
Derived from the Greek word for '5', and "domino", a pentomino is a polyomino of order 5, that is, a polygon in the plane made of 5 equal-sized squares connected edge-to-edge. When rotations and reflections are not considered to be distinct shapes, there are 12 different free pentominoes. When reflections are considered distinct, there are 18 one-sided pentominoes. When rotations are also considered distinct, there are 63 fixed pentominoes.

The Rubik's Cube is a 3-D combination puzzle originally invented in 1974 by Hungarian sculptor and professor of architecture Ernő Rubik. Originally called the Magic Cube, the puzzle was licensed by Rubik to be sold by Pentangle Puzzles in the UK in 1978, and then by Ideal Toy Corp in 1980 via businessman Tibor Laczi and Seven Towns founder Tom Kremer. The cube was released internationally in 1980 and became one of the most recognized icons in popular culture. It won the 1980 German Game of the Year special award for Best Puzzle. As of March 2021, over 450 million cubes had been sold worldwide, making it the world's bestselling puzzle game and bestselling toy. The Rubik's Cube was inducted into the US National Toy Hall of Fame in 2014.

In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is a polyhedron with eight triangular, six square, and twelve rectangular faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle, one square, and two rectangles meeting at each one. If all the rectangles are themselves square, it is an Archimedean solid. The polyhedron has octahedral symmetry, like the cube and octahedron. Its dual is called the deltoidal icositetrahedron or trapezoidal icositetrahedron, although its faces are not really true trapezoids.

A mechanical puzzle is a puzzle presented as a set of mechanically interlinked pieces in which the solution is to manipulate the whole object or parts of it. While puzzles of this type have been in use by humanity as early as the 3rd century BC, one of the most well-known mechanical puzzles of modern day is the Rubik's Cube, invented by the Hungarian architect Ernő Rubik in 1974. The puzzles are typically designed for a single player, where the goal is for the player to see through the principle of the object, rather than accidentally coming up with the right solution through trial and error. With this in mind, they are often used as an intelligence test or in problem solving training.

Packing problems are a class of optimization problems in mathematics that involve attempting to pack objects together into containers. The goal is to either pack a single container as densely as possible or pack all objects using as few containers as possible. Many of these problems can be related to real-life packaging, storage and transportation issues. Each packing problem has a dual covering problem, which asks how many of the same objects are required to completely cover every region of the container, where objects are allowed to overlap.

Nonograms, also known as Hanjie, Paint by Numbers, Picross, Griddlers, and Pic-a-Pix, and by various other names, are picture logic puzzles in which cells in a grid must be colored or left blank according to numbers at the side of the grid to reveal a hidden pixel art-like picture. In this puzzle type, the numbers are a form of discrete tomography that measures how many unbroken lines of filled-in squares there are in any given row or column. For example, a clue of "4 8 3" would mean there are sets of four, eight, and three filled squares, in that order, with at least one blank square between successive sets.
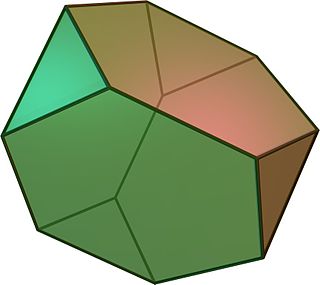
In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 equilateral triangle faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges. It can be constructed by truncating all 4 vertices of a regular tetrahedron at one third of the original edge length.

Rubik's Magic, like the Rubik's Cube, is a mechanical puzzle invented by Ernő Rubik and first manufactured by Matchbox in the mid-1980s.

The 15 Puzzle is a sliding puzzle which has 15 square tiles numbered 1 to 15 in a frame that is 4 tile positions high and 4 positions wide, with one unoccupied position. Tiles in the same row or column of the open position can be moved by sliding them horizontally or vertically, respectively. The goal of the puzzle is to place the tiles in numerical order.

In mathematics, Sperner's lemma is a combinatorial result on colorings of triangulations, analogous to the Brouwer fixed point theorem, which is equivalent to it. It states that every Sperner coloring of a triangulation of an -dimensional simplex contains a cell whose vertices all have different colors.

