Related Research Articles

An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback from the cavity is suppressed. Optical amplifiers are important in optical communication and laser physics. They are used as optical repeaters in the long distance fiber-optic cables which carry much of the world's telecommunication links.
Noise figure (NF) and noise factor (F) are figures of merit that indicate degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that is caused by components in a signal chain. These figures of merit are used to evaluate the performance of an amplifier or a radio receiver, with lower values indicating better performance.

In fiber optics, polarization-maintaining optical fiber is a single-mode optical fiber in which linearly polarized light, if properly launched into the fiber, maintains a linear polarization during propagation, exiting the fiber in a specific linear polarization state; there is little or no cross-coupling of optical power between the two polarization modes. Such fiber is used in special applications where preserving polarization is essential.
Mode locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s). A laser operated in this way is sometimes referred to as a femtosecond laser, for example, in modern refractive surgery. The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. Constructive interference between these modes can cause the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. The laser is then said to be "phase-locked" or "mode-locked".
Polarization mode dispersion (PMD) is a form of modal dispersion where two different polarizations of light in a waveguide, which normally travel at the same speed, travel at different speeds due to random imperfections and asymmetries, causing random spreading of optical pulses. Unless it is compensated, which is difficult, this ultimately limits the rate at which data can be transmitted over a fiber.
Power-system automation is the act of automatically controlling the power system via instrumentation and control devices. Substation automation refers to using data from Intelligent electronic devices (IED), control and automation capabilities within the substation, and control commands from remote users to control power-system devices.
Dispersion-shifted fiber (DSF) is a type of optical fiber made to optimize both low dispersion and low attenuation.

An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are immune to electromagnetic interference. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, such as fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers.

Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared or visible light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. Fiber is preferred over electrical cabling when high bandwidth, long distance, or immunity to electromagnetic interference is required. This type of communication can transmit voice, video, and telemetry through local area networks or across long distances.

In optics, a supercontinuum is formed when a collection of nonlinear processes act together upon a pump beam in order to cause severe spectral broadening of the original pump beam, for example using a microstructured optical fiber. The result is a smooth spectral continuum. There is no consensus on how much broadening constitutes a supercontinuum; however researchers have published work claiming as little as 60 nm of broadening as a supercontinuum. There is also no agreement on the spectral flatness required to define the bandwidth of the source, with authors using anything from 5 dB to 40 dB or more. In addition the term supercontinuum itself did not gain widespread acceptance until this century, with many authors using alternative phrases to describe their continua during the 1970s, 1980s and 1990s.
A distributed-feedback laser (DFB) is a type of laser diode, quantum-cascade laser or optical-fiber laser where the active region of the device contains a periodically structured element or diffraction grating. The structure builds a one-dimensional interference grating, and the grating provides optical feedback for the laser. This longitudinal diffraction grating has periodic changes in refractive index that cause reflection back into the cavity. The periodic change can be either in the real part of the refractive index or in the imaginary part. The strongest grating operates in the first order, where the periodicity is one-half wave, and the light is reflected backwards. DFB lasers tend to be much more stable than Fabry–Perot or DBR lasers and are used frequently when clean single-mode operation is needed, especially in high-speed fiber-optic telecommunications. Semiconductor DFB lasers in the lowest loss window of optical fibers at about 1.55 μm wavelength, amplified by erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs), dominate the long-distance communication market, while DFB lasers in the lowest dispersion window at 1.3 μm are used at shorter distances.

A laser beam profiler captures, displays, and records the spatial intensity profile of a laser beam at a particular plane transverse to the beam propagation path. Since there are many types of lasers—ultraviolet, visible, infrared, continuous wave, pulsed, high-power, low-power—there is an assortment of instrumentation for measuring laser beam profiles. No single laser beam profiler can handle every power level, pulse duration, repetition rate, wavelength, and beam size.
Noise-immune cavity-enhanced optical-heterodyne molecular spectroscopy (NICE-OHMS) is an ultra-sensitive laser-based absorption technique that utilizes laser light to assess the concentration or the amount of a species in gas phase by absorption spectrometry (AS).
Moving target indication (MTI) is a mode of operation of a radar to discriminate a target against the clutter. It describes a variety of techniques used for finding moving objects, like an aircraft, and filter out unmoving ones, like hills or trees. It contrasts with the modern stationary target indication (STI) technique, which uses details of the signal to directly determine the mechanical properties of the reflecting objects and thereby find targets whether they are moving or not.

