Related Research Articles

The afterlife or life after death is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's stream of consciousness or identity continues to exist after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit, which carries with it one's personal identity.
Nirvana is a concept in the Indian religions of Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, and Sikhism that refers to the extinguishing of the passions which is the ultimate state of salvational release and the liberation from duḥkha ('suffering') and saṃsāra, the cycle of birth and rebirth.

In many religious and philosophical traditions, the soul is the non-material essence of a person, which includes one's identity, personality, and memories, an immaterial aspect or essence of a living being that is believed to be able to survive physical death. The concept of the soul is generally applied to humans, although it can also be applied to other living or even non-living entities, as in animism.
Ātman is a Sanskrit word for the true or eternal Self or the self-existent essence or impersonal witness-consciousness within each individual. Atman is conceptually different from Jīvātman, which persists across multiple bodies and lifetimes. Some schools of Indian philosophy regard the Ātman as distinct from the material or mortal ego (Ahankara), the emotional aspect of the mind (Citta), and existence in an embodied form (Prakṛti). The term is often translated as soul, but is better translated as "Self", as it solely refers to pure consciousness or witness-consciousness, beyond identification with phenomena. In order to attain moksha (liberation), a human being must acquire self-knowledge.
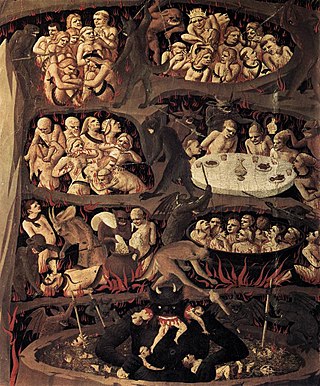
Damnation is the concept of divine punishment and torment in an afterlife for sins that were committed, or in some cases, good actions not done on Earth.

Saṃsāra is a Sanskrit word that means "wandering" as well as "world," wherein the term connotes "cyclic change" or, less formally, "running around in circles." Saṃsāra is referred to with terms or phrases such as transmigration/reincarnation, karmic cycle, or Punarjanman, and "cycle of aimless drifting, wandering or mundane existence". When related to the theory of karma it is the cycle of death and rebirth.
Moksha, also called vimoksha, vimukti, and mukti, is a term in Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism for various forms of emancipation, liberation, nirvana, or release. In its soteriological and eschatological senses, it refers to freedom from saṃsāra, the cycle of death and rebirth. In its epistemological and psychological senses, moksha is freedom from ignorance: self-realization, self-actualization and self-knowledge.

Immortality is the concept of eternal life. Some species possess 'biological immortality' due to an apparent lack of the Hayflick limit.
Jiva, also referred as Jivātman, is a living being or any entity imbued with a life force in Hinduism and Jainism. The word itself originates from the Sanskrit verb-root jīv, which translates as 'to breathe' or 'to live'. The jiva, as a metaphysical entity, has been described in various scriptures such as the Bhagavad Gita and the Upanishads. Each subschool of Vedanta describes the role of the jiva with the other metaphysical entities in varying capacities. The closest translation into English and abrahamic philosophies would be the soul.

Evelyn Underhill was an English Anglo-Catholic writer and pacifist known for her numerous works on religion and spiritual practice, in particular Christian mysticism. Her best-known work is Mysticism, published in 1911.
Nizari Isma'ilism are the largest segment of the Ismaili Muslims, who are the second-largest branch of Shia Islam after the Twelvers. Nizari teachings emphasize independent reasoning or ijtihad; pluralism—the acceptance of racial, ethnic, cultural and inter-religious differences; and social justice. Nizaris, along with Twelvers, adhere to the Jaʽfari school of jurisprudence. The Aga Khan, currently Aga Khan IV, is the spiritual leader and Imam of the Nizaris. The global seat of the Ismaili Imamate is in Lisbon, Portugal.
Satguru, or sadguru, means a "true guru" in Sanskrit. The term is distinguished from other forms of gurus, such as musical instructors, scriptural teachers, parents, and so on. A satguru has some special characteristics that are not found in any other types of spiritual guru. Satguru is a title given specifically only to an enlightened rishi or sant whose life's purpose is to guide the initiated shishya on the spiritual path, the summation of which is the realization of the Self through realization of God.

Dvaita Vedanta ;, is a sub-school in the Vedanta tradition of Hindu philosophy. The term Tattvavada literally means "arguments from a realist viewpoint". The Tattvavada (Dvaita) Vedanta sub-school was founded by the 13th-century Indian philosopher-saint Madhvacharya. Madhvacharya believed in three entities: God, jiva (soul), and jada. The Dvaita Vedanta school believes that God and the individual souls (jīvātman) exist as independent realities, and these are distinct, being said that Vishnu (Narayana) is independent (svatantra), and Souls are dependent (paratantra) on him.
Nitya-samsarins or nitya-samsaris is a concept in Hindu philosophy, referring to an individual who believes that their self is eternally bound in the cycle of rebirth called samsara. The existence of nitya-samsari is used to offer credibility to the concept of the periodical creation and the dissolution of the universe.
In Dvaita philosophy, Tamo-yogyas are a group of souls, classified by Madhvacharya, which consists of the souls who are damnable. Madhvacharya divides souls into three classes: one class of souls which qualifies for moksha, or liberation (Mukti-yogyas); another as subject to samsara, eternal rebirth or transmigration (Nitya-samsarins); and a third class that is eventually condemned to eternal hellish life in Andhatamisra (Tamo-yogyas).
Karma is a concept of Hinduism which describes a system in which beneficial effects are derived from past beneficial actions and harmful effects from past harmful actions, creating a system of actions and reactions throughout a soul's (jivatman's) reincarnated lives, forming a cycle of rebirth. The causality is said to apply not only to the material world but also to our thoughts, words, actions, and actions that others do under our instructions.
The Brahma Kumaris is a spiritual movement that originated in Hyderabad, Sindh, during the 1930s. Founded by Lekhraj Kripalani, the organisation teaches the importance of moving beyond labels associated with the human body, including race, nationality, religion, and gender, through meditation that emphasizes the concept of identity as souls rather than bodies. It aims to establish a global culture centered around what they refer to as "soul-consciousness". The members of the organisation believe that all souls are good by nature and that God is the source of all goodness.
Pyār is the Punjabi and Hindi word for love. It is derived from Sanskrit priya (love) and kāra (act). It is one of the five virtues of Sikhism.
Videha mukti refers to the moksha after death. It is a concept found in Hinduism and Jainism in relation to ending the samsara. The concept contrasts with Jivanmukti, which refers to achieving "liberation while alive". The concepts of Jivanmukta and Videhamukta are particularly discussed in Vedanta and Yoga schools of Hindu philosophy.
Kaivalya is the ultimate goal of aṣṭāṅga yoga and means "solitude", "detachment" or "isolation", a vrddhi-derivation from kevala "alone, isolated". It is the isolation of purusha from prakṛti, and liberation from rebirth, i.e., Moksha. Kaivalya-Mukti is described in some Upanishads, such as Muktika and Kaivalya as the most superior form of Moksha which can grant liberation both within this life, as Jivanmukti, and after death, as Videhamukti.
References
- ↑ Tapasyananda, Swami. Bhakti Schools of Vedanta pg. 177.