Related Research Articles

Momordica charantia is a tropical and subtropical vine of the family Cucurbitaceae, widely grown in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean for its edible fruit. Its many varieties differ substantially in the shape and bitterness of the fruit.

Cucurbitacins are a class of biochemical compounds that some plants – notably members of the pumpkin and gourd family, Cucurbitaceae – produce and which function as a defense against herbivores. Cucurbitacins and their derivatives have also been found in many other plant families, in some mushrooms and even in some marine mollusks.

Momordicin I, or 3,7,23-trihydroxycucurbitan-5,24-dien-19-al, is a chemical compound found in the leaves of the bitter melon vine, possibly responsible for its reputed medicinal properties.
Momordicin is one of several compounds found in the bitter melon vine, including:
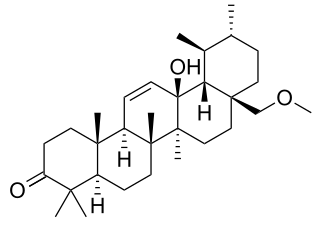
Momordicin-28 or 13-hydroxy-28-methoxy-urs-11-en-3-one is a triterpene compound with formula C
31H
50O
3 found in the fresh fruit of the bitter melon.

Momordicinin (13β,28-epoxy-urs-11-en-3-one) is chemical compound, a triterpene with formula C
30H
46O
2, found in the fresh fruit of the bitter melon.

Momordicilin or 24-[1′-hydroxy,1′-methyl-2′-pentenyloxyl]-ursan-3-one is a chemical compound, a triterpenoid with formula C
36H
60O
3, found in the fresh fruit of the bitter melon.
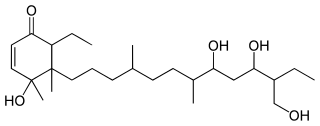
Momordol or 1-hydroxy-1,2-dimethyl-2-[8′,10′-dihydroxy-4′,7′-dimethyl-11′-hydroxy methyl-trideca]-3-ethyl-cyclohex-5-en-4-one is a chemical compound with formula C
26H
48O
5, found in the fresh fruit of the bitter melon.
Charantoside is any of several related cucurbitane triterpenoid glycosides found in the fruits bitter melon vine. They include:
Momordicoside is any of several related cucurbitane triterpenoid glycosides that can be extracted from the bitter melon vine (Momordica charantia). They include:
Goyaglycoside is any of several related triterpenoid glycosides found in the fruits bitter melon vine, called goya in Okinawan language. They include:
Karaviloside is any of several related cucurbitane triterpenoid glycosides found in bitter melon vine. They include:

Cucurbalsaminol A or cucurbita-5,23(E)-diene-3β,12β,25-triol, is a chemical compound with formula C
30H
50O
4, found in the Balsam apple vine. It is a cucurbitane-type triterpenoid, related to cucurbitacin, isolated by C. Ramalhete and others in 2009.
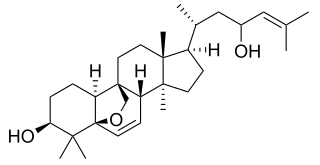
Karavilagenin E is a chemical compound found in the Balsam apple vine. It is a cucurbitane-type triterpenoid, related to cucurbitacin.

Momordica foetida is a perennial climbing vine native of tropical Africa, closely related to the bitter melon and balsam apple. Its species name ("bad-smelling") refers to its unpleasant smell. It was previously named M. morkorra and M. cordata (Cogn.)
Charantin is a chemical substance obtained from the Asian bitter melon, reputed to be responsible for the hypoglycaemic properties of those plants. It was identified by Lolitkar and Rao in 1960. It was also found in the similar African species M. foetida, by A. Olaniyi in 1975, under the name foetidin.
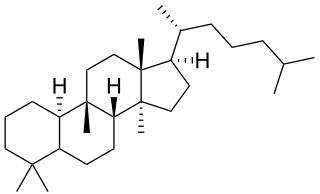
Cucurbitane is a class of tetracyclic chemical compounds with formula C
30H
54. It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon, specifically triterpene. It is also an isomer of lanostane, from which it differs by the formal shift of a methyl group from the 10 to the 9β position in the standard steroid numbering scheme.
A kuguaglycoside is one of several chemical compounds isolated from the roots of the bitter melon vine by J.-C. Chen and others.
A kuguacin is one of several chemical compounds isolated from the bitter melon vine by J.-C. Chen and others.

Neokuguaglucoside is a chemical compound with formula C
42H
66O
14, isolated from the fruit of the bitter melon vine, where it occurs at 23 mg/35 kg. It is a triterpene glucoside with the cucurbitane skeleton. It is a white powder, soluble in methanol and butanol.