
Fruitarianism is a diet that consists primarily of consuming fruits and possibly nuts and seeds, but without any animal products. Fruitarian diets are subject to criticism and health concerns.

Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain the required amount of nutrients causes malnutrition. Nutritional science is the study of nutrition, though it typically emphasizes human nutrition.

Vitamins are organic molecules that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolic function. Essential nutrients cannot be synthesized in the organism in sufficient quantities for survival, and therefore must be obtained through the diet. For example, vitamin C can be synthesized by some species but not by others; it is not considered a vitamin in the first instance but is in the second. Most vitamins are not single molecules, but groups of related molecules called vitamers. For example, there are eight vitamers of vitamin E: four tocopherols and four tocotrienols.

"Junk food" is a term used to describe food that is high in calories from macronutrients such as sugar and/or fat, and possibly sodium, making it hyperpalatable, but with insufficient dietary fiber, protein, or micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. It is also known as HFSS food. The term junk food is a pejorative dating back to the 1950s. Many variations of junk food can be easily found in most supermarkets and fast-food restaurants. Due to easy accessibility, commercially-oriented packaging, and often-low prices, people are most likely to consume it.

A kitten is a juvenile cat. After being born, kittens display primary altriciality and are fully dependent on their mothers for survival. They normally do not open their eyes for seven to ten days. After about two weeks, kittens develop quickly and begin to explore the world outside their nest. After a further three to four weeks, they begin to eat solid food and grow baby teeth. Domestic kittens are highly social animals and usually enjoy human companionship.
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excreted by cells to create non-cellular structures such as hair, scales, feathers, or exoskeletons. Some nutrients can be metabolically converted into smaller molecules in the process of releasing energy such as for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and fermentation products leading to end-products of water and carbon dioxide. All organisms require water. Essential nutrients for animals are the energy sources, some of the amino acids that are combined to create proteins, a subset of fatty acids, vitamins and certain minerals. Plants require more diverse minerals absorbed through roots, plus carbon dioxide and oxygen absorbed through leaves. Fungi live on dead or living organic matter and meet nutrient needs from their host.

Human nutrition deals with the provision of essential nutrients in food that are necessary to support human life and good health. Poor nutrition is a chronic problem often linked to poverty, food security, or a poor understanding of nutritional requirements. Malnutrition and its consequences are large contributors to deaths, physical deformities, and disabilities worldwide. Good nutrition is necessary for children to grow physically and mentally, and for normal human biological development.
Vitamin deficiency is the condition of a long-term lack of a vitamin. When caused by not enough vitamin intake it is classified as a primary deficiency, whereas when due to an underlying disorder such as malabsorption it is called a secondary deficiency. An underlying disorder can have 2 main causes:

Maximilian Oskar Bircher-Benner, M.D. was a Swiss physician and a pioneer nutritionist credited for popularizing muesli and raw food vegetarianism.

Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues and form.

In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. The word diet often implies the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management reasons. Although humans are omnivores, each culture and each person holds some food preferences or some food taboos. This may be due to personal tastes or ethical reasons. Individual dietary choices may be more or less healthy.

A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.

In human nutrition, empty calories are those calories found in foods and beverages composed primarily or solely of calorie-rich macronutrients such as sugars and fats, but little or no micronutrients, fibre, or protein. Foods composed mostly of empty calories have low nutrient density, meaning few other nutrients relative to their energy content. Empty calories are more difficult to fit into a diet that is both balanced and within TDEE, and so readily create an unhealthy diet.

The Grapefruit diet is a short-term fad diet that has existed in the United States since at least the 1930s. There are variations on the diet, although it generally consists of eating one grapefruit at each meal, along with meat, eggs, other foods that are rich in fat and protein, and certain vegetables. Sugar, fruits, sweet vegetables, grains and starchy vegetables are to be avoided. The grapefruit diet is thus a low-carbohydrate diet. A typical breakfast menu usually includes bacon and eggs. The diet is based on the claim that grapefruit has a fat-burning enzyme or similar property. The grapefruit diet does not require exercise. The grapefruit diet lasts for 10 to 12 days followed by 2 days off.

Nathan Pritikin was an American inventor, engineer, nutritionist and longevity researcher. He promoted the Pritikin diet, a high-carbohydrate low-fat plant-based diet combined with regular aerobic exercise to prevent cardiovascular disease. The Pritikin diet emphasizes the consumption of legumes, whole grains, fresh fruit and vegetables and non-fat dairy products with small amounts of lean meat, fowl and fish.

Micronutrient deficiency is defined as the sustained insufficient supply of vitamins and minerals needed for growth and development, as well as to maintain optimal health. Since some of these compounds are considered essentials, micronutrient deficiencies are often the result of an inadequate intake. However, it can also be associated to poor intestinal absorption, presence of certain chronic illnesses and elevated requirements.
Panic Nation: Unpicking the Myths We're Told About Food and Health, also published as Panic Nation: Exposing the Myths We're Told About Food and Health, is a nonfiction book by Stanley Feldman and Vincent Marks. It was published by John Blake in 2005.
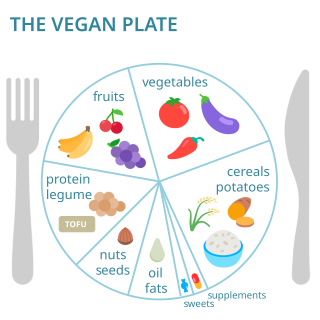
Vegan nutrition refers to the nutritional and human health aspects of vegan diets. A well-planned vegan diet is suitable to meet all recommendations for nutrients in every stage of human life. Vegan diets tend to be higher in dietary fiber, magnesium, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E, and phytochemicals; and lower in calories, saturated fat, iron, cholesterol, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, calcium, zinc, and vitamin B12.
Toddler nutrition is the description of the dietary needs of toddlers aged one to two years old. Food provides the energy and nutrients that toddlers need to be healthy. An adequate intake in nutrient rich food is good nutrition. A diet lacking essential calories, minerals, fluid and vitamins could be considered 'bad' nutrition. Nutrition needs are different for toddlers. For a baby, breast milk is "best" and it has all the necessary vitamins and minerals. Toddlers typically have been weaned from breast milk and infant formula. Though infants usually start eating solid foods between 4 and 6 months of age, more and more solid foods are consumed by a growing toddler. If a food introduced one at a time, a potential allergen can be identified. Food provides the energy and nutrients that young children need to be healthy. Toddlers are learning to feed themselves and to eat new foods. They should eat a variety of foods from all the food groups. Each day, toddlers need enough nutrients, including
Vincent Marks was an English pathologist and clinical biochemist known for his works on studying insulin and hypoglycemia. His contributions to medical science include simplifying low blood glucose testing, introducing insulin radioimmunoassay, and advancing diabetes research. Marks played an important role in high-profile medico-legal cases, notably providing expert testimony that helped acquit Danish-born British socialite Claus von Bülow in 1985, a case that was the basis of the Oscar-winning movie Reversal of Fortune (1990).













