
Macau is a Special Administrative Region on the southern coast of China. It is located at the south of Guangdong Province, on the tip of the peninsula formed by the Zhujiang estuary on the east and the Xijiang on the west. Macau is situated 60 km (37 mi) west of Hong Kong, and 145 km (90 mi) southwest of Guangzhou, the capital of Guangdong Province. It is situated immediately east and south of Zhuhai.

Pemba Island is a Tanzanian island forming part of the Zanzibar Archipelago, lying within the Swahili Coast in the Indian Ocean.

Mafia Island or Chole Shamba is an island of The Mafia Archipelago located in Mafia District in the southern Pwani Region of Tanzania across the Mafia Channel. The island is the third largest in Tanzanian ocean territory, but is not administratively included within the semi-autonomous region of Zanzibar, which has been politically separate since 1890. Mafia Island forms the largest part of Mafia District, one of the six administrative districts in the Pwani Region. As the Mafia Archipelago's main island, it's sometimes called Chole Shamba, meaning Chole farmlands in Swahili. This is in opposition to the historic settlement of Chole Mjini on Chole Island inside Mafia Bay. The island's population is over 65,000. The economy is based on fishing, subsistence agriculture and the market in Kilindoni. The island attracts some tourists, mainly scuba divers, birdwatchers, game fishermen, and people seeking relaxation.
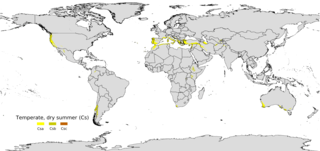
A Mediterranean climate, also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen as Cs, is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes. Such climates typically have dry summers and wet winters, with summer conditions ranging from warm to hot and winter conditions typically being mild to cool. These weather conditions are typically experienced in the majority of Mediterranean-climate regions and countries, but remain highly dependent on proximity to the ocean, altitude and geographical location.

Ibiza is a city and municipality located on the southeast coast of the island of Ibiza in the Balearic Islands autonomous community.

Singapore is a city-state and island country in maritime Southeast Asia, located at the end of the Malayan Peninsula between Malaysia and Indonesia as well as the Straits of Malacca and the South China Sea. It is heavily compact and urbanised. As of 2023, Singapore has a total land area of approximately 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi). Singapore is separated from Indonesia by the Singapore Strait and from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor.

Pemba is a port city and district in Mozambique. It is the capital and largest city of the Cabo Delgado province and lies on a peninsula in Pemba Bay, the third largest in Africa. It is located northeast of Maputo, Mozambique's capital.
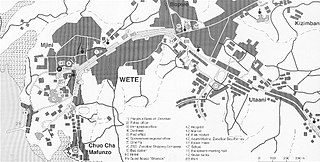
Wete is a town located on the Tanzanian island of Pemba. It is the capital of Pemba North Region, as well as the administrative seat for Wete District. It lies on the west side of the north part of the island. The town has a population of 35,951.

Kilindoni is the capital of Mafia District in Pwani Region, Tanzania. It is the largest settlement on Mafia Island.

Naraingarh is a town, municipal committee and assembly constituency in the Ambala district of the Indian state of Haryana, located on the border with the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. Due to its geographical location, the Naraingarh plays an important role in local tourism, being located 39 km from Ambala, the district headquarter, 52 km of Chandigarh, the state capital, 144 km of Shimla, and 230 km of New Delhi.

