A mole shrew is a shrew that resembles a mole. Species with that name include:

The shrew is a small mole-like mammal classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, or the West Indies shrews, which belong to different families or orders.

Moles are small mammals adapted to a subterranean lifestyle. They have cylindrical bodies; velvety fur; very small, inconspicuous ears and eyes; reduced hindlimbs; and short, powerful forelimbs with large paws adapted for digging.
- Two species in the genus Surdisorex , native to Kenya:
- Aberdare mole shrew (Surdisorex norae)
- Mt. Kenya mole shrew (Surdisorex polulus)
- Four species in the genus Anourosorex , native to Asia:
- Assam mole shrew (Anourosorex assamensis)
- Giant mole shrew (Anourosorex schmidi)
- Chinese mole shrew (Anourosorex squamipes).
- Taiwanese mole shrew (Anourosorex yamashinai)

The giant mole shrew is a species of red-toothed shrew native to the southeastern slopes of the Himalaya of Bhutan and India.

The Chinese mole shrew is one of four species of Asian mole shrew in the genus Anourosorex.

The Taiwanese mole shrew is one of four species of red-toothed shrews in the genus Anourosorex. This species is endemic to Taiwan.
Surdisorex is a genus of mammals in the family Soricidae. Surdisorex is one of three genera of African shrews, which, in turn, are one of three living subfamilies of shrews. Species in the genus Surdisorex are called African mole shrews because of their similarity to moles, to which they are not closely related.

The Aberdare mole shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae endemic to the Aberdare Mountains in Kenya. Its natural habitat is tropical high-altitude bamboo and grassland.

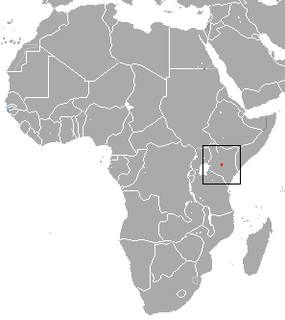
The Assam mole shrew is a species of red-toothed shrew endemic to northeast India.
| This page is an index of articles on animal species (or higher taxonomic groups) with the same common name (vernacular name). If an internal link led you here, you may wish to edit the linking article so that it links directly to the intended article. |