
Duke of Marlborough is a title in the Peerage of England. It was created by Queen Anne in 1702 for John Churchill, 1st Earl of Marlborough (1650–1722), the noted military leader. In historical texts, unqualified use of the title typically refers to the 1st Duke. The name of the dukedom refers to Marlborough in Wiltshire.

Terence Hanbury "Tim" White was an English writer. He is best known for his Arthurian novels, which were published together in 1958 as The Once and Future King. One of his best known is the first of the series, The Sword in the Stone, which was published as a stand-alone book in 1938.

Gulliver's Travels, or Travels into Several Remote Nations of the World. In Four Parts. By Lemuel Gulliver, First a Surgeon, and then a Captain of Several Ships is a 1726 prose satire by the Anglo-Irish writer and clergyman Jonathan Swift, satirising both human nature and the "travellers' tales" literary subgenre. It is Swift's best-known full-length work and a classic of English literature. Swift claimed that he wrote Gulliver's Travels "to vex the world rather than divert it".

General John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, 1st Prince of Mindelheim, 1st Count of Nellenburg, Prince of the Holy Roman Empire, was an English soldier and statesman. From a gentry family, he served as a page at the court of the House of Stuart under James, Duke of York, through the 1670s and early 1680s, earning military and political advancement through his courage and diplomatic skill. He is known for never having lost a battle.

Blenheim Palace is a country house in Woodstock, Oxfordshire, England. It is the seat of the Dukes of Marlborough. Originally called Blenheim Castle, it has been known as Blenheim Palace since the 19th century. One of England's largest houses, it was built between 1705 and 1722, and designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987.

Sarah Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough, Princess of Mindelheim, Countess of Nellenburg, was an English courtier who rose to be one of the most influential women of her time through her close relationship with Anne, Queen of Great Britain. The Duchess of Marlborough's relationship and influence with Anne were widely known, and leading public figures often turned their attentions to her, hoping for favour from Anne.
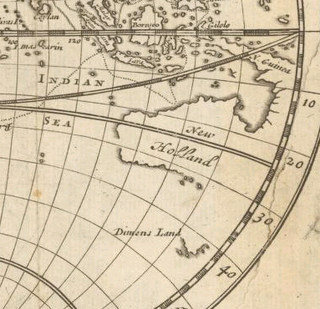
Lilliput and Blefuscu are two fictional island nations that appear in the first part of the 1726 novel Gulliver's Travels by Jonathan Swift. The two islands are neighbours in the South Indian Ocean, separated by a channel 800 yards (730 m) wide. Both are inhabited by tiny people who are about one-twelfth the height of ordinary human beings. Both are empires, i.e. realms ruled by an emperor. The capital of Lilliput is Mildendo. In some pictures, the islands are arranged like an egg, as a reference to their egg-dominated histories and cultures.

Consuelo Vanderbilt-Balsan was an American socialite and member of the Vanderbilt family. Her first marriage to the 9th Duke of Marlborough has become a well-known example of the advantageous, but loveless marriages common during the Gilded Age. The Duke obtained a large dowry through the marriage and reportedly told her just after the wedding that he married her in order to "save Blenheim Palace", his ancestral home.

Lieutenant-Colonel Charles Richard John Spencer-Churchill, 9th Duke of Marlborough,, styled Earl of Sunderland until 1883 and Marquess of Blandford between 1883 and 1892, was a British soldier and Conservative politician, and a close friend of his first cousin Winston Churchill. He was often known as "Sunny" Marlborough after his courtesy title of Earl of Sunderland.

Lemuel Gulliver is the fictional protagonist and narrator of Gulliver's Travels, a novel written by Jonathan Swift, first published in 1726.

Woodstock is a market town and civil parish, 8 miles (13 km) north-west of Oxford in West Oxfordshire in the county of Oxfordshire, England. The 2011 Census recorded a parish population of 3,100.
Malplaquet is the name of two places in Belgium and a place in France:

Abigail Masham, Baroness Masham, was an English courtier. She was a favourite of Queen Anne, and a cousin of Sarah, Duchess of Marlborough.
Dagmar Rosita Astrid Libertas, Duchess of Marlborough, is a British artist of Swedish and German descent. She was the third wife of John Spencer-Churchill, 11th Duke of Marlborough, from 1972 until their divorce in 2008.

Gulliver's Travels is an American-British TV miniseries based on Jonathan Swift's 1726 satirical novel of the same name, produced by Jim Henson Productions and Hallmark Entertainment. This miniseries is notable for being one of the very few adaptations of Swift's novel to feature all four voyages. The miniseries aired in the United Kingdom on Channel 4, and in the United States on NBC in February 1996. The miniseries stars Ted Danson, Mary Steenburgen, Tom Sturridge, James Fox, Omar Sharif, Peter O'Toole, Alfre Woodard, Kristin Scott Thomas, and John Gielgud.

St Martin's Church in Bladon near Woodstock, Oxfordshire, England, is the Church of England parish church of Bladon-with-Woodstock. It is also the mother church of St Mary Magdalene at Woodstock, which was originally a chapel of ease. It is best known for the graves of the Spencer-Churchill family, including Sir Winston Churchill, in its churchyard.

Elizabeth Seymour, Duchess of Somerset and suo jureBaroness Percy was an English courtier.

Frances Anne Spencer-Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough, VA was an English noblewoman, the wife of British peer and statesman John Spencer-Churchill, 7th Duke of Marlborough. One of her sons, Lord Randolph Churchill, was the father of Prime Minister Sir Winston Churchill. She had a total of 11 children, and her principal home was the monumental Blenheim Palace, which she rejuvenated with her "lavish and exciting entertainments", and transformed into a "social and political focus for the life of the nation". She was invested as a Lady of the Royal Order of Victoria and Albert for her efforts at famine relief in Ireland.

Gladys Marie Spencer-Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough was a French American aristocrat and socialite. She was the mistress and later the second wife of Charles Spencer-Churchill, 9th Duke of Marlborough.
Amaryllis Virginia Garnett was an English actress and diarist.

