Zanzibar City or Mjini District, often simply referred to as Zanzibar is one of two administrative districts of Mjini Magharibi Region in Tanzania. The district covers an area of 15.4 km2 (5.9 sq mi). The district is comparable in size to the land area of Nauru. The district has a water border to the west by the Indian Ocean. The district is bordered to the east by Magharibi District. The district seat is in Stonetown. The city is the largest on the island of Zanzibar. It is located on the west coast of Unguja, the main island of the Zanzibar Archipelago, north of the much larger city of Dar es Salaam across the Zanzibar Channel. The city also serves as the capital of the Zanzibar Urban/West Region. In 2022 its population was 219,007.
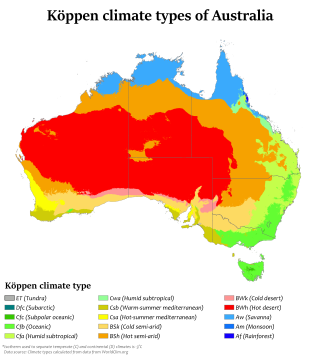
Australia's climate is governed mostly by its size and by the hot, sinking air of the subtropical high pressure belt. This moves north-west and north-east with the seasons. The climate is variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons, thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Australia has a wide variety of climates due to its large geographical size. The largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid. Only the south-east and south-west corners have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate, varying between grasslands and desert. Australia holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, and the highest sunshine duration.

Chake-Chake is a town located on the Tanzanian island of Pemba and capital of Chake Chake District. It is in the centre of a deep indentation in the west coast called Chake-Chake Bay. Chake-Chake is historically the capital of Pemba Island, and the seat of Pemba's court. Pemba's only airport is 7 km south-east of Chake-Chake. The Mkama Ndume ruins are close to the airport in Pujini village.
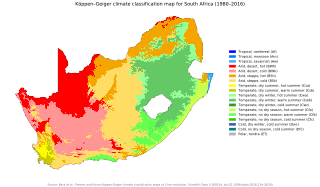
The climate of South Africa is determined by South Africa's situation between 22°S and 35°S, in the Southern Hemisphere's subtropical zone, and its location between two oceans, Atlantic and the Indian.

Tasmania has a cool temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The highest recorded maximum temperature in Tasmania is 42.2 °C (108.0 °F) at Scamander on 30 January 2009, during the 2009 southeastern Australia heat wave. Tasmania's lowest recorded minimum temperature is −14.2 °C (6.4 °F) on 7 August 2020, at Central Plateau.
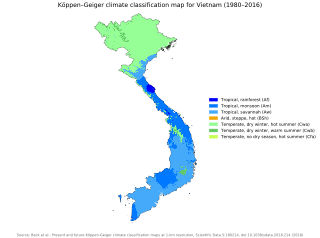
Vietnam has a monsoon-influenced climate typical of that of mainland Southeast Asia. The diverse topography, long latitude, and influences from the South China Sea lead to climatic conditions varying significantly between regions. The northern region experiences a monsoonal and temperate climate (Cfa) with four distinct seasons with winters typically dry and summers ranging from hot to mild. In southern and central areas, the climate is tropical monsoon (Aw) with only two seasons. In addition, a temperate climate exists in mountainous areas, which are found in Sa Pa and Da Lat, while a more continental climate exists in Lai Châu Province and Sơn La Province.

The Climate of Venezuela is characterized for being tropical and megathermal as a result of its geographical location near the Equator, but because of the topography and the dominant wind direction, several climatic types occur which can be the same as found in temperate latitudes, and even polar regions. Latitude exerts little influence on the Venezuelan climate. While the coastal cities of Maracaibo, Barcelona, Porlamar and Maiquetia can get extremely hot, cities in valleys such as Mérida, Caracas, Los Teques and San Cristobal have cooler climates, and the highest towns of Mucuchies and Apartaderos have cold (tundra) climates.
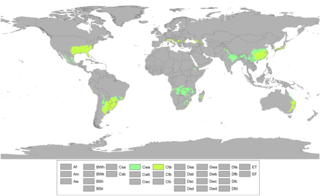
A humid subtropical climate is a temperate climate type characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents, generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates, and equatorward from either humid continental or oceanic climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications.

The climate of Wales refers to the weather conditions prevailing in Wales in general or over a long period.

Cyprus has a subtropical climate - Mediterranean and semi-arid type - Csa and BShaccording to Köppen climate classification, with very mild winters on sea level and warm to hot summers. Snow is possible only in the Troodos mountains in the central part of the island. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry.






















