
Parallel ATA (PATA), originally AT Attachment, is an interface standard for the connection of storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, and optical disc drives in computers. The standard is maintained by the X3/INCITS committee. It uses the underlying AT Attachment (ATA) and AT Attachment Packet Interface (ATAPI) standards.

Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles.
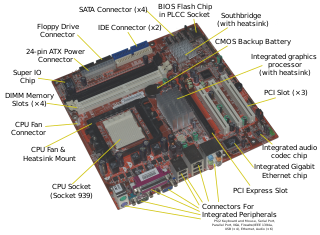
A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) found in general purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general purpose use and applications.
In telecommunications, RS-232, Recommended Standard 232 refers to a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a DTE such as a computer terminal, and a DCE, such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, issued in 1997. The RS-232 standard had been commonly used in computer serial ports.

A sound card is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications.

The TurboGrafx-16 Entertainment SuperSystem, known in Japan and France as the PC Engine, is a cartridge based home video game console manufactured and marketed by NEC Home Electronics, and designed by Hudson Soft. It was released in Japan on October 30, 1987 and in the United States on August 29, 1989. It also had a limited release in the United Kingdom and Spain in 1990, known as simply TurboGrafx and based on the American model, while the Japanese model was imported and distributed in France in 1989. It was the first console released in the 16-bit era, although it used an 8-bit CPU. Originally intended to compete with the Nintendo Entertainment System (NES), it ended up competing with the Sega Genesis, and later on the Super Nintendo Entertainment System (SNES).

In computing, PC Card is a configuration for computer parallel communication peripheral interface, designed for laptop computers. Originally introduced as PCMCIA, the PC Card standard as well as its successors like CardBus were defined and developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA).

In computing, the expansion card, expansion board, adapter card or accessory card is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot, on a computer motherboard, backplane or riser card to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.
Message Passing Interface (MPI) is a standardized and portable message-passing standard designed by a group of researchers from academia and industry to function on a wide variety of parallel computing architectures. The standard defines the syntax and semantics of a core of library routines useful to a wide range of users writing portable message-passing programs in C, C++, and Fortran. There are several well-tested and efficient implementations of MPI, many of which are open-source or in the public domain. These fostered the development of a parallel software industry, and encouraged development of portable and scalable large-scale parallel applications.

MultiMediaCard, officially abbreviated as MMC, is a memory card standard used for solid-state storage. Unveiled in 1997 by SanDisk and Siemens AG, MMC is based on a surface-contact low pin-count serial interface using a single memory stack substrate assembly, and is therefore much smaller than earlier systems based on high pin-count parallel interfaces using traditional surface-mount assembly such as CompactFlash. Both products were initially introduced using SanDisk NOR-based flash technology. MMC is about the size of a postage stamp: 24 mm × 32 mm × 1.4 mm. MMC originally used a 1-bit serial interface, but newer versions of the specification allow transfers of 4 or 8 bits at a time. MMC can be used in many devices that can use Secure Digital (SD) cards.

ExpressCard, initially called NEWCARD, is an interface to connect peripheral devices to a computer, usually a laptop computer. The ExpressCard technical standard specifies the design of slots built into the computer and of expansion cards to insert in the slots. The cards contain electronic circuits and sometimes connectors for external devices. The ExpressCard standard replaces the PC Card standards.
RS-485, also known as TIA-485(-A), EIA-485, is a standard defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in serial communications systems. Electrical signaling is balanced, and multipoint systems are supported. The standard is jointly published by the Telecommunications Industry Association and Electronic Industries Alliance (TIA/EIA). Digital communications networks implementing the standard can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear, multidrop bus. These characteristics make RS-485 useful in industrial control systems and similar applications.
The IBM PC Network was IBM's first LAN system. It consisted of network cards, cables, and a small device driver known as NetBIOS. It used a data rate of 2 Mbit/s and carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection.

The SIMpad is a portable computer developed by the company Keith & Koep by order of Siemens AG, with an 8.4" TFT touchscreen. Commonly used with wireless network cards, it was marketed as a device to browse the World Wide Web. Initially announced in January 2001 at the Consumer Electronics Show, the SIMpad was not very popular in the mainstream US market.
The Simatic S5 PLC is an automation system based on Programmable Logic Controllers. It was manufactured and sold by Siemens AG. Such automation systems control process equipment and machinery used in manufacturing. This product line is considered obsolete, as the manufacturer has since replaced it with their newer Simatic S7 PLC. However, the S5 PLC still has a huge installation base in factories around the world. Most automation systems integrators still have the ability to provide support for the platform.
In computing, the form factor is the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case. Small form factors have been developed and implemented.
Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical or optical connectors for carrying audio and video signals. Audio interfaces and video interfaces define physical parameters and interpretation of signals. For digital audio and digital video, this can be thought of as defining the physical layer, data link layer, and most or all of the application layer. For analog audio and analog video these functions are all represented in a single signal specification like NTSC or the direct speaker-driving signal of analog audio. Physical characteristics of the electrical or optical equipment includes the types and numbers of wires required, voltages, frequencies, optical intensity, and the physical design of the connectors. Any data link layer details define how application data is encapsulated. Application layer details define the actual audio or video format being transmitted, often incorporating a codecs not specific to the interface, such as PCM, MPEG-2, or the DTS Coherent Acoustics codec. In some cases, the application layer is left open; for example, HDMI contains an Ethernet channel for general data transmission.
SIMATIC WinCC is a supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) and human-machine interface (HMI) system from Siemens. SCADA systems are used to monitor and control physical processes involved in industry and infrastructure on a large scale and over long distances. SIMATIC WinCC can be used in combination with Siemens controllers. WinCC is written for the Microsoft Windows operating system. It uses Microsoft SQL Server for logging and comes with a VBScript and ANSI C application programming interface.















