Related Research Articles
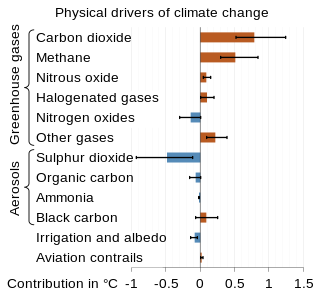
The scientific community has been investigating the causes of climate change for decades. After thousands of studies, it came to a consensus, where it is "unequivocal that human influence has warmed the atmosphere, ocean and land since pre-industrial times." This consensus is supported by around 200 scientific organizations worldwide, The dominant role in this climate change has been played by the direct emissions of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels. Indirect CO2 emissions from land use change, and the emissions of methane, nitrous oxide and other greenhouse gases play major supporting roles.

The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) set up the IPCC in 1988. The United Nations endorsed the creation of the IPCC later that year. It has a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, hosted by the WMO. It has 195 member states who govern the IPCC. The member states elect a bureau of scientists to serve through an assessment cycle. A cycle is usually six to seven years. The bureau selects experts in their fields to prepare IPCC reports. There is a formal nomination process by governments and observer organizations to find these experts. The IPCC has three working groups and a task force, which carry out its scientific work.

The University of Bremen is a public university in Bremen, Germany, with approximately 23,500 people from 115 countries. It is one of 11 institutions which were successful in the category "Institutional Strategies" of the Excellence Initiative launched by the Federal Government and the Federal States in 2012. The university was also successful in the categories "Graduate Schools" and "Clusters of Excellence" of the initiative.

The IPCC Third Assessment Report (TAR), Climate Change 2001, is an assessment of available scientific and socio-economic information on climate change by the IPCC. Statements of the IPCC or information from the TAR were often used as a reference showing a scientific consensus on the subject of global warming. The Third Assessment Report (TAR) was completed in 2001 and consists of four reports, three of them from its Working Groups: Working Group I: The Scientific Basis; Working Group II: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; Working Group III: Mitigation; Synthesis Report. A number of the TAR's conclusions are given quantitative estimates of how probable it is that they are correct, e.g., greater than 66% probability of being correct. These are "Bayesian" probabilities, which are based on an expert assessment of all the available evidence.

The First Assessment Report (FAR) of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was completed in 1990. It served as the basis of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). This report had effects not only on the establishment of the UNFCCC, but also on the first session of the Conference of the Parties (COP), held in Berlin in 1995. The executive summary of the WG I Summary for Policymakers report that said they were certain that emissions resulting from human activities are substantially increasing the atmospheric concentrations of the greenhouse gases, resulting on average in an additional warming of the Earth's surface. They calculated with confidence that CO2 had been responsible for over half the enhanced greenhouse effect.
The Jean Monnet Programme, also known as the Jean Monnet Project or Jean Monnet Actions, is a European Union initiative to encourage teaching, research and reflection in the field of European integration studies in higher education institutions. It is named for Jean Monnet, regarded by many as a chief architect of European Unity. It is part of the European Union's education, youth and sports programme Erasmus+. There are additional funds to increase the participation of higher education institutions from countries outside the European Union as part of the EU partnership instrument, which is specifically designed to promote the Union's strategic interests worldwide by reinforcing its external strategies, policies and actions.

The Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) of the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the fifth in a series of such reports and was completed in 2014. As had been the case in the past, the outline of the AR5 was developed through a scoping process which involved climate change experts from all relevant disciplines and users of IPCC reports, in particular representatives from governments. Governments and organizations involved in the Fourth Report were asked to submit comments and observations in writing with the submissions analysed by the panel. Projections in AR5 are based on "Representative Concentration Pathways" (RCPs). The RCPs are consistent with a wide range of possible changes in future anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. Projected changes in global mean surface temperature and sea level are given in the main RCP article.
Lynne Talley is a physical oceanographer at Scripps Institution of Oceanography known for her research into the large-scale circulation of water masses in the global ocean.

Antje Boetius is a German marine biologist. She is a professor of geomicrobiology at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology, University of Bremen. Boetius received the Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize in March 2009 for her study of sea bed microorganisms that affect the global climate. She is also the director of Germany's polar research hub, the Alfred Wegener Institute.
The Deutsches Klima-Konsortium e. V. is located in Berlin, Germany, and represents the leading players of German climate and climate impact research encompassing 26 renowned research organisations. The federation is also an important international partner acting as a guidepost, strategic partner, project partner and information broker.

