This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy. Heat engines, like the internal combustion engine, burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to do work. Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, pneumatic motors use compressed air, and clockwork motors in wind-up toys use elastic energy. In biological systems, molecular motors, like myosins in muscles, use chemical energy to create forces and eventually motion.

A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the niche application Stirling engine. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.

A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force is transformed, by a connecting rod and flywheel, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine.

The Watt steam engine, alternatively known as the Boulton and Watt steam engine, was the first practical steam engine and was one of the driving forces of the industrial revolution. James Watt developed the design sporadically from 1763 to 1775 with support from Matthew Boulton. Watt's design saved significantly more fuel compared to earlier designs that they were licensed based on the amount of fuel they would save. Watt never ceased developing the steam engine, introducing double-acting designs and various systems for taking off rotary power. Watt's design became synonymous with steam engines, and it was many years before significantly new designs began to replace the basic Watt design.

A traction engine is a self-propelled steam engine used to move heavy loads on roads, plough ground or to provide power at a chosen location. The name derives from the Latin tractus, meaning 'drawn', since the prime function of any traction engine is to draw a load behind it. They are sometimes called road locomotives to distinguish them from railway locomotives – that is, steam engines that run on rails.

A steam car is a car (automobile) propelled by a steam engine. A steam engine is an external combustion engine (ECE) in which the fuel is combusted outside of the engine, unlike an internal combustion engine (ICE) in which fuel is combusted inside the engine. ECEs have a lower thermal efficiency, but carbon monoxide production is more readily regulated.

The Great Western Railway (GWR) 9400 Class is a class of 0-6-0 pannier tank steam locomotive, used for shunting and banking duties.

A steam tractor is a vehicle powered by a steam engine which is used for pulling.
A boiler feedwater pump is a specific type of pump used to pump feedwater into a steam boiler. The water may be freshly supplied or returning condensate produced as a result of the condensation of the steam produced by the boiler. These pumps are normally high pressure units that take suction from a condensate return system and can be of the centrifugal pump type or positive displacement type.
The Antique Gas & Steam Engine Museum (AGSEM) is a living-history museum founded in 1969 located on 55 acres (220,000 m2) of county-owned land on the outskirts of Vista, California. The museum is a non-profit 501c(3) organization. It is located at 2040 N Santa Fe Ave. in Vista. It is run by several paid employees, along with volunteer help.

Nathan Read was an American engineer and steam pioneer.

Thomas Green & Son, Ltd. were engineers who manufactured a wide range of products at the Smithfield Foundry, Leeds, United Kingdom.

TSS Maianbar was a coastal steamship of the North Coast Steam Navigation Company. She was built in Scotland in 1910 and ran aground in Newcastle, New South Wales in 1940.

Straker-Squire was a British automobile manufacturer based in Bristol, and later Edmonton in North London.

Steam is water in the gas phase, which is formed when water boils or evaporates. Steam is invisible; however, "steam" often refers to wet steam, the visible mist or aerosol of water droplets formed as this water vapour condenses. At lower pressures, such as in the upper atmosphere or at the top of high mountains, water boils at a lower temperature than the nominal 100 °C (212 °F) at standard pressure. If heated further it becomes superheated steam.
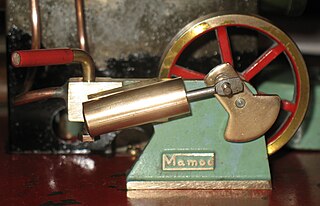
An oscillating cylinder steam engine is a simple steam-engine design that requires no valve gear. Instead the cylinder rocks, or oscillates, as the crank moves the piston, pivoting in the mounting trunnion so that ports in the cylinder line up with ports in a fixed port face alternately to direct steam into or out of the cylinder.

A model steam engine is a small steam engine built as an educational toy for children or for adult live steam enthusiasts. Between the 18th and early 20th centuries, demonstration models were also in use at universities and engineering schools, frequently designed and built by students as part of their curriculum.


