A CD-ROM is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold both computer data and audio with the latter capable of being played on a CD player, while data is only usable on a computer.
A superluminescent diode is an edge-emitting semiconductor light source based on superluminescence. It combines the high power and brightness of laser diodes with the low coherence of conventional light-emitting diodes. Its emission optical bandwidth, also described as full-width at half maximum, can range from 5 up to 750 nm.
Time stretch dispersive Fourier transform (TS-DFT), otherwise known as time-stretch transform (TST), temporal Fourier transform or photonic time-stretch (PTS) is a spectroscopy technique that uses optical dispersion instead of a grating or prism to separate the light wavelengths and analyze the optical spectrum in real-time. It employs group-velocity dispersion (GVD) to transform the spectrum of a broadband optical pulse into a time stretched temporal waveform. It is used to perform Fourier transformation on an optical signal on a single shot basis and at high frame rates for real-time analysis of fast dynamic processes. It replaces a diffraction grating and detector array with a dispersive fiber and single-pixel detector, enabling ultrafast real-time spectroscopy and imaging. Its nonuniform variant, warped-stretch transform, realized with nonlinear group delay, offers variable-rate spectral domain sampling, as well as the ability to engineer the time-bandwidth product of the signal's envelope to match that of the data acquisition systems acting as an information gearbox.
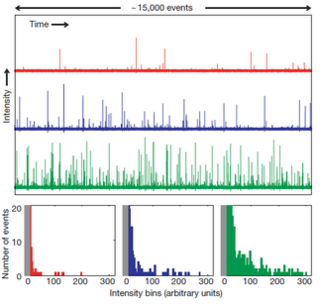
Optical rogue waves are rare pulses of light analogous to rogue or freak ocean waves. The term optical rogue waves was coined to describe rare pulses of broadband light arising during the process of supercontinuum generation—a noise-sensitive nonlinear process in which extremely broadband radiation is generated from a narrowband input waveform—in nonlinear optical fiber. In this context, optical rogue waves are characterized by an anomalous surplus in energy at particular wavelengths or an unexpected peak power. These anomalous events have been shown to follow heavy-tailed statistics, also known as L-shaped statistics, fat-tailed statistics, or extreme-value statistics. These probability distributions are characterized by long tails: large outliers occur rarely, yet much more frequently than expected from Gaussian statistics and intuition. Such distributions also describe the probabilities of freak ocean waves and various phenomena in both the man-made and natural worlds. Despite their infrequency, rare events wield significant influence in many systems. Aside from the statistical similarities, light waves traveling in optical fibers are known to obey the similar mathematics as water waves traveling in the open ocean, supporting the analogy between oceanic rogue waves and their optical counterparts. More generally, research has exposed a number of different analogies between extreme events in optics and hydrodynamic systems. A key practical difference is that most optical experiments can be done with a table-top apparatus, offer a high degree of experimental control, and allow data to be acquired extremely rapidly. Consequently, optical rogue waves are attractive for experimental and theoretical research and have become a highly studied phenomenon. The particulars of the analogy between extreme waves in optics and hydrodynamics may vary depending on the context, but the existence of rare events and extreme statistics in wave-related phenomena are common ground.

The Panasonic Lumix DMC-FS3 is a digital ultracompact camera announced by Panasonic on January 29, 2008. It has eight megapixels, triple optical zoom, 16:9 wide VGA video recording at 30 frames per second, versatile scene modes, and an accelerometer sensor for orientation tagging.
An erbium-doped waveguide amplifier is a type of an optical amplifier enhanced with erbium. It is a close relative of an EDFA, erbium-doped fiber amplifier, and in fact EDWA's basic operating principles are identical to those of the EDFA. Both of them can be used to amplify infrared light at wavelengths in optical communication bands between 1500 and 1600 nm. However, whereas an EDFA is made using a free-standing fiber, an EDWA is typically produced on a planar substrate, sometimes in ways that are very similar to the methods used in electronic integrated circuit manufacturing. Therefore, the main advantage of EDWAs over EDFAs lies in their potential to be intimately integrated with other optical components on the same planar substrate and thus making EDFAs unnecessary.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.