Related Research Articles

The National Security Agency (NSA) is an intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the Director of National Intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collection, and processing of information and data for foreign and domestic intelligence and counterintelligence purposes, specializing in a discipline known as signals intelligence (SIGINT). The NSA is also tasked with the protection of U.S. communications networks and information systems. The NSA relies on a variety of measures to accomplish its mission, the majority of which are clandestine. The NSA has roughly 32,000 employees.
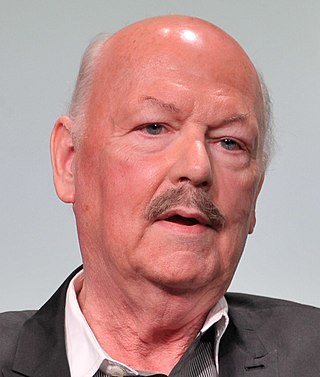
James Bamford is an American author, journalist and documentary producer noted for his writing about United States intelligence agencies, especially the National Security Agency (NSA). The New York Times has called him "the nation's premier journalist on the subject of the National Security Agency" and The New Yorker named him "the NSA's chief chronicler."

The FISA Amendments Act of 2008, also called the FAA and Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act of 1978 Amendments Act of 2008, is an Act of Congress that amended the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act. It has been used as the legal basis for surveillance programs disclosed by Edward Snowden in 2013, including PRISM.

"Stellar Wind" was the code name of a warrantless surveillance program begun under the George W. Bush administration's President's Surveillance Program (PSP). The National Security Agency (NSA) program was approved by President Bush shortly after the September 11, 2001 attacks and was revealed by Thomas Tamm to The New York Times in 2004. Stellar Wind was a prelude to new legal structures that allowed President Bush and President Barack Obama to reproduce each of those programs and expand their reach.

The Utah Data Center (UDC), also known as the Intelligence Community Comprehensive National Cybersecurity Initiative Data Center, is a data storage facility for the United States Intelligence Community that is designed to store data estimated to be on the order of exabytes or larger. Its purpose is to support the Comprehensive National Cybersecurity Initiative (CNCI), though its precise mission is classified. The National Security Agency (NSA) leads operations at the facility as the executive agent for the Director of National Intelligence. It is located at Camp Williams near Bluffdale, Utah, between Utah Lake and Great Salt Lake and was completed in May 2014 at a cost of $1.5 billion.

Jewel v. National Security Agency, 673 F.3d 902, was a class action lawsuit argued before the District Court for the Northern District of California and the Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, filed by Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) on behalf of American citizens who believed that they had been surveilled by the National Security Agency (NSA) without a warrant. The EFF alleged that the NSA's surveillance program was an "illegal and unconstitutional program of dragnet communications surveillance" and claimed violations of the Fourth Amendment.

PRISM is a code name for a program under which the United States National Security Agency (NSA) collects internet communications from various U.S. internet companies. The program is also known by the SIGAD US-984XN. PRISM collects stored internet communications based on demands made to internet companies such as Google LLC and Apple under Section 702 of the FISA Amendments Act of 2008 to turn over any data that match court-approved search terms. Among other things, the NSA can use these PRISM requests to target communications that were encrypted when they traveled across the internet backbone, to focus on stored data that telecommunication filtering systems discarded earlier, and to get data that is easier to handle.

Edward Joseph Snowden is an American and naturalized Russian citizen who was a computer intelligence consultant and whistleblower who leaked highly classified information from the National Security Agency (NSA) in 2013 when he was an employee and subcontractor. His disclosures revealed numerous global surveillance programs, many run by the NSA and the Five Eyes intelligence alliance with the cooperation of telecommunication companies and European governments and prompted a cultural discussion about national security and individual privacy.

Fairview is a secret program under which the National Security Agency cooperates with the American telecommunications company AT&T in order to collect phone, internet and e-mail data mainly of foreign countries' citizens at major cable landing stations and switching stations inside the United States. The FAIRVIEW program started in 1985, one year after the Bell breakup.

The practice of mass surveillance in the United States dates back to wartime monitoring and censorship of international communications from, to, or which passed through the United States. After the First and Second World Wars, mass surveillance continued throughout the Cold War period, via programs such as the Black Chamber and Project SHAMROCK. The formation and growth of federal law-enforcement and intelligence agencies such as the FBI, CIA, and NSA institutionalized surveillance used to also silence political dissent, as evidenced by COINTELPRO projects which targeted various organizations and individuals. During the Civil Rights Movement era, many individuals put under surveillance orders were first labelled as integrationists, then deemed subversive, and sometimes suspected to be supportive of the communist model of the United States' rival at the time, the Soviet Union. Other targeted individuals and groups included Native American activists, African American and Chicano liberation movement activists, and anti-war protesters.
During the 2010s, international media news reports revealed new operational details about the Anglophone cryptographic agencies' global surveillance of both foreign and domestic nationals. The reports mostly relate to top secret documents leaked by ex-NSA contractor Edward Snowden. The documents consist of intelligence files relating to the U.S. and other Five Eyes countries. In June 2013, the first of Snowden's documents were published, with further selected documents released to various news outlets through the year.
The global surveillance disclosure released to media by Edward Snowden has caused tension in the bilateral relations of the United States with several of its allies and economic partners as well as in its relationship with the European Union. In August 2013, U.S. President Barack Obama announced the creation of "a review group on intelligence and communications technologies" that would brief and later report to him. In December, the task force issued 46 recommendations that, if adopted, would subject the National Security Agency (NSA) to additional scrutiny by the courts, Congress, and the president, and would strip the NSA of the authority to infiltrate American computer systems using "backdoors" in hardware or software. Geoffrey R. Stone, a White House panel member, said there was no evidence that the bulk collection of phone data had stopped any terror attacks.

