
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is one of several components of kinematics, the study of motion. Accelerations are vector quantities. The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the net force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes:
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force F proportional to the displacement x: where k is a positive constant.

In mechanics and physics, simple harmonic motion is a special type of periodic motion an object experiences by means of a restoring force whose magnitude is directly proportional to the distance of the object from an equilibrium position and acts towards the equilibrium position. It results in an oscillation that is described by a sinusoid which continues indefinitely.

Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a dimensionless quantity defined as the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for solids and liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its densest ; for gases, the reference is air at room temperature. The term "relative density" is preferred in SI, whereas the term "specific gravity" is gradually being abandoned.
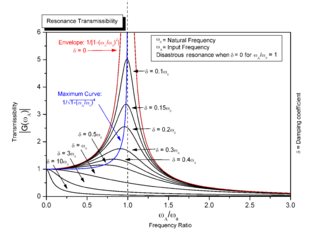
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration that matches its resonant frequency, defined as the frequency that generates the maximum amplitude response in the system. When this happens, the object or system absorbs energy from the external force and starts vibrating with a larger amplitude. Resonance can occur in various systems, such as mechanical, electrical, or acoustic systems, and it is often desirable in certain applications, such as musical instruments or radio receivers. However, resonance can also be detrimental, leading to excessive vibrations or even structural failure in some cases.
Longitudinal waves are waves which oscillate in the direction which is parallel to the direction in which the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called compressional or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when travelling through a medium, and pressure waves, because they produce increases and decreases in pressure. A wave along the length of a stretched Slinky toy, where the distance between coils increases and decreases, is a good visualization. Real-world examples include sound waves and seismic P waves.

In science, work is the energy transferred to or from an object via the application of force along a displacement. In its simplest form, for a constant force aligned with the direction of motion, the work equals the product of the force strength and the distance traveled. A force is said to do positive work if it has a component in the direction of the displacement of the point of application. A force does negative work if it has a component opposite to the direction of the displacement at the point of application of the force.

A spring is a device consisting of an elastic but largely rigid material bent or molded into a form that can return into shape after being compressed or extended. Springs can store energy when compressed. In everyday use, the term most often refers to coil springs, but there are many different spring designs. Modern springs are typically manufactured from spring steel. An example of a non-metallic spring is the bow, made traditionally of flexible yew wood, which when drawn stores energy to propel an arrow.
In continuum mechanics, the Froude number is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the flow inertia to the external force field. The Froude number is based on the speed–length ratio which he defined as: where u is the local flow velocity, g is the local gravity field, and L is a characteristic length.
In analytical mechanics, generalized coordinates are a set of parameters used to represent the state of a system in a configuration space. These parameters must uniquely define the configuration of the system relative to a reference state. The generalized velocities are the time derivatives of the generalized coordinates of the system. The adjective "generalized" distinguishes these parameters from the traditional use of the term "coordinate" to refer to Cartesian coordinates.
Acoustic impedance and specific acoustic impedance are measures of the opposition that a system presents to the acoustic flow resulting from an acoustic pressure applied to the system. The SI unit of acoustic impedance is the pascal-second per cubic metre, or in the MKS system the rayl per square metre (Rayl/m2), while that of specific acoustic impedance is the pascal-second per metre (Pa·s/m), or in the MKS system the rayl (Rayl). There is a close analogy with electrical impedance, which measures the opposition that a system presents to the electric current resulting from a voltage applied to the system.

A torsion spring is a spring that works by twisting its end along its axis; that is, a flexible elastic object that stores mechanical energy when it is twisted. When it is twisted, it exerts a torque in the opposite direction, proportional to the amount (angle) it is twisted. There are various types:

In structural engineering, buckling is the sudden change in shape (deformation) of a structural component under load, such as the bowing of a column under compression or the wrinkling of a plate under shear. If a structure is subjected to a gradually increasing load, when the load reaches a critical level, a member may suddenly change shape and the structure and component is said to have buckled. Euler's critical load and Johnson's parabolic formula are used to determine the buckling stress of a column.

Weight transfer and load transfer are two expressions used somewhat confusingly to describe two distinct effects:
In mechanics, virtual work arises in the application of the principle of least action to the study of forces and movement of a mechanical system. The work of a force acting on a particle as it moves along a displacement is different for different displacements. Among all the possible displacements that a particle may follow, called virtual displacements, one will minimize the action. This displacement is therefore the displacement followed by the particle according to the principle of least action.
The work of a force on a particle along a virtual displacement is known as the virtual work.
Slip ratio is a means of calculating and expressing the slipping behavior of the wheel of an automobile. It is of fundamental importance in the field of vehicle dynamics, as it allows to understand the relationship between the deformation of the tire and the longitudinal forces acting upon it. Furthermore, it is essential to the effectiveness of any anti-lock braking system.
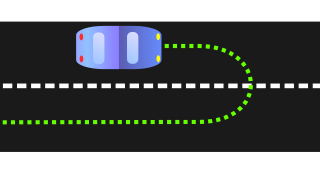
The turning radius of a vehicle defines the minimum dimension of available space required for that vehicle to make a semi-circular U-turn without skidding. The Oxford English Dictionary describes turning circle as "the smallest circle within which a ship, motor vehicle, etc., can be turned round completely". The term thus refers to a theoretical minimal circle in which for example an aeroplane, a ground vehicle or a watercraft can be turned around.
Automotive suspension design is an aspect of automotive engineering, concerned with designing the suspension for cars and trucks. Suspension design for other vehicles is similar, though the process may not be as well established.

In physics, Lagrangian mechanics is a formulation of classical mechanics founded on the stationary-action principle. It was introduced by the Italian-French mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange in his presentation to the Turin Academy of Science in 1760 culminating in his 1788 grand opus, Mécanique analytique.
Contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of solids that touch each other at one or more points. This can be divided into compressive and adhesive forces in the direction perpendicular to the interface, and frictional forces in the tangential direction. Frictional contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of bodies in the presence of frictional effects, whereas frictionless contact mechanics assumes the absence of such effects.















