
The Comoros, officially the Union of the Comoros, is an independent country made up of three islands in Southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city is Moroni. The religion of the majority of the population, and the official state religion, is Sunni Islam. Comoros proclaimed its independence from France on 6 July 1975. A member of the Arab League, it is the only country in the Arab world which is entirely in the Southern Hemisphere. It is a member state of the African Union, the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, and the Indian Ocean Commission. The country has three official languages: Shikomori, French and Arabic.
The history of the Comoros extends to about 800–1000 AD when the archipelago was first inhabited. The Comoros have been inhabited by various groups throughout this time. France colonised the islands in the 19th century, and they became independent in 1975.

The Union of the Comoros consists of the three islands Njazidja, Mwali (Moheli) and Nzwani (Anjouan) while the island of Mayotte remains under French administration. The Politics of the Union of the Comoros take place in a framework of a federal presidential republic, whereby the President of the Comoros is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Federal legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. The precolonial legacies of the sultanates linger while the political situation in Comoros has been extremely fluid since the country's independence in 1975, subject to the volatility of coups and political insurrection.

Mayotte, officially the Department of Mayotte, is an overseas department and region and single territorial collectivity of France. It is located in the northern part of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean off the coast of Southeastern Africa, between Northwestern Madagascar and Northeastern Mozambique. Mayotte consists of a main island, Grande-Terre, a smaller island, Petite-Terre, as well as several islets around these two. Mayotte is the most prosperous territory in the Mozambique Channel, making it a major destination for immigration.

Anjouan is an autonomous volcanic island in the Comoro Islands in the southwestern Indian Ocean, part of the Union of the Comoros. It is known in Shikomori as Ndzuani, Ndzuwani or Nzwani, and, until the early twentieth century when the name fell out of general use, in English as Johanna. Historically it was also called Hinzuan or Hanzoan.

The National Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate. The National Assembly's legislators are known as députés, meaning "delegate" or "envoy" in English; etymologically, it is a cognate of the English word deputy, which is the standard term for legislators in many parliamentary systems).

The Comoro Islands or the Comoros are an archipelago of volcanic islands situated off the southeastern coast of Africa, to the east of Mozambique and northwest of Madagascar. The islands are politically divided between the Union of the Comoros, a sovereign country, and Mayotte, an Overseas Department of France.
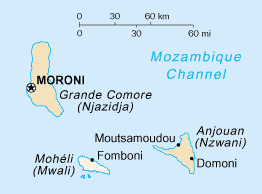
Mohéli[mɔ.e.li], also known as Mwali, is an autonomous island that forms part of the Union of the Comoros. It is the smallest of the three major islands in the country. It is located in the Indian Ocean off the coast of Africa and it is the smallest of the four major Comoro Islands. Its capital and largest city is Fomboni.

Ali Soilih M'Tsashiwa was a Comorian socialist revolutionary and political figure who served as the 3rd President of the Comoros from 3 January 1976 to 13 May 1978.

Elections in the Comoros take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. The President and the majority of the seats in the Assembly of the Union are directly elected.

The unicameral Assembly of the Union of the Comoros is the country's legislative body. It was established in 2004.
Prince Said Ibrahim Ben Sultan Said Ali El Maceli Al Ba'alawi was a Comorian politician. He served as a member of the French National Assembly from 1959 until 1970, and as Prime Minister of the Comoros from 2 April 1970 until 16 July 1972. He was the son of Sultan Said Ali Bin Sultan Said Omar, Sultan of Grande Comore.
The Comoros is an island nation in the Indian Ocean, located off the eastern coast of Africa. France first established colonial rule in the Comoros in 1841. Agreement was reached with France in 1973 for the Comoros to become independent in 1978. On July 6, 1975, but the Comorian parliament passed a unilateral resolution declaring independence. The deputies of Mayotte, which remained under French control, abstained. Referendums on all four of the islands excluding Mayotte showed strong support for independence. Ahmed Abdallah proclaimed the Comoros' independence on September 5, 1975 and became its first president.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Comoros:
Saïd Mohamed Ben Chech Abdallah Cheikh was the head of the Government of Comoros from 1962 until his death in 1970. Cheikh served in the French National Assembly from 1946 until 1962 and was also the president of the Parti Vert.

An independence referendum was held in the Comoros on 22 December 1974. The overall result was a strong "yes" vote, with 94.57% of voters voting for independence and almost all the "no" votes being cast in Mayotte, where there was a majority for remaining under French control. In contrast, on Mohéli only five out of 6,059 votes were against independence. Voter turnout was 93.3%.

A referendum on remaining in the Comoros was held in Mayotte on 8 February 1976. The proposal was rejected by 99.42% of voters.

The Constitution of the Comoros was adopted on 23 December 2001 and last amended in May 2009.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Comoros on 19 January 2020; in constituencies where no candidate received a majority, a second round was held alongside local elections on 23 February. The elections were boycotted by the main opposition parties, including the two largest parties in the outgoing Assembly, the Union for the Development of the Comoros and Juwa Party, in protest at constitutional reform and political repression, The result was a landslide victory for President Azali Assoumani's Convention for the Renewal of the Comoros, which won 20 of the 24 elected seats.








