Related Research Articles

In vitro studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from in vitro experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to in vitro experiments, in vivo studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, known as clinical trials, and whole plants.

In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer in animals, such mutagens can therefore be carcinogens, although not all necessarily are. All mutagens have characteristic mutational signatures with some chemicals becoming mutagenic through cellular processes.

Arsenic poisoning is a medical condition that occurs due to elevated levels of arsenic in the body. If arsenic poisoning occurs over a brief period of time, symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, encephalopathy, and watery diarrhea that contains blood. Long-term exposure can result in thickening of the skin, darker skin, abdominal pain, diarrhea, heart disease, numbness, and cancer.

Cypermethrin (CP) is a synthetic pyrethroid used as an insecticide in large-scale commercial agricultural applications as well as in consumer products for domestic purposes. It behaves as a fast-acting neurotoxin in insects. It is easily degraded on soil and plants but can be effective for weeks when applied to indoor inert surfaces. It is a non-systemic and non-volatile insecticide that acts by contact and ingestion, used in agriculture and in pest control products. Exposure to sunlight, water and oxygen will accelerate its decomposition. Cypermethrin is highly toxic to fish, bees and aquatic insects, according to the National Pesticide Information Center (NPIC) in the USA. It is found in many household ant and cockroach killers, including Raid, Ortho, Combat, ant chalk, and some products of Baygon in Southeast Asia.
Genotoxicity is the property of chemical agents that damage the genetic information within a cell causing mutations, which may lead to cancer. While genotoxicity is often confused with mutagenicity, all mutagens are genotoxic, but some genotoxic substances are not mutagenic. The alteration can have direct or indirect effects on the DNA: the induction of mutations, mistimed event activation, and direct DNA damage leading to mutations. The permanent, heritable changes can affect either somatic cells of the organism or germ cells to be passed on to future generations. Cells prevent expression of the genotoxic mutation by either DNA repair or apoptosis; however, the damage may not always be fixed leading to mutagenesis.

Wilms tumor protein (WT33) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WT1 gene on chromosome 11p.

Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), also known as nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2, is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the NFE2L2 gene. NRF2 is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) protein that may regulate the expression of antioxidant proteins that protect against oxidative damage triggered by injury and inflammation, according to preliminary research. In vitro, NRF2 binds to antioxidant response elements (AREs) in the promoter regions of genes encoding cytoprotective proteins. NRF2 induces the expression of heme oxygenase 1 in vitro leading to an increase in phase II enzymes. NRF2 also inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome.

Transcription factor E2F4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the E2F4 gene.

Transcription factor E2F3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the E2F3 gene.
Homeobox protein Hox-B7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HOXB7 gene.
DNA polymerase kappa is a DNA polymerase that in humans is encoded by the POLK gene. It is involved in translesion synthesis.

YY1 is a transcriptional repressor protein in humans that is encoded by the YY1 gene.

General transcription factor IIH subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GTF2H4 gene.

Forkhead box protein H1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXH1 gene.
Homeobox protein DLX-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DLX2 gene.

Protein Jumonji is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JARID2 gene. JARID2 is a member of the alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase superfamily.

A genetically modified mouse, genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM) or transgenic mouse is a mouse that has had its genome altered through the use of genetic engineering techniques. Genetically modified mice are commonly used for research or as animal models of human diseases and are also used for research on genes. Together with patient-derived xenografts (PDXs), GEMMs are the most common in vivo models in cancer research. Both approaches are considered complementary and may be used to recapitulate different aspects of disease. GEMMs are also of great interest for drug development, as they facilitate target validation and the study of response, resistance, toxicity and pharmacodynamics.

Verbascoside is a polyphenol glycoside in which the phenylpropanoid caffeic acid and the phenylethanoid hydroxytyrosol form an ester and an ether bond respectively, to the rhamnose part of a disaccharide, namely β-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→3)-β-D-(4-O-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside.
The murine local lymph node assay (LLNA) is an in vivo test for skin sensitisation.
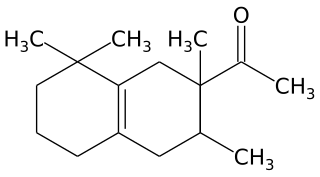
Tetramethyl acetyloctahydronaphthalenes is a synthetic ketone fragrance also known as OTNE and by other commercial trade names such as: Iso E Super, Iso Gamma Super, Anthamber, Amber Fleur, Boisvelone, Iso Ambois, Amberlan, Iso Velvetone, Orbitone, Amberonne. It is a synthetic woody odorant and is used as a fragrance ingredient in perfumes, laundry products and cosmetics.
References
- ↑ Gad, S. C. (1994-09-22). "The mouse ear swelling test (MEST) in the 1990s". Toxicology . 93 (1): 33–46. Bibcode:1994Toxgy..93...33G. doi:10.1016/0300-483x(94)90194-5. PMID 7974503.
- ↑ Gad SC; Dunn BJ; Dobbs DW; Reilly C; Walsh RD (1986), "Development and validation of an alternative dermal sensitization test: the mouse ear swelling test (MEST)", Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology , 86 (1): 93–114, Bibcode:1986ToxAP..84...93G, doi:10.1016/0041-008x(86)90419-9, PMID 3715870