The contributions of women in climate change have received increasing attention in the early 21st century. Feedback from women and the issues faced by women have been described as "imperative" by the United Nations and "critical" by the Population Reference Bureau. A report by the World Health Organization concluded that incorporating gender-based analysis would "provide more effective climate change mitigation and adaptation."
Albert Joseph Maria Defant was an Austrian meteorologist, oceanographer and climatologist. He published fundamental works on the physics of the atmosphere and ocean and is regarded as one of the founders of physical oceanography.

Angelika Brandt is the world leader in Antarctic deep-sea biodiversity and has developed, organised and led several oceanographic expeditions to Antarctica, notably the series of ANDEEP cruises, which have contributed significantly to Antarctica and deep-sea biology. Brandt was the senior scientist of ANDEEP which was devoted entirely to benthic research in the Antarctic abyss.

Kim M. Cobb is an American climate scientist, who is professor of Environment and Society and professor of Earth, Environmental and Planetary Sciences at Brown University, where she directs the Institute at Brown for Environment and Society. Cobb was previously a professor in the School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences at the Georgia Institute of Technology. She is particularly interested in oceanography, geochemistry and paleoclimate modeling.
Petra Döll is a German hydrologist whose research focuses on global water resources and methods for transdisciplinary knowledge integration. She is a professor of hydrology at the Institute of Physical Geography, Goethe University Frankfurt.

The United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Special Report on Climate Change and Land (SRCCL), also known as the "Special Report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems", is a landmark study from 2019 by 107 experts from 52 countries. The SRCCL provides a comprehensive overview of the entire land-climate system for the first time and decided to enlist land as a "critical resource". The IPCC's 50th session (IPCC-50) formally adopted the SRCCL's Summary for policymakers (SPM) and approved the underlying report. The SPM and the full text of Special Report on Climate Change and Land—in an unedited form—were released on 8 August 2019. The report is over 1,300 pages long and includes the work of 107 experts from 52 countries.

The United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate (SROCC) is a report about the effects of climate change on the world's seas, sea ice, icecaps and glaciers. It was approved at the IPCC's 51st Session (IPCC-51) in September 2019 in Monaco. The SROCC's approved Summary for Policymakers (SPM) was released on 25 September 2019. The 1,300-page report by 104 authors and editors representing 36 countries referred to 6,981 publications. The report is the third in the series of three Special Reports in the current Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) cycle, which began in 2015 and was completed in 2022. The first was the Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C, while the second was the Special Report on Climate Change and Land (SRCCL), also known as the "Special Report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems", which was released on 7 August 2019.
Kirsten Zickfeld is a German climate physicist who is now based in Canada. She is a member of the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, and was one of the authors on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C (SR15).Zickfeld completed a Master of Science degree in physics at the Free University of Berlin in 1998, followed by a doctorate in physics at the University of Potsdam in 2004.[7]

Joellen Louise Russell is an American oceanographer and climate scientist.

The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess the available scientific information on climate change. Three Working Groups covered the following topics: The Physical Science Basis (WGI); Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability (WGII); Mitigation of Climate Change (WGIII). Of these, the first study was published in 2021, the second report February 2022, and the third in April 2022. The final synthesis report was finished in March 2023. It includes a summary for policymakers and was the basis for the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28) in Dubai.
References
- 1 2 3 "Monika Rhein". www.marum.de. Retrieved 2019-04-12.
- 1 2 "Institute of Environmental Physics – Oceanography: Prof. Dr. Monika Rhein". www.ocean.uni-bremen.de. Retrieved 2019-04-12.
- 1 2 "Previous Union officers". European Geosciences Union (EGU). Retrieved 2019-04-12.
- ↑ "IPCC Working Group I". www.climatechange2013.org. Retrieved 2019-04-12.
- ↑ "International Oversight Committee". OSNAP. 2015-03-02. Retrieved 2019-04-12.
- ↑ Hamburg, CEN Universität. "Albert Defant Medal for Jürgen Sündermann". www.cen.uni-hamburg.de. Retrieved 2019-04-12.