minimum age for admission to employment or work. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions. Convention C138 replaces several similar ILO conventions in specific fields of labour.

Ex parte H.V. McKay, commonly referred to as the Harvester case, is a landmark Australian labour law decision of the Commonwealth Court of Conciliation and Arbitration. The case arose under the Excise Tariff Act 1906 which imposed an excise duty on goods manufactured in Australia, £6 in the case of a stripper harvester, however if a manufacturer paid "fair and reasonable" wages to its employees, it was be excused from paying the excise duty. The Court therefore had to consider what was a "fair and reasonable" wage for the purpose of the act.
The Right to Organise and Collective Bargaining Convention (1949) No 98 is an International Labour Organization Convention. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.
Minimum Wage Fixing Machinery (Agriculture) Convention, 1951 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Minimum Wage Fixing Convention 1970 is a Convention by the International Labour Organization established in 1970. The preamble stated:
Noting the terms of the Minimum Wage-Fixing Machinery Convention, 1928, and the Equal Remuneration Convention, 1951, which have been widely ratified, as well as of the Minimum Wage Fixing Machinery (Agriculture) Convention, 1951, and
Considering that these Convention have played a valuable part in protecting disadvantaged groups of wage earners, and
Considering that the time has come to adopt a further instrument complementing these Conventions and providing protection for wage earners against unduly low wages, which, while of general application, pays special regard to the needs of developing countries, and
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to minimum wage fixing machinery and related problems, with special reference to developing countries,..
Minimum wage law is the body of law which prohibits employers from hiring employees or workers for less than a given hourly, daily or monthly minimum wage. More than 90% of all countries have some kind of minimum wage legislation.
The Nevada State Democratic Party (NSDP) is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the U.S. state of Nevada. It has been chaired by Judith Whitmer since March 2021.

The Congressional Apportionment Amendment is a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution that addresses the number of seats in the House of Representatives. It was proposed by Congress on September 25, 1789, but was never ratified by the requisite number of state legislatures. As Congress did not set a time limit for its ratification, the Congressional Apportionment Amendment is still pending before the states. As of 2021, it is one of six unratified amendments.
C99 is a past version of the C programming language standard.
A maximum wage, also often called a wage ceiling, is a legal limit on how much income an individual can earn. It is a prescribed limitation which can be used to affect change in an economic structure, but its effects are unrelated to those of minimum wage laws used currently by some states to enforce minimum earnings.

The Convention on Domestic Workers, formally the Convention concerning Decent Work for Domestic Workers is a convention setting labour standards for domestic workers. It is the 189th ILO convention and was adopted during the 100th session of the International Labour Organization. It entered into force on 5 September 2013.
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating the workplace. The International Labour Organization and the World Trade Organization have been the main international bodies involved in reforming labour markets. The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank have indirectly driven changes in labour policy by demanding structural adjustment conditions for receiving loans or grants. Issues regarding Conflict of laws arise, determined by national courts, when people work in more than one country, and supra-national bodies, particularly in the law of the European Union, has a growing body of rules regarding labour rights.

The Minimum Wages Act 1948 is an Act of Parliament concerning Indian labour law that sets the minimum wages that must be paid to skilled and unskilled labours.
The Isle of Man is a Crown Dependency located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland with a population in 2015 estimated to be approximately 88,000. It enjoys a high degree of domestic, legislative and political autonomy through its ancient Parliament Tynwald. By convention, the United Kingdom Government is responsible for the conduct of the international relations and defence of the island. The Isle of Man does not have a written constitution, or a Bill of Rights which sets out its Human Rights. These rights are addressed in the Human Rights Act 2001. The island has also ratified a number of international treaties.
Israel signed the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities on 30 March 2007 and ratified it on 28 September 2012.