
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo. A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armies of the Seventh Coalition. One of these was a British-led coalition consisting of units from the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Hanover, Brunswick, and Nassau, under the command of the Duke of Wellington. The other was composed of three corps of the Prussian army under the command of Field Marshal von Blücher. The battle marked the end of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle was contemporaneously known as the Battle of Mont Saint-Jean (France) or La Belle Alliance.

The Battle of Ligny, in which French troops of the Armée du Nord under the command of Napoleon I defeated part of a Prussian army under Field Marshal Blücher, was fought on 16 June 1815 near Ligny in what is now Belgium. The result was a tactical victory for the French, but the bulk of the Prussian army survived the battle in good order, was reinforced by Prussian troops who had not fought at Ligny, and played a role two days later at the Battle of Waterloo. The Battle of Ligny was the last victory in Napoleon's military career.

Waterloo is a municipality in Wallonia, located in the province of Walloon Brabant, Belgium, which in 2011 had a population of 29,706 and an area of 21.03 km2 (8.12 sq mi). Waterloo lies a short distance south of Brussels, and immediately north-east of the larger town of Braine-l'Alleud. It is the site of the Battle of Waterloo, where the resurgent Napoleon was defeated for the final time in 1815. Waterloo lies immediately south of the official language border between Flanders and Wallonia.

La Haye Sainte is a walled farmhouse compound at the foot of an escarpment on the Charleroi-Brussels road in Belgium. It has changed very little since it played a crucial part in the Battle of Waterloo on 18 June 1815.

Château d'Hougoumont is a walled manorial compound, situated at the bottom of an escarpment near the Nivelles road in the Braine-l'Alleud municipality, near Waterloo, Belgium. The site served as one of the advanced defensible positions of the Anglo-allied army under the Duke of Wellington, that faced Napoleon's Army at the Battle of Waterloo on 18 June 1815.

The Sonian Forest or Sonian Wood is a 4,421-hectare (10,920-acre) forest at the southeast edge of Brussels, Belgium.

The Battle of Wavre was the final major military action of the Hundred Days campaign and the Napoleonic Wars. It was fought on 18–19 June 1815 between the Prussian rearguard, consisting of the Prussian III Corps under the command of General Johann von Thielmann and three corps of the French army under the command of Marshal Grouchy. A blocking action, this battle kept 33,000 French soldiers from reaching the Battle of Waterloo and so helped in the defeat of Napoleon at Waterloo.

The Waterloo campaign was fought between the French Army of the North and two Seventh Coalition armies, an Anglo-allied army and a Prussian army. Initially the French army was commanded by Napoleon Bonaparte, but he left for Paris after the French defeat at the Battle of Waterloo. Command then rested on Marshals Soult and Grouchy, who were in turn replaced by Marshal Davout, who took command at the request of the French Provisional Government. The Anglo-allied army was commanded by the Duke of Wellington and the Prussian army by Prince Blücher.

Jean Maximilien Lamarque was a French general of the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars who later became a member of the French Parliament. Lamarque served with distinction in many of Napoleon's campaigns. He was particularly noted for his capture of Capri from the British, and for his defeat of Royalist forces in the Vendée in 1815. The latter campaign received great praise from Napoleon, who said Lamarque had "performed wonders, and even surpassed my hopes".

The Lion's Mound is a large conical artificial hill in the municipality of Braine-l'Alleud, Walloon Brabant, Belgium. King William I of the Netherlands ordered its construction in 1820, and it was completed in 1826. It commemorates the location on the battlefield of Waterloo where a musket ball hit the shoulder of King William II of the Netherlands and knocked him from his horse during the battle. It is also a memorial of the Battle of Quatre Bras, which had been fought two days earlier, on 16 June 1815.

Joseph Jean François, count de Ferraris was an Austrian general and cartographer. He was married to the daughter of Charles, 2nd Duke d'Ursel.
Mont-Saint-Jean may refer to several places:
Arnouph Louis Joseph Deshayes de Cambronne was a former governor of the Château de Compiègne and the major adjudant of the National Guard (France).

After the fighting at Quatre Bras the two opposing commanders Marshal Ney and the Duke of Wellington initially held their ground while they obtained information about what had happened at the larger Battle of Ligny. They received intelligence that the Prussian army under the command of Prince Blücher had been defeated by the French Army of the North under the command of Napoleon Bonaparte.

On 16 June 1815, the French defeated the Prussians at the Battle of Ligny. The Prussians successfully disengaged and withdrew north to Wavre where they regrouped, and later advanced westward with three corps to attack the right flank of the French army at the Battle of Waterloo. The French were slow to exploit Ligny; Napoleon wasted the morning of 17 June with a late breakfast and touring the previous day's battlefield before organising a pursuit of the two Coalition armies. Napoleon and Marshal Michel Ney took the French reserves to pursue the Duke of Wellington's Anglo-allied army. Marshal Emmanuel de Grouchy was ordered to pursue and harry the Prussians and prevent them from regrouping.
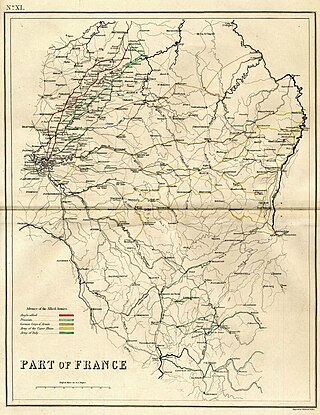
After their defeat at the Battle of Waterloo on 18 June 1815, the French Army of the North, under the command of Napoleon Bonaparte retreated in disarray back towards France. As agreed by the two Seventh Coalition commanders in chief, the Duke of Wellington, commander of the Anglo-allied army, and Prince Blücher, commander of the Prussian army, the French were to be closely pursued by units of the Prussian cavalry.

Decoster's house was a landmark location during the Battle of Waterloo. It stood on the eastern side of the Waterloo–Genappe main road south of the junction with the minor road to Plancenoit. According to Jean-Baptiste Decoster Napoleon spent the early part of the Battle of Waterloo and around Rossomme and then at about 17:00 moved to a position near Decoster's house where he remained until about 19:00.
The Trois Burettes Inn was situated at the crossroads of Namur high road and the Old Roman Road, in Belgium. It was a notable location in two battles:

The Memorial of Waterloo 1815 is a Belgian museum complex located on the site of the Waterloo battlefield in Belgium. It includes a museum inaugurated in 2015, the Lion's Mound, the Panorama of the Battle of Waterloo and the Hougoumont farm.
















