The Missouri Escarpment is a ridge in North Dakota approximately 100 miles to the west of the Red River Valley, at the edge of the Missouri Plateau. It divides the Central Lowlands province from the Great Plains province.

South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than 2,850 kilometres from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian (eastern) coast. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although much of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography. The total land area is 1,220,813 km2 (471,359 sq mi). It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,535,538 km2 (592,875 sq mi).

Côte-d'Or is a département in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region of Northeastern France. In 2019, it had a population of 534,124. Its prefecture is Dijon and subprefectures are Beaune and Montbard.
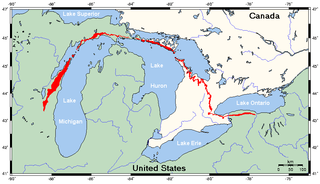
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in Canada and the United States that starts from the south shore of Lake Ontario westward, circumscribes the top of the Great Lakes Basin running from New York through Ontario, Michigan, and Wisconsin. The escarpment is the cliff over which the Niagara River plunges at Niagara Falls, for which it is named.

The Pennyroyal Plateau or Pennyroyal Region, often spelled Pennyrile, is a large physiographic region of Kentucky that features rolling hills, caves, and karst topography in general. It is named for Hedeoma pulegioides, a wild mint that grows in the area. It is also called the "Mississippian Plateau," for the Mississippian geologic age in which it was formed.
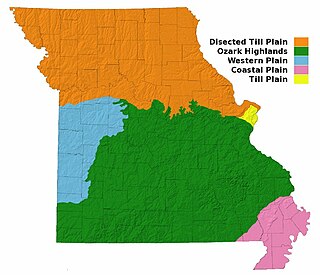
Missouri, a state near the geographical center of the United States, has three distinct physiographic divisions:

An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.

The Drakensberg is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – 2,000 to 3,482 metres within the border region of South Africa and Lesotho.

The Texas panhandle is a region of the U.S. state of Texas consisting of the northernmost 26 counties in the state. The panhandle is a square-shaped area bordered by New Mexico to the west and Oklahoma to the north and east. It is adjacent to the Oklahoma Panhandle, land which Texas previously claimed. The 1820 Missouri Compromise declared no slavery would be allowed in states admitted from the Louisiana Purchase above 36°30′ north latitude. Texas was annexed in 1845 from still more westerly land. The Compromise of 1850 removed territory north of this line from Texas, and set the border between the Texas Panhandle and the New Mexico Territory at the 103rd meridian west. The eastern border at the 100th meridian west was inherited from the Adams–Onís Treaty of 1819, which defined the border between the United States and New Spain. The Handbook of Texas defines the southern border of Swisher County as the southern boundary of the Texas Panhandle region.

The Great Lakes region of Northern America is a binational Canadian–American region centered around the Great Lakes that includes the U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin and the Canadian province of Ontario. Canada's Quebec province is at times included as part of the region because the St. Lawrence River watershed is part of the continuous hydrologic system. The region forms a distinctive historical, economic, and cultural identity. A portion of the region also encompasses the Great Lakes megalopolis.

The Allegheny Front is the major southeast- or east-facing escarpment in the Allegheny Mountains in southern Pennsylvania, western Maryland, eastern West Virginia, and western Virginia. The Allegheny Front forms the boundary between the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians to its east and the Appalachian Plateau to its west. The Front is closely associated with the Appalachian Mountains' Eastern Continental Divide, which in this area divides the waters of the Ohio/Mississippi river system, flowing to the Gulf of Mexico, from rivers flowing into Chesapeake Bay and from there into the Atlantic Ocean.

The Gulf Coastal Plain extends around the Gulf of Mexico in the Southern United States and eastern Mexico.

Tataouine Governorate is the southernmost of the twenty-four governorates of Tunisia, the only one to border both Algeria and Libya. It is also the largest, covering an area of 38,889 km2. It had a population of 149,453, nearly tied for second least-populated with Kebili (156,961) after Tozeur (107,912). The capital is Tataouine.

The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateau downward in the direction of the oceans that surround southern Africa on three sides. While it lies predominantly within the borders of South Africa, in the east the escarpment extends northward to form the border between Mozambique and Zimbabwe, continuing on beyond the Zambezi river valley to form the Muchinga Escarpment in eastern Zambia. In the west, it extends northward into Namibia and Angola. It is the combination of this escarpment and the aridity of Southern Africa that leads to the lack of navigable rivers in South Africa.

The Greenbelt is a protected area of green space, farmland, forests, wetlands, and watersheds, located in Southern Ontario, Canada. It surrounds a significant portion of the Golden Horseshoe.

Walden Ridge is a mountain ridge and escarpment located in Tennessee in the United States. It marks the eastern edge of the Cumberland Plateau and is generally considered part of it. Walden Ridge is about 74 miles (119 km) long, running generally north-south. Its highest point is at Hinch Mountain, which reaches 3,048 feet (929 m) above sea level. Sometimes Walden Ridge is called the Cumberland Escarpment.
Manitou, akin to the Haudenosaunee orenda, is the spiritual and fundamental life force in the theologies of Algonquian peoples. It is omnipresent and manifests everywhere: organisms, the environment, events, etc. Aashaa monetoo means "good spirit", while otshee monetoo means "bad spirit". When the world was created, the Great Spirit, Aasha Monetoo, gave the land to the indigenous peoples, the Shawnee in particular.

U.S. Highway 20 (US-20) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that runs for 3,365 miles (5,415 km) from Newport, Oregon, to Boston, Massachusetts. Within the state of Nebraska, it is a state highway that begins on the Wyoming–Nebraska state line west of Harrison near the Niobrara River and runs to the Nebraska–Iowa state line in South Sioux City. Throughout its 431.60-mile (694.59 km) length, the route passes through a diverse range of landscapes, including bluffs and escarpments in the Nebraska Panhandle, the Sandhills in the northern part of the state, and rolling hills and plains as the highway approaches the Missouri River valley south of Sioux City, Iowa. Throughout its length, US-20 is a two-lane highway with the exception of the easternmost 8.45 miles (13.60 km), which is a four-lane divided highway, the last 3.21 miles (5.17 km) of which is concurrent with Interstate 129 (I-129). The 197 miles (317 km) between the Wyoming border and Valentine is designated as the Bridges to Buttes Byway, one of nine scenic byways in the state of Nebraska.
The Zambezi is the fourth largest river in Africa, and the largest to flow into the Indian Ocean.

Muchinga Province is one of the ten provinces of Zambia. It is located in the northeast of the country and borders with Tanzania in the north, Malawi in the east, Eastern Province in the south, Central Province in the southwest, Luapula Province in the west, and Northern Province in the northwest. The administrative center of the province is Chinsali.
The Urema Valley, also known as the Urema Graben, is a lowland valley in Sofala Province of central Mozambique.