The FISA Improvements Act is a proposed act by Senator Dianne Feinstein, Chair of the Senate Intelligence Committee. Prompted by the disclosure of NSA surveillance by Edward Snowden, it would establish the surveillance program as legal, but impose some limitations on availability of the data. Opponents say the bill would codify warrantless access to many communications of American citizens for use by domestic law enforcement.

Former U.S. President Barack Obama favored some levels of mass surveillance. He has received some widespread criticism from detractors as a result. Due to his support of certain government surveillance, some critics have said his support violated acceptable privacy rights, while others dispute or attempt to provide justification for the expansion of surveillance initiatives under his administration.

American Civil Liberties Union v. Clapper, 785 F.3d 787, was a lawsuit by the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) and its affiliate, the New York Civil Liberties Union, against the United States federal government as represented by then-Director of National Intelligence James Clapper. The ACLU challenged the legality and constitutionality of the National Security Agency's (NSA) bulk phone metadata collection program.

Litigation over global surveillance has occurred in multiple jurisdictions since the global surveillance disclosures of 2013.

This timeline of global surveillance disclosures from 2013 to the present day is a chronological list of the global surveillance disclosures that began in 2013. The disclosures have been largely instigated by revelations from the former American National Security Agency contractor Edward Snowden.

MYSTIC is a former secret program used since 2009 by the US National Security Agency (NSA) to collect the metadata as well as the content of phone calls from several countries. The program was first revealed in March 2014, based upon documents leaked by Edward Snowden.

Citizenfour is a 2014 documentary film directed by Laura Poitras, concerning Edward Snowden and the NSA spying scandal. The film had its US premiere on October 10, 2014, at the New York Film Festival and its UK premiere on October 17, 2014, at the BFI London Film Festival. The film features Snowden and Glenn Greenwald, and was co-produced by Poitras, Mathilde Bonnefoy, and Dirk Wilutzky, with Steven Soderbergh and others serving as executive producers. Citizenfour received critical acclaim upon release, and was the recipient of numerous accolades, including Best Documentary Feature at the 87th Academy Awards. This film is the third part to a 9/11 trilogy following My Country, My Country (2006) and The Oath (2010).

Wikimedia Foundation, et al. v. National Security Agency, et al. is a lawsuit filed by the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) on behalf of the Wikimedia Foundation and several other organizations against the National Security Agency (NSA), the United States Department of Justice (DOJ), and other named individuals, alleging mass surveillance of Wikipedia users carried out by the NSA. The suit claims the surveillance system, which NSA calls "Upstream", breaches the First Amendment to the United States Constitution, which protects freedom of speech, and the Fourth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which prohibits unreasonable searches and seizures.
References
- ↑ Fung, Brian (August 13, 2014). "The NSA has a secret program that automatically hacks back against enemy targets" . Washington Post.
- ↑ James Bamford. Edward Snowden: The Untold Story // Wired : magazine. — 2014-08-13. — ISSN 1059-1028.
- ↑ Flood, Alison (August 1, 2019). "Edward Snowden memoir to reveal whistleblower's secrets" – via The Guardian.
- ↑ Edward Snowden (September 17, 2019). Permanent Record. Henry Holt and Company. ISBN 978-1-250-23724-8
- ↑ Kim Zetter. Meet MonsterMind, the NSA Bot That Could Wage Cyberwar Autonomously // Wired : magazine. — 2014-08-13. — ISSN 1059-1028
- ↑ "Snowden Speaks: A Vanity Fair Special Report". Vanity Fair. April 23, 2014.
- ↑ "What we know about NSA leaker Edward Snowden - U.S. News". web.archive.org. 2013-06-13. Archived from the original on 2013-06-13. Retrieved 2023-12-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ Chernenko, E., Demidov, O., & Lukyanov, F. (2018). Increasing International Cooperation in Cybersecurity and Adapting Cyber Norms. Council on Foreign Relations. http://www.jstor.org/stable/resrep29959
- ↑ "ACLU Comment on Edward Snowden Lawsuit".