Related Research Articles
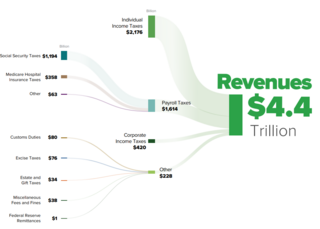
The United States has separate federal, state, and local governments with taxes imposed at each of these levels. Taxes are levied on income, payroll, property, sales, capital gains, dividends, imports, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. In 2020, taxes collected by federal, state, and local governments amounted to 25.5% of GDP, below the OECD average of 33.5% of GDP.
A capital gains tax (CGT) is the tax on profits realized on the sale of a non-inventory asset. The most common capital gains are realized from the sale of stocks, bonds, precious metals, real estate, and property.
Form 1099 is one of several IRS tax forms used in the United States to prepare and file an information return to report various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips. The term information return is used in contrast to the term tax return although the latter term is sometimes used colloquially to describe both kinds of returns.
An instalment usually refers to:
In accounting, the revenue recognitionprinciple states that revenues are earned and recognized when they are realized or realizable, no matter when cash is received.
Before 2006, a private annuity trust (PAT) was an arrangement to enable the value of highly appreciated assets, such as real estate, collectables or an investment portfolio, to be realized without directly selling them and incurring substantial taxes from their sale.
A structured sale or structured installment sale, is a special type of installment sale pursuant to the Internal Revenue Code. In an installment sale, the seller defers recognition of gain on the sale of a business or real estate to the tax year in which the related sale proceeds are received. In a structured sale, the seller is able to pay U.S. Federal income tax over time while having the seller's right to receive those payments guaranteed by a high credit quality alternate obligor. This obligor assumes the buyer's periodic payment obligation. Transactions can be arranged for amounts as small as $100,000.
A wash sale is a sale of a security at a loss and repurchase of the same or substantially identical security shortly before or after. Losses from such sales are not deductible in most cases under the Internal Revenue Code in the United States. Wash sale regulations disallow an investor who holds an unrealized loss from accelerating a tax deduction into the current tax year, unless the investor is out of the position for some significant length of time. A wash sale can take place at any time during the year, or across year boundaries.
For federal income tax purposes, the doctrine of constructive receipt is used to determine when a cash-basis taxpayer has received gross income. A taxpayer is subject to tax in the current year if he or she has unfettered control in determining when items of income will or should be paid. Unlike actual receipt, constructive receipt does not require physical possession of the item of income in question.
Under Section 1031 of the United States Internal Revenue Code, a taxpayer may defer recognition of capital gains and related federal income tax liability on the exchange of certain types of property, a process known as a 1031 exchange. In 1979, this treatment was expanded by the courts to include non-simultaneous sale and purchase of real estate, a process sometimes called a Starker exchange.
A self-directed individual retirement account is an individual retirement account (IRA) which allows alternative investments for retirement savings. Some examples of these alternative investments are real estate, private mortgages, private company stock, oil and gas limited partnerships, precious metals, digital assets, horses and livestock, and intellectual property. The increased investment options available in self-directed IRAs prompted the SEC to issue a public notice in 2011 due an increased risk of fraud in alternative assets.
A structured settlement factoring transaction means a transfer of structured settlement payment rights made for consideration by means of sale, assignment, pledge, or other form of encumbrance or alienation for consideration. In order for such transfer to be approved, the transfer must comply with Internal Revenue Code section 5891 and any applicable state structured settlement protection law.
Tenants in common 1031 Exchange is a form of real estate asset ownership in the United States in which two or more persons have an undivided, fractional interest in the asset, where ownership shares are not required to be equal, and where ownership interests can be inherited. Each co-owner receives an individual deed at closing for his or her undivided percentage interest in the entire property. In brief, a TIC owner has the same rights and benefits as a single owner of property.
In the United States, individuals and corporations pay a tax on the net total of all their capital gains. The tax rate depends on both the investor's tax bracket and the amount of time the investment was held. Short-term capital gains are taxed at the investor's ordinary income tax rate and are defined as investments held for a year or less before being sold. Long-term capital gains, on dispositions of assets held for more than one year, are taxed at a lower rate.
In United States income tax law, an installment sale is generally a "disposition of property where at least 1 loan payment is to be received after the close of the taxable year in which the disposition occurs." The term "installment sale" does not include, however, a "dealer disposition" or, generally, a sale of inventory. The installment method of accounting provides an exception to the general principles of income recognition by allowing a taxpayer to defer the inclusion of income of amounts that are to be received from the disposition of certain types of property until payment in cash or cash equivalents is received. The installment method defers the recognition of income when compared with both the cash and accrual methods of accounting. Under the cash method, the taxpayer would recognize the income when it is received, including the entire sum paid in the form of a negotiable note. The deferral advantages of the installment method are the most pronounced when comparing to the accrual method, under which a taxpayer must recognize income as soon as he or she has a right to the income.
A like-kind exchange under United States tax law, also known as a 1031 exchange, is a transaction or series of transactions that allows for the disposal of an asset and the acquisition of another replacement asset without generating a current tax liability from the sale of the first asset. A like-kind exchange can involve the exchange of one business for another business, one real estate investment property for another real estate investment property, livestock for qualifying livestock, and exchanges of other qualifying assets. Like-kind exchanges have been characterized as tax breaks or "tax loopholes".
The installment sales method is one of several approaches used to recognize revenue under the US GAAP, specifically when revenue and expense are recognized at the time of cash collection rather than at the time of sale. Under the US GAAP, it is the principal method of revenue recognition when the recognition occurs subsequently to the sale.

The United States Tax Court decided two cases, both titled Veit v. Commissioner, in 1947 and 1949. These cases deal with the doctrine of constructive receipt. In both cases, the taxpayer was an executive vice president of a corporation. He was entitled to a fixed salary plus a bonus of 10% of the corporation's profits for the years 1939 and 1940, with the bonus to be paid in 1941. However, his contract was revised in November 1940 to provide that the bonus from the 1939 profits would be paid in 1941, and the bonus from the 1940 profits would be paid in 1942.

Warren Jones Company v. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, 524 F.2d 788 was a taxation decision by the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit.
An Opportunity Zone is a designation and investment program created by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 allowing for certain investments in lower income areas to have tax advantages. The purpose of this program is to put capital to work that would otherwise be locked up due to the asset holder's unwillingness to trigger a capital gains tax.
References
- ↑ "26 CFR 15a.453-1 - Installment method reporting for sales of real property and casual sales of personal property". Law.cornell.edu. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- ↑ "GREIF INC (Form: 8-K)". Investquest.com. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- ↑ "Kimberly Clark Sale" (PDF). Files.shareholder.com. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- ↑ "Plum Creek Sale" (PDF). Investor.weyerhaeuser.com. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- ↑ "Office Depot - Max - Investor Relations -Timber Notes FAQs". Investor.officedepot.com. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- 1 2 "General Counsel Memorandum 20123401f" (PDF). Internal Revenue Service, U.S. July 18, 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- ↑ "Draft letter sample : Number: 200836019" (PDF). Internal Revenue Service, U.S. Retrieved 13 January 2018.