Kakuro or Kakkuro or Kakoro is a kind of logic puzzle that is often referred to as a mathematical transliteration of the crossword. Kakuro puzzles are regular features in many math-and-logic puzzle publications across the world. In 1966, Canadian Jacob E. Funk, an employee of Dell Magazines, came up with the original English name Cross Sums and other names such as Cross Addition have also been used, but the Japanese name Kakuro, abbreviation of Japanese kasan kurosu, seems to have gained general acceptance and the puzzles appear to be titled this way now in most publications. The popularity of Kakuro in Japan is immense, second only to Sudoku among Nikoli's famed logic-puzzle offerings.

Sudoku is a logic-based, combinatorial number-placement puzzle. In classic Sudoku, the objective is to fill a 9 × 9 grid with digits so that each column, each row, and each of the nine 3 × 3 subgrids that compose the grid contains all of the digits from 1 to 9. The puzzle setter provides a partially completed grid, which for a well-posed puzzle has a single solution.

The Square-1 is a variant of the Rubik's Cube. Its distinguishing feature among the numerous Rubik's Cube variants is that it can change shape as it is twisted, due to the way it is cut, thus adding an extra level of challenge and difficulty. The Super Square One and Square Two puzzles have also been introduced. The Super Square One has two additional layers that can be scrambled and solved independently of the rest of the puzzle, and the Square Two has extra cuts made to the top and bottom layer, making the edge and corner wedges the same size.

The Megaminx or Mégaminx is a dodecahedron-shaped puzzle similar to the Rubik's Cube. It has a total of 50 movable pieces to rearrange, compared to the 20 movable pieces of the Rubik's Cube.

A sliding puzzle, sliding block puzzle, or sliding tile puzzle is a combination puzzle that challenges a player to slide pieces along certain routes to establish a certain end-configuration. The pieces to be moved may consist of simple shapes, or they may be imprinted with colours, patterns, sections of a larger picture, numbers, or letters.

A combination puzzle, also known as a sequential move puzzle, is a puzzle which consists of a set of pieces which can be manipulated into different combinations by a group of operations. Many such puzzles are mechanical puzzles of polyhedral shape, consisting of multiple layers of pieces along each axis which can rotate independently of each other. Collectively known as twisty puzzles, the archetype of this kind of puzzle is the Rubik's Cube. Each rotating side is usually marked with different colours, intended to be scrambled, then 'solved' by a sequence of moves that sort the facets by colour. As a generalisation, combination puzzles also include mathematically defined examples that have not been, or are impossible to, physically construct.

The Void Cube is a 3-D mechanical puzzle similar to a Rubik's Cube, with the notable difference being that the center pieces are missing, which causes the puzzle to resemble a level 1 Menger sponge. The core used on the Rubik's Cube is also absent, creating holes straight through the cube on all three axes. Due to the restricted volume of the puzzle it employs an entirely different structural mechanism from a regular Rubik's Cube, though the possible moves are the same. The Void Cube was invented by Katsuhiko Okamoto. Gentosha Education, in Japan, holds the license to manufacture official Void Cubes. These official designs are also sold under the Rubik's brand, owned by Spin Master Ltd., and workalikes are available from a variety of manufacturers. Speed-solving the Void Cube is common in exhibition but is not an official World Cube Association competition event.

The Nine-Colour Cube is a cubic twisty puzzle. It was invented in 2005 by Milan Vodicka and mass-produced by Meffert's seven years later. Mechanically, the puzzle is identical to the Rubik's Cube; however, unlike the Rubik's Cube, which only has 6 different colours, the Nine-Colour Cube has 9 colours, with the individual pieces having one colour each.

The Gear Cube is a 3-D combination puzzle designed and created by Dutch puzzle maker Oskar van Deventer based on an idea by Bram Cohen. It was initially produced by Shapeways in 2009 and known as "Caution Cube" due to the likelihood of getting one's fingers stuck between the gears while speedcubing. Later, in 2010, it was mass-produced by Meffert's as the "Gear Cube".

Hoffman's packing puzzle is an assembly puzzle named after Dean G. Hoffman, who described it in 1978. The puzzle consists of 27 identical rectangular cuboids, each of whose edges have three different lengths. Its goal is to assemble them all to fit within a cube whose edge length is the sum of the three lengths.






















