
The Bloch MB.210 and MB.211 were the successors of the French Bloch MB.200 bomber developed by Société des Avions Marcel Bloch in the 1930s and differed primarily in being low wing monoplanes rather than high wing monoplanes.

The Bloch MB.170 and its derivatives were French reconnaissance bombers designed and built shortly before the Second World War. They were the best aircraft of this type available to the Armée de l'Air at the outbreak of the war, with speed, altitude and manoeuvrability that allowed them to evade interception by the German fighters. Although the aircraft could have been in service by 1937, debate over what role to give the aircraft delayed deliveries until 1940.

The RWD 3 was a 1930 Polish sports aircraft and liaison aircraft prototype, constructed by the RWD team, a single-engine high-wing monoplane.

The Dewoitine 37 was the first of a family of 1930s French-built monoplane fighter aircraft.

The Gregor FDB-1 was a Canadian biplane fighter, designed in 1938 by Michael Gregor and manufactured by Canadian Car and Foundry. Despite having some advanced design features such as flush rivetted all-metal construction and a retractable undercarriage, the final generation of biplane fighters was being supplanted by monoplanes and the Gregor FDB-1 was obsolete before it flew. Despite the Royal Canadian Air Force's desperation for modern fighters, the sole example remained unsold and was eventually lost in a fire in 1945. The Gregor FDB-1's model designation stood for Fighter Dive Bomber indicating its intended roles.

The PZL P.6 was a Polish fighter, designed by the engineer Zygmunt Puławski, manufactured by PZL state-owned factory. It remained a prototype.
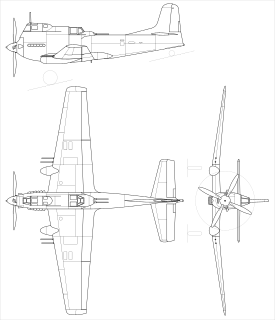
The Ilyushin Il-20 was a Soviet prototype for a heavily armored ground-attack aircraft to replace the Ilyushin Il-10. It featured a number of innovative concepts including a cockpit mounted on top of the engine, directly behind the propeller, and wing-mounted autocannon that could be adjusted on the ground to fire level or depressed 23° to allow the aircraft to strafe ground targets while remaining in level flight. However it was slower than the Il-10, and its M-47 engine was problematic in flight tests in 1948–49. It was not placed into production. The test pilots called the aircraft the Gorbach (Hunchback).
The PZL.48 Lampart (leopard) was a Polish heavy fighter-bomber design, that remained only a project, owing to the outbreak of World War II.

The SPAD S.A was a French two-seat tractor biplane first flown in 1915. It was used by France and Russia in the early stages of the First World War in the fighter and reconnaissance roles. It was a unique aircraft that carried its observer in a nacelle ahead of both wing and engine.

The Morane-Saulnier G was a two-seat sport and racing monoplane produced in France before the First World War. It was a development of the racing monoplanes designed by Léon Morane and Raymond Saulnier after leaving Borel and, like its predecessors, was a wire-braced, shoulder-wing monoplane. Construction was of fabric-covered wood throughout, except for the undercarriage struts which were of steel tube.
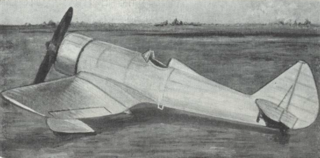
The IAR 15 was a low-wing monoplane fighter designed in Romania in 1933.

The Westland Wizard was Westland Aircraft's first attempt to produce a monoplane fighter. The project was privately funded and the prototype design was done in the spare time of the company's engineers. This all happened during 1926, with high-speed performance as the primary goal.
The Nikitin-Schyevchyenko IS series,, were single seat polymorphic fighters designed and produced in the USSR from 1938.
The Farman F.420 was a twin engine monoplane, built in France in the mid-1930s to compete in a government contest for an aircraft capable of fulfilling bomber, fighter and reconnaissance roles. Two prototypes were constructed but no production followed.
The Mitsubishi J4M Senden or Navy Experimental 17-Shi Otsu B Type Interceptor Fighter Senden, Allied reporting name Luke, was a Japanese World War II fighter aircraft proposed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries for use by the Imperial Japanese Navy. The J4M project did not proceed beyond the design stage.

The Hispano Suiza E-30, later renamed Hispano E-30, was designed in Spain in 1930 as a multi-purpose intermediate trainer. It was a single engine, parasol wing monoplane. About 25 served with the Spanish armed forces until 1945.

The Bernard SIMB AB 12 was a French single engine, single-seat monoplane fighter aircraft built in the 1920s. Though advanced for its time, it failed to gain a production order and only one was built.
The Gabardini biplane was an Italian single seat biplane, designed and built near the beginning of World War I. It was an advanced trainer and could be fitted with engines of output between about 40 to 80 kW.
The Wibault 313, Wibault Wib 313 or Penhoët Wibault Wib 313 was a single engine, single seat low wing monoplane fighter aircraft, designed and built in France in the early 1930s. It was entered into a government competitive tender programme but was not ordered.

The Wibault 10/II Tramontane was a two-seat reconnaissance aircraft designed and built by Société des Avions Michel Wibault in France for the French military 1923 A.2 competition for a 2-seater reconnaissance aircraft.













