This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2014) |
Muhammad 'Ali 'Alluba (November 1875/1878 - 25 March 1956) was an Egyptian lawyer, Arab nationalist and diplomat. [1]
This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2014) |
Muhammad 'Ali 'Alluba (November 1875/1878 - 25 March 1956) was an Egyptian lawyer, Arab nationalist and diplomat. [1]
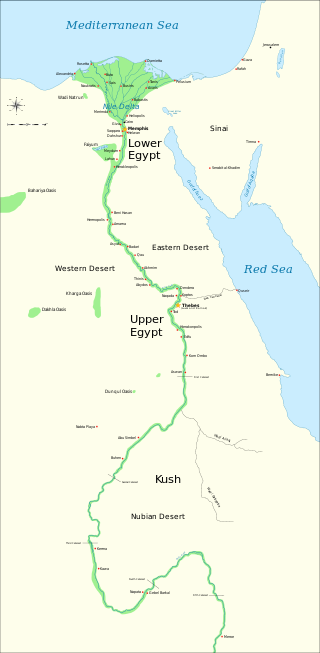
Ancient Egypt was a civilization of ancient Northeast Africa. It was concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River, situated within the contemporary territory of modern-day Egypt. Ancient Egyptian civilization followed prehistoric Egypt and coalesced around 3100 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under pharaoh or king Menes. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by periods of relative instability known as "Intermediate Periods". The various kingdoms fall into one of three categories: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age, or the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age.

Alexandria is the second largest city in Egypt and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile River delta. Founded in c. 331 BC by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilisation, eventually replacing Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" internationally, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and oil pipelines from Suez.

Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East. The Greater Cairo metropolitan area is the 12th-largest in the world by population with over 22.1 million people.

The Coptic Orthodox Church, also known as the Coptic Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria, is an Oriental Orthodox Christian church based in Egypt. The head of the church and the See of Alexandria is the pope of Alexandria on the Holy Apostolic See of Saint Mark, who also carries the title of Father of fathers, Shepherd of shepherds, Ecumenical Judge and the 13th among the Apostles.

Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the southeast, and South Sudan to the south. Sudan has a population of 50 million people as of 2024 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres, making it Africa's third-largest country by area and the third-largest by area in the Arab League. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the secession of South Sudan in 2011; since then both titles have been held by Algeria. Sudan's capital and most populous city is Khartoum.

The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai, is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north.

The Suez Canal is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The 193.30-kilometre-long (120.11 mi) canal is a key trade route between Europe and Asia.

The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was fought from 6 to 25 October 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egypt and Syria. Most of the fighting occurred in the Sinai Peninsula and Golan Heights, territories occupied by Israel in 1967. Some combat also took place in Egypt and northern Israel. Egypt aimed to secure a foothold on the eastern bank of the Suez Canal and use it to negotiate the return of the Sinai Peninsula.

Gamal Abdel Nasser Hussein was an Egyptian military officer and politician who served as the second president of Egypt from 1954 until his death in 1970. Nasser led the Egyptian revolution of 1952 and introduced far-reaching land reforms the following year. Following a 1954 attempt on his life by a Muslim Brotherhood member, he cracked down on the organization, put President Mohamed Naguib under house arrest and assumed executive office. He was formally elected president in June 1956.

Muhammad Hosni El Sayed Mubarak was an Egyptian politician and military officer who served as the fourth president of Egypt from 1981 to 2011.

The Suez Crisis also known as the Second Arab–Israeli War, the Tripartite Aggression in the Arab world and as the Sinai War in Israel, was a British–French–Israeli invasion of Egypt in 1956. Israel invaded on 29 October, having done so with the primary objective of re-opening the Straits of Tiran and the Gulf of Aqaba as the recent tightening of the eight-year-long Egyptian blockade further prevented Israeli passage. After issuing a joint ultimatum for a ceasefire, the United Kingdom and France joined the Israelis on 5 November, seeking to depose Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser and regain control of the Suez Canal, which Nasser had earlier nationalised by transferring administrative control from the foreign-owned Suez Canal Company to Egypt's new government-owned Suez Canal Authority. Shortly after the invasion began, the three countries came under heavy political pressure from both the United States and the Soviet Union, as well as from the United Nations, eventually prompting their withdrawal from Egypt. Israel's four-month-long occupation of the Egyptian-occupied Gaza Strip and Egypt's Sinai Peninsula enabled it to attain freedom of navigation through the Straits of Tiran, but the Suez Canal was closed from October 1956 to March 1957.

Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler. A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian Greek general and companion of Alexander the Great. Her first language was Koine Greek, and she is the only Ptolemaic ruler known to have learned the Egyptian language. After her death, Egypt became a province of the Roman Empire, marking the end of the last Hellenistic-period state in the Mediterranean, a period which had lasted since the reign of Alexander.

Egyptology is the scientific study of ancient Egypt. The topics studied include ancient Egyptian history, language, literature, religion, architecture and art from the 5th millennium BC until the end of its native religious practices in the 4th century AD.

The Prince of Egypt is a 1998 American animated musical drama film produced by DreamWorks Animation and distributed by DreamWorks Pictures. The second feature film from DreamWorks and the first to be traditionally animated, it is an adaptation of the Book of Exodus and follows the life of Moses from being a prince of Egypt to a prophet chosen by God to carry out his ultimate destiny of leading the Hebrews out of Egypt. The film was directed by Brenda Chapman, Steve Hickner, and Simon Wells, and produced by Jeffrey Katzenberg, Penney Finkelman Cox, and Sandra Rabins, from a screenplay written by Philip LaZebnik. It features songs written by Stephen Schwartz and a score composed by Hans Zimmer. The film stars the voices of Val Kilmer, Ralph Fiennes, Michelle Pfeiffer, Sandra Bullock, Jeff Goldblum, Danny Glover, Patrick Stewart, Helen Mirren, Steve Martin, and Martin Short.

The Egypt national football team, nicknamed "Pharaohs", represents Egypt in men's international football, and is governed by the Egyptian Football Association (EFA), the governing body of football in Egypt.

Egypt, officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and the Sinai Peninsula in the southwest corner of Asia. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 110 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world, and the third-most populated in Africa.

The 2011 Egyptian revolution, also known as the 25 January Revolution, began on 25 January 2011 and spread across Egypt. The date was set by various youth groups to coincide with the annual Egyptian "Police holiday" as a statement against increasing police brutality during the last few years of Hosni Mubarak's presidency. It consisted of demonstrations, marches, occupations of plazas, non-violent civil resistance, acts of civil disobedience and strikes. Millions of protesters from a range of socio-economic and religious backgrounds demanded the overthrow of Egyptian President Hosni Mubarak. Violent clashes between security forces and protesters resulted in at least 846 people killed and over 6,000 injured. Protesters retaliated by burning over 90 police stations across the country.

The Arab Spring or the First Arab Spring was a series of anti-government protests, uprisings and armed rebellions that spread across much of the Arab world in the early 2010s. It began in Tunisia in response to corruption and economic stagnation. From Tunisia, the protests then spread to five other countries: Libya, Egypt, Yemen, Syria and Bahrain. Rulers were deposed or major uprisings and social violence occurred including riots, civil wars, or insurgencies. Sustained street demonstrations took place in Morocco, Iraq, Algeria, Lebanon, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman and Sudan. Minor protests took place in Djibouti, Mauritania, Palestine, Saudi Arabia and the Western Sahara. A major slogan of the demonstrators in the Arab world is ash-shaʻb yurīd isqāṭ an-niẓām!.

Mohamed Salah Hamed Mahrous Ghaly, known as Mohamed Salah or Mo Salah, is an Egyptian professional footballer who plays as a right winger or forward for Liverpool and captains the Egypt national team. Widely regarded as one of the greatest wingers in the history of the sport, he is known for his clinical finishing, dribbling, speed, and playmaking abilities.

Abd el-Fattah Sisi is an Egyptian politician, dictator, and retired military officer who has been serving as the sixth and current president of Egypt since 2014. Before retiring as a general in the Egyptian military in 2014, Sisi served as Egypt's deputy prime minister from 2013 to 2014, minister of defense from 2012 to 2013, and director of military intelligence from 2010 to 2012. He was promoted to the rank of Field Marshal in January 2014.