| Look up minority in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Minority may refer to:
| Look up minority in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Minority may refer to:

Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of race, gender, age, religion, or sexual orientation, as well as other categories. Discrimination especially occurs when individuals or groups are unfairly treated in a way which is worse than other people are treated, on the basis of their actual or perceived membership in certain groups or social categories. It involves restricting members of one group from opportunities or privileges that are available to members of another group.
A hate crime is a prejudice-motivated crime which occurs when a perpetrator targets a victim because of their membership of a certain social group or racial demographic.
Hate speech is defined by the Cambridge Dictionary as "public speech that expresses hate or encourages violence towards a person or group based on something such as race, religion, sex, or sexual orientation". Hate speech is "usually thought to include communications of animosity or disparagement of an individual or a group on account of a group characteristic such as race, colour, national origin, sex, disability, religion, or sexual orientation". Legal definitions of hate speech varies from country to country.
Ethnic minorities in China are the non-Han Chinese population in the People's Republic of China (PRC).
A minority group, by its original definition, refers to a group of people whose practices, race, religion, ethnicity, or other characteristics are fewer in numbers than the main groups of those classifications. However, in present-day sociology, a minority group refers to a category of people who experience relative disadvantage as compared to members of a dominant social group. Minority group membership is typically based on differences in observable characteristics or practices, such as: ethnicity, race, religion, sexual orientation, or disability. Utilizing the framework of intersectionality, it is important to recognize that an individual may simultaneously hold membership in multiple minority groups. Likewise, individuals may also be part of a minority group in regard to some characteristics, but part of a dominant group in regard to others.
A visible minority is defined by the Government of Canada as "persons, other than aboriginal peoples, who are non-Caucasian in race or non-white in colour". The term is used primarily as a demographic category by Statistics Canada, in connection with that country's Employment Equity policies. The qualifier "visible" was chosen by the Canadian authorities as a way to single out newer immigrant minorities from both Aboriginal Canadians and other "older" minorities distinguishable by language and religion, which are "invisible" traits.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Liechtenstein enjoy many, but not all, of the same rights as non-LGBT people. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 1989, with an equal age of consent since 2001. Same-sex couples have had access to registered partnerships since 2011, and discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been outlawed in some areas since 2016.
Minority rights are the normal individual rights as applied to members of racial, ethnic, class, religious, linguistic or gender and sexual minorities, and also the collective rights accorded to any minority group.
A social issue is a problem that affects many people within a society. It is a group of common problems in present-day society and ones that many people strive to solve. It is often the consequence of factors extending beyond an individual's control. Social issues are the source of conflicting opinions on the grounds of what is perceived as morally correct or incorrect personal life or interpersonal social life decisions. Social issues are distinguished from economic issues; however, some issues have both social and economic aspects. Some issues do not fall into either category, such as warfare.
White Americans are Americans who identify as and are perceived to be white people. This group constitutes the majority of the people in the United States. As of the 2020 Census, 61.6%, or 204,277,273 people, were white alone, and 71.0%, or 235,411,507 people, were white alone or combined with another race. Non-Hispanic whites totaled roughly 191,697,647, or 57.8%. White Hispanic and Latino Americans totaled about 12,579,626, or 3.8% of the population. European Americans are the largest panethnic group of white Americans and have constituted the majority population of the United States since the nation's founding.
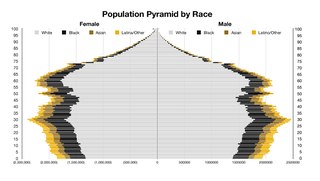
The United States of America has a racially and ethnically diverse population. At the federal level, race and ethnicity have been categorized separately. The most recent United States Census officially recognized five racial categories as well as people of two or more races. The Census Bureau also classified respondents as "Hispanic or Latino" or "Not Hispanic or Latino", identifying Hispanic and Latino as an ethnicity, which comprises the largest minority group in the nation. The Census also asked an "Ancestry Question," which covers the broader notion of ethnicity, in the 2000 Census long form and the 2010 American Community Survey; the question worded differently on “origins” will return in the 2020 Census.
A sexual minority is a group whose sexual identity, orientation or practices differ from the majority of the surrounding society. Primarily used to refer to lesbian, gay, bisexual, or non-heterosexual individuals, it can also refer to transgender, non-binary or intersex individuals.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Montenegro may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in Montenegro, but households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.

Liberal democracy, also referred to as Western democracy, is the combination of a liberal political ideology that operates under an indirect democratic form of government. It is characterised by elections between multiple distinct political parties, a separation of powers into different branches of government, the rule of law in everyday life as part of an open society, a market economy with private property, and the equal protection of human rights, civil rights, civil liberties and political freedoms for all people. To define the system in practice, liberal democracies often draw upon a constitution, either codified or uncodified, to delineate the powers of government and enshrine the social contract. After a period of expansion in the second half of the 20th century, liberal democracy became a prevalent political system in the world.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Honduras may face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in Honduras.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in the British Virgin Islands face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in the British Virgin Islands since 2001.

Non-citizens or Aliens in Latvian law are individuals who are not citizens of Latvia or any other country, but who, in accordance with the Latvian law "Regarding the status of citizens of the former USSR who possess neither Latvian nor other citizenship", have the right to a non-citizen passport issued by the Latvian government as well as other specific rights. Approximately two thirds of them are ethnic Russians, followed by Belarusians, Ukrainians, Poles, and Lithuanians.
Employment equity, as defined in federal Canadian law by the Employment Equity Act, requires federal jurisdiction employers to engage in proactive employment practices to increase the representation of four designated groups: women, people with disabilities, Aboriginal peoples, and visible minorities. The act states that "employment equity means more than treating persons the same way but also requires special measures and the accommodation of differences".

The structure of social class in Cambodia has altered several times throughout its history. The traditional hereditary elites were marginalised in the 1970s, when military leaders gained prominence, before the Khmer Rouge attempted to dramatically eliminate existing class structures in the late 1970s. Since the emergence of peace in the early 1990s, social inequality has increased in Cambodia.
Tamil sexual minorities are Tamil people who do not conform to heterosexual gender norms, although the term can be expanded to refer to women as well. They may identify as LGBTQIA. It has been estimated that India has a population of 2.5 million homosexuals, though not all of them are Tamil, and not all Tamils live